El dengue es endémico en Asia, el sudeste de Asia, varios países del Pacífico sur y central y de las Américas. Hubo varios brotes de dengue en India. Más de 2,5 billones de personas (más del 40% de la población mundial) están ahora en riesgo de padecer el dengue. La OMS estima actualmente que pueden estar ocurriendo 50-100 millones de infecciones por dengue en todo el mundo cada año. Un estimado de 500000 personas con dengue grave requieren hospitalización anualmente, una gran proporción de los cuales son niños y alrededor del 2,5% de los afectados mueren.
El modelado sugiere que el calentamiento global aumentará la cantidad de tierra con un clima adecuado para la transmisión de la fiebre del dengue, lo que podría colocar en riesgo a una mayor proporción de la población mundial. Se estimó que había 96 millones de infecciones de dengue aparentes a nivel mundial en 2010, con un adicional de 294 (217-392) millones de infecciones inaparentes también. Sólo la India aportó el 34% [33 (24-44) millones de infecciones] del total mundial. Estas estimaciones de la carga total de la infección (aparente y no aparente) son más de tres veces superiores a las que predijo la OMS. La carga mundial de dengue es formidable y representa un creciente desafío para los funcionarios y las políticas de salud pública.
La epidemiología de la fiebre del dengue en el subcontinente indio ha sido muy compleja y ha cambiado sustancialmente en las seis décadas pasadas en términos de cepas prevalentes, ubicaciones geográficas afectadas y en la gravedad de la enfermedad. En la India, Indonesia y Myanmar, los brotes focales lejos de las zonas urbanas han reportado tasas de letalidad de 3-5%. Las epidemias cíclicas están aumentando en frecuencia y se está produciendo la expansión geográfica en Bangladesh, India y Maldivas. Estos son los países en la zona climática seca y húmeda con múltiples serotipos de virus circulantes.
El dengue ya no se limita a los centros urbanos, ahora se producen brotes en la India rural. Casi todos los estados de India, incluyendo las islas aisladas como Andaman y Nicobar, ahora reportan casos. Aunque el dengue ha sido predominantemente una enfermedad de los niños, ahora afecta a todos los grupos de edad en todo el mundo. Se ha informado que en la India aproximadamente el 20% de los casos se había producido en bebés menores de 1 año. Se afectan por igual pacientes masculinos y femeninos.
1. El virus
El virus del dengue virus (VD) es un único virus ARN de cadena perteneciente a la familia Flaviridae. Se ha clasificado en cuatro serotipos, DENV-1, DENV-2, DENV-3 y DENV-4, que son genética y antigénicamente diferentes. La infección con un serotipo produce inmunidad de por vida sólo a ese serotipo particular. El virus es sensible al calor y es susceptible a muchos desinfectantes comunes incluyendo etanol, hipoclorito de sodio y glutaraldehído. Es, sin embargo, estable en sangre y exudados secos durante varios días a temperatura ambiente.
Una vez infectado, el mosquito vector es portador del virus de por vida (uno a cuatro meses). En un estudio realizado en la India durante un brote, el análisis filogenético reveló que el Dengue-4 indio aislado pertenecía al genotipo I. Este estudio indica claramente la dominancia repentina del DENV-4 en un brote de Dengue Indio. El estado de Orissa en el este de la India informó el primer brote de dengue en 2010, seguido por brotes extensos en 2011, afectando a un gran número de personas.
El análisis filogenético puso de manifiesto la circulación del linaje indio de DENV-2 (genotipo IV) y DENV-3 (genotipo-III) en suero de vectores y pacientes en Orissa de 2010 a 2011, siendo el DENV-2 el serotipo prevalente. La co-circulación de varios serotipos de virus del dengue se ha traducido en infección concurrente en algunos pacientes con múltiples serotipos de VD. También fue reportada la infección concurrente con Chikungunya en India.
2. El vector
El dengue es transmitido por los mosquitos Aedes aegypti y Aedes albopictus, que son omnipresentes. El mosquito vector primario prefiere reproducirse en recipientes artificiales con agua, aunque los recipientes naturales también pueden actuar como sitios de reproducción. Son mordedores de día y son más activos justo después del amanecer y justo antes del atardecer.
Un humano virémico es la fuente de infección de un mosquito adulto, que puede transmitir el virus dentro de la población de mosquitos después de 8-10 días. En los seres humanos, el período de incubación intrínseca es de 3-14 días, comúnmente 4-7 días. Un paciente con dengue es infeccioso para los mosquitos justo antes a después del período febril. La infección con un serotipo del dengue confiere inmunidad de por vida a ese serotipo pero puede llevar a un mayor riesgo de complicaciones si posteriormente se infecta con otro serotipo.
3. Patogénesis
Varias teorías tratan de explicar la patogénesis incluyendo la "hipótesis de mejora inmunológica" y la "hipótesis de presión de selección". La hipótesis de la mejora inmunológica propone que los pacientes con una segunda infección con un serotipo heterólogo del dengue tienen un mayor riesgo de desarrollar dengue grave. El anticuerpo heterólogo de dengue existente reconoce el virus invasor y establece un complejo antígeno anticuerpo, que se une al receptor Fc sobre la membrana celular de los leucocitos.
El virus se replica libremente a través de la mejora dependiente de anticuerpos. Los anticuerpos anti virus del dengue dan una reacción cruzada con las plaquetas, los factores de coagulación y las células endoteliales en humanos. Los anticuerpos anti-NS1 inducen apoptosis en las células endoteliales y aumentan la permeabilidad vascular, dando lugar a hipovolemia y shock. La hipótesis de presión de selección asegura que el virus del dengue varía y muta como resultado de la presión de selección, ya que se replica en seres humanos y/o mosquitos.
4. Clasificación del Dengue
4.1. Antigua clasificación
La enfermedad por dengue exhibe una extensa variedad de presentaciones clínicas que van desde la infección asintomática y la fiebre leve indiferenciada al shock fatal. Hasta hace poco la OMS identificó dos tipos de enfermedad del dengue, la fiebre del dengue (FD) una enfermedad febril autolimitada leve y la fiebre hemorrágica del dengue (FHD) una condición potencialmente fatal caracterizada por vasculopatía húmeda.
De acuerdo con la gravedad de la enfermedad FHD se dividió en cuatro categorías:
Grado I: trombocitopenia, hemoconcentración, prueba del torniquete positiva y ausencia de sangrado espontáneo.
Grado II: trombocitopenia, hemoconcentración, prueba del torniquete positiva y presencia de sangrado espontáneo.
Grado III: trombocitopenia, hemoconcentración, prueba del torniquete positiva e insuficiencia circulatoria (pulso débil, caída de 20mmHg o mayor en la presión sanguínea arterial, extremidades frías y aprehensión).
Grado IV: trombocitopenia, prueba de torniquete positiva, hemoconcentración, pulso y presión sanguínea imperceptible.
.
4.2 Nueva clasificación
De acuerdo con las nuevas guías de dengue ahora se clasifica en tres categorías:
- dengue
- dengue con signos de alarma
- dengue severo en el que el curso clínico de la enfermedad se divide en tres fases- febril, crítica, y recuperación.
5. Características clínicas
Los virus del dengue causan infecciones sintomáticas o seroconversión asintomática. La infección por dengue sintomático es una enfermedad sistémica y dinámica. Cuenta con un amplio espectro clínico que incluye tanto manifestaciones clínicas graves y no graves. Aunque la mayoría de los pacientes con dengue recuperan tras un curso clínico autolimitado no grave, una pequeña proporción progresa a enfermedad grave. El dengue es una enfermedad dinámica que puede tener tres fases: febril, crítica y de recuperación.
La fase febril puede durar 2-7 días. La fase crítica puede ocurrir en cualquier momento entre los 3 y los 7 días después del inicio de la enfermedad. Una prueba de torniquete positiva en esta fase indica una mayor probabilidad de dengue. La fase de recuperación ocurre 2-3 días después de la fase crítica.
El dengue tiene un amplio espectro de presentaciones clínicas, a menudo con una evolución y resultado clínico impredecible. Los niños son más propensos a desarrollar shock debido a su microvasculatura intrínsecamente más permeable, a pesar de que la hemorragia mayor, la encefalopatía y el compromiso hepático son más comunes en los adultos. Petequias, melena, dolor de cabeza, dolor retro-orbital, mialgia, dolor en las articulaciones, náuseas y vómitos se han observado más comúnmente en adultos, en contraste con la ocurrencia más frecuente de epistaxis, oliguria y compromiso hepático en los niños.
Fase crítica - durante la transición de la fase febril a la fase afebril, los pacientes sin un aumento de la permeabilidad capilar mejorarán sin pasar por la fase crítica. En lugar de mejorar con el descenso de la fiebre alta, los pacientes con aumento de la permeabilidad capilar pueden manifestar las señales de alerta, sobre todo como resultado de la pérdida de plasma.
Los pacientes empeoran en el momento de desaparición de la fiebre, cuando la temperatura desciende a 37,5-38ºC o menos y permanece por debajo de este nivel, por lo general en los días 3-8 de la enfermedad. La leucopenia progresiva seguida por una rápida disminución en el recuento de plaquetas por lo general precede a la pérdida de plasma.
Un hematocrito creciente por encima de la línea de base puede ser uno de los signos adicionales más precoces. El período de pérdida de plasma clínicamente significativo normalmente dura 24-48hs. El grado de hemoconcentración por encima del hematocrito base refleja la gravedad de la pérdida de plasma. Además de la pérdida de plasma, a menudo se presentan manifestaciones hemorrágicas tales como moretones y sangrado en los sitios de venopunción.
Señales de advertencia de dengue - vómitos persistentes y dolor abdominal severo son los primeros indicios de pérdida de plasma. Se observa con frecuencia el aumento de tamaño del hígado y un hígado blando. Una disminución rápida y progresiva en el recuento de plaquetas a alrededor 100000 células/mm3 y un hematocrito elevado por encima del basal puede ser la primera señal de pérdida de plasma generalmente precedida por leucopenia.
Fase de recuperación - si el paciente sobrevive a la 24-48hs de la fase crítica, se lleva a cabo una reabsorción gradual del fluido del compartimento extravascular en las siguientes 48-72hs. Mejora el estado general, regresa el apetito, disminuyen los síntomas gastrointestinales, se estabiliza el estado hemodinámico y sobreviene la diuresis. Algunos pacientes tienen erupciones eritematosas confluentes o petequiales con pequeñas áreas de piel normal, que se describe como "islas de blanco en el mar de rojo".
Algunos pueden experimentar prurito generalizado. Son comunes la bradicardia y los cambios electrocardiográficos durante esta etapa. El hematocrito se estabiliza o puede ser inferior debido al efecto de dilución del fluido reabsorbido. Puede ocurrir dificultad respiratoria por derrame pleural masivo y ascitis, edema pulmonar o insuficiencia cardíaca congestiva durante las fases críticas y/o de recuperación si se administraron líquidos excesivos por vía intravenosa.
Dengue severo - Un caso de dengue grave se define como un paciente con sospecha de dengue con uno o más de los siguientes:
(i) pérdida de plasma grave que conduce al shock (shock dengue) y/o acumulación de fluidos con dificultad respiratoria.
(ii) hemorragia severa
(iii) deterioro de órganos severo
Pérdida de plasma severa y shock por dengue - el síndrome de shock por dengue (SSD) es una forma de shock hipovolémico y se produce por permeabilidad vascular y extravasación continua de plasma. Esto por lo general se produce cerca de la desaparición de la fiebre, es decir, en los días 4-5 de la enfermedad (rango de 3-8 días), y es a menudo precedida por señales de advertencia.
Desde este punto en adelante, los pacientes que no reciben inmediatamente fluidos intravenosos progresan rápidamente a un estado de shock. La taquicardia (sin fiebre durante la defervescencia), es una respuesta cardiaca temprana a la hipovolemia.
Durante la etapa inicial del shock, el mecanismo de compensación que mantiene una presión sistólica normal produce taquicardia, taquipnea tranquila (taquipnea sin mayor esfuerzo) y vasoconstricción periférica con una reducción de la perfusión cutánea (manifestada por extremidades frías y relleno capilar demorado >2 segundos y pulsos periféricos débiles). Como aumenta la resistencia vascular periférica, la presión diastólica se eleva hacia la presión sistólica y la presión de pulso se estrecha (la diferencia entre la presión sistólica y diastólica).
Se considera que el paciente tiene un shock compensado si la presión sistólica se mantiene normal o ligeramente por encima del rango normal, pero la presión de pulso es ≤20 mmHg en los niños (por ejemplo, 100/85 mmHg) o si tienen signos de mala perfusión capilar (extremidades frías, retraso del llenado capilar o taquicardia). En este momento la respiración se vuelve más rápida y aumenta en profundidad - una compensación para la acidosis metabólica (respiración de Kussmaul).
Finalmente, hay descompensación, tanto la presión sistólica como la diastólica desaparecen de repente y dramáticamente, y se dice que el paciente tiene un shock hipotensor o descompensado. Un signo clínico principal de este deterioro es un cambio en el estado mental a medida que disminuye la perfusión cerebral. El paciente se vuelve inquieto, confuso y extremadamente letárgico. Pueden producirse convulsiones y la agitación puede alternar con el letargo.
Por el otro lado, los niños y los adultos jóvenes pueden tener un estado mental claro incluso en shock profundo. El fracaso de los bebés y los niños en reconocer, focalizar o hacer contacto visual con los padres puede ser un signo ominoso temprano de hipoperfusión cortical, al igual que la falta de respuesta a los estímulos dolorosos tales como la venopunción.
El shock hipotensivo prolongado y la hipoxia llevan a una acidosis metabólica severa, falla orgánica múltiple y a un curso clínico muy difícil. Los pacientes con severa pérdida de plasma pueden no tener un shock si se lleva a cabo una rápida reposición de líquidos. En cambio, se manifiestan con dificultad respiratoria debido al derrame pleural masivo y la ascitis que también puede ser exacerbada por la terapia de líquidos intravenosos sin control.
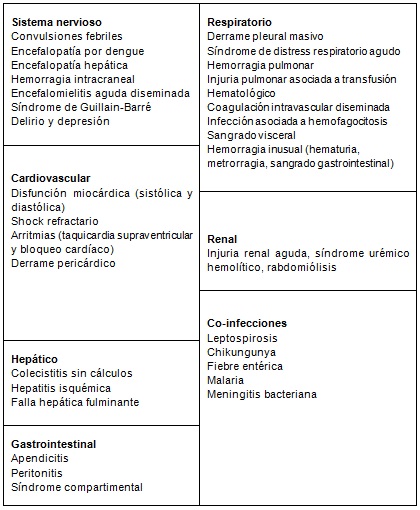
Las complicaciones sistémicas del dengue se muestran en la Tabla a continuación
6. El diagnóstico de laboratorio del dengue
Las características clínicas del dengue no son específicas, por lo tanto, el diagnóstico de laboratorio de confirmación temprano es esencial para la oportuna intervención ya que la enfermedad puede ser fatal en poco tiempo. El diagnóstico puede involucrar el aislamiento del virus, la detección de ácido nucleico, antígenos o anticuerpos del virus. En la etapa temprana de la enfermedad se debe hacer el aislamiento viral, o la detección del ácido nucleico o del antígeno viral.
Después de la fase aguda de la infección se utiliza para el diagnóstico la detección de anticuerpos. Las pruebas altamente sensibles y específicas como el aislamiento del virus y la identificación del ácido nucleico requieren experiencia y están disponibles solamente en pocos centros en comparación con las pruebas con menor sensibilidad y especificidad es decir, la detección de anticuerpos que son baratos y fácilmente disponibles.
6.1. Aislamiento viral
Debe hacerse antes de los 5 días de la enfermedad del suero, plasma o células mononucleares en sangre periférica. Como el virus es extremadamente sensible al calor la muestra debería llegar al laboratorio central a temperaturas entre 4°C y 8°C. Los resultados están disponibles en cuestión de 1-2 semanas. El procedimiento es caro, puede identificar los serotipos, pero es incapaz de distinguir entre infección primaria y secundaria y está reservado para fines de investigación.
6.2. Detección de ácido nucleico viral
El ARN del virus de dengue también es lábil al calor, por lo tanto el transporte de la muestra al laboratorio requiere mantenimiento de la temperatura como en el aislamiento del virus. Como la contaminación de la muestra dará lugar a un informe erróneo, es importante contar con técnicos expertos con un control de calidad adecuado. EL equipamiento caro y el conocimiento limitan su disponibilidad.
Se utiliza usualmente RT-PCR (transcriptasa inversa-reacción en cadena de la polimerasa) con un tiempo de respuesta de 1-2 días pero la prueba es cara, es incapaz de distinguir entre infección primaria y secundaria y se debe hacer en los primeros 5 días del inicio de los síntomas. La precisión de la prueba aumenta si el ácido nucleico es extraído de esa región del genoma del dengue que es específico para el dengue y que no se conserva entre otros Flavivirus o virus relacionados. Esta prueba tiene una sensibilidad de 80-90% y una especificidad de más de 95%. La prueba puede ser negativa en la fase aguda, es decir, dentro de los primeros 5 días de síntomas debido a niveles indetectables de virus.
6.3. Detección de antígenos del virus
La NS1, proteína no estructural 1 es producida por todos los flavivirus. Este antígeno de glicoproteína puede ser detectado en todos los pacientes tanto con dengue primario como secundario desde el primer día de los síntomas hasta nueve días y aun a veces hasta 18 días luego del inicio de los síntomas. Esta prueba se puede hacer mediante ELISA o por otros métodos rápidos como cromatografía inmunológica donde los resultados se obtienen en minutos. Las características de rendimiento de la prueba siguen siendo objeto de evaluación por las autoridades competentes. La prueba Elisa debido a su especificidad puede ser útil para diagnósticos diferenciales entre flavivirus pero otras pruebas rápidas tienen el inconveniente de la reactividad cruzada con el grupo flavivirus.
6.4. Pruebas serológicas
Después de la infección por dengue la respuesta inmune es la producción de anticuerpos IgM e IgG dirigidos contra la proteína de la envoltura del virus dependiendo del estado inmune del huésped. Una persona que no ha sido previamente infectada con dengue o cualquier otro flavivirus desarrolla una respuesta de anticuerpos primaria que se manifiesta por un título lento y bajo.
Los anticuerpos IgM son los primeros en aparecer en alrededor del 50% de los pacientes en cuestión de 3-5 días después de la aparición de la enfermedad. Aumenta gradualmente a 99% en el día 10 y luego disminuye lentamente a niveles indetectables cerca de los 2-3 meses. Los anticuerpos IgG son detectables a título bajo al final de la primera semana de enfermedad aumentando lentamente a partir de entonces y persisten durante varios meses y, a veces, incluso de por vida.
En contraste, los pacientes que han sufrido de dengue u otras infecciones por flavivirus en el pasado o se han inmunizado con la vacuna contra flavivirus muestran una respuesta secundaria en la que el título de anticuerpos aumenta muy rápidamente y en general reacciona con muchos flavivirus. Los anticuerpos IgG son detectables en la fase aguda y aumentan dramáticamente en las siguientes dos semanas y persisten desde los 10 meses al resto de la vida.
Los niveles de anticuerpos IgM son significativamente más bajos después de la infección secundaria a diferencia de la primaria. El 80% puede tener niveles detectables de anticuerpos IgM al quinto día de la enfermedad, en los que el 99% de los pacientes en que son detectables al día diez de la enfermedad continua siendo detectable durante más de 90 días.
Los anticuerpos IgM e IgG son detectables por diversos métodos. Las pruebas rápidas que producen un resultado en 30 minutos se hacen por el método cromatográfico inmune mientras que la prueba de ELISA requiere más tiempo (1-2 días), pero tiene la recomendación de las autoridades competentes. Los anticuerpos IgM para dengue detectados por MAC-ELISA se clasifican como que el paciente está teniendo una probable infección reciente por dengue.
La prueba de MAC-ELISA tiene una buena sensibilidad y especificidad sólo cuando se realiza a los cinco o más días después de la aparición de la enfermedad. Los niveles bajos o indetectables de respuesta IgM contra dengue en alguna infección secundaria reduce la precisión del diagnóstico del ensayo IgM ELISA. Hay que tener en cuenta que los anticuerpos IgM del dengue pueden permanecer elevados durante 2-3 meses después de la enfermedad y también con reactividad cruzada con otras infecciones por flavivirus como el virus de la encefalitis japonés.
El ensayo IgG ELISA también muestra reactividad cruzada dentro del grupo flavivirus. Se utiliza para la detección de infección reciente o pasada de dengue. Las muestras con IgG negativo en fase aguda, pero positivas en la fase de convalecencia de la infección son dengue primario. Por el contrario, las muestras con IgG positivo en la fase aguda y un aumento de cuatro veces en la fase de convalecencia, con al menos 7 días entre las dos muestras es dengue secundario.
6.5 Pruebas hematológicas
Estas pruebas son sugestivas, pero nunca diagnósticas de dengue. La trombocitopenia se observa generalmente entre el día 3 y el día 8 después de la aparición de la enfermedad, pero es una característica constante de la fiebre hemorrágica del dengue. La leucopenia precede a la trombocitopenia y una disminución progresiva en el recuento de leucocitos debería alertar al personal de salud.
7. Tratamiento
Los pacientes deberían clasificarse en los siguientes grupos:
-Grupo A: pacientes ambulatorios con indicaciones
-Grupo B: pacientes hospitalizados
-Grupo C: tratamiento de emergencia y derivación urgente.
7.1. Grupo A: pacientes de manejo ambulatorio con indicaciones (para aquellos que pueden ser enviados a casa)
Deben controlarse todos los días con un examen clínico y evaluación de laboratorio. Deberían ser alentados a tomar solución de rehidratación oral y jugo de fruta para reponer las pérdidas de la fiebre y los vómitos y reducir el riesgo de hospitalización. El paracetamol es el antipirético preferido con un intervalo de dosificación mínima de 6hs. Los fármacos anti-inflamatorios no esteroideos puede agravar la gastritis y/o el sangrado y deben evitarse.
Los cuidadores deben ser informados de que el paciente debe ser llevado al hospital de inmediato si ocurre alguno de los siguientes: no presentar mejoría clínica, deterioro en el momento de desaparición de la fiebre, dolor abdominal intenso, vómitos persistentes, extremidades frías y pegajosas, letargo o irritabilidad/inquietud, sangrado (por ejemplo, heces negras o vómitos borra de café) o no orinar durante más de 4-6 hs.
7.2. Grupo B: aquellos que deben ser ingresados en el hospital
Este grupo incluye a aquellos con signos de alarma, condiciones co-mórbidas o situaciones sociales donde no puede asegurarse una atención domiciliaria adecuada.
Elección de los líquidos intravenosos - La mayoría de los estudios sobre el papel de los diferentes fluidos en el tratamiento de la infección por dengue no encontraron diferencia en términos de recuperación del shock o de los resultados, aunque se informó que los coloides proporcionan la más rápida normalización del hematocrito y la restauración del índice cardíaco, sin efectos adversos. Las guías actuales de la OMS recomiendan el uso de cualquier cristaloide isotónico o fluidos coloidales para el tratamiento del shock hipotensivo.
7.3. Grupo C: aquellos que requieren tratamiento de emergencia para el dengue grave
Estos pacientes requieren reanimación intravenosa urgente con cristaloides o coloides, destinadas a mantener una adecuada perfusión y la producción de orina y a mejorar la taquicardia. En pacientes con shock compensado, los fluidos se inician a 5-10 ml/kg/h y se valora en base a la respuesta clínica y a las mediciones de hematocrito seriado.
Los pacientes con shock hipotensor deben recibir bolos de cristaloides isotónicos intravenosos o solución coloidal a una velocidad de 10-20 ml/kg durante 15 min. Otros fluidos se ajustan en base a la respuesta y a las mediciones de hematocrito seriadas. Una caída del hematocrito en esta etapa puede indicar hemorragia y debe ser tratada con transfusión de sangre (sangre entera fresca o glóbulos rojos desplasmatizados). Hay tres etapas de shock del dengue - shock compensado, shock hipotensor y shock refractario.
8. Hemorragias graves
Los pacientes con riesgo de hemorragia severa son los que tuvieron shock prolongado o refractario, insuficiencia renal o hepática, acidosis metabólica severa y persistente, terapia anticoagulante, cualquier trauma, incluyendo inyección intramuscular y condiciones hemolíticas subyacentes.
Se puede reconocer la hemorragia severa por la disminución del hematocrito después de la reanimación con líquidos con un estado hemodinámico inestable, shock refractario que no responde a la reanimación consecutiva con líquidos a 40-60 ml/kg, shock hipotensor con hematocrito bajo/normal antes de la reanimación con líquidos, acidosis metabólica persistente o que empeora manteniendo o no la presión arterial sistólica.
La intervención más importante para un paciente con shock por dengue y hemorragia potencialmente mortal es la restauración de la capacidad de transporte de oxígeno. Transfundir sangre fresca total o glóbulos rojos desplasmatizados. No está indicado trasfundir plaquetas, crioprecipitados o plasma fresco congelado en la mayoría de los pacientes con sangrado grave, ya que pueden contribuir a la sobrecarga de volumen. Se indican sólo si continúa el sangrado a pesar de 2-3 alícuotas de transfusión de sangre.
9. Sobrecarga de líquidos
Las causas de la sobrecarga de líquidos en los pacientes con dengue grave son líquidos intravenosos excesivos y/o demasiado rápidos, el uso incorrecto de soluciones hipotónicas, grandes volúmenes de líquido en pacientes con hemorragias graves no reconocidas, la transfusión inadecuada de plasma fresco congelado, concentrados de plaquetas y crioprecipitados, continuación de líquidos por vía intravenosa después de que se resuelve la pérdida de plasma (24-48 hs de desaparición de la fiebre), así como condiciones comórbidas, tales como cardiopatía congénita o isquémica, enfermedad pulmonar y renal crónica.
Las indicaciones de manejo de UTI en pacientes con sobrecarga de fluidos son distress respiratorio grave/insuficiencia respiratoria hipoxémica, edema pulmonar, ascitis a tensión y shock irreversible (insuficiencia cardíaca, a menudo en combinación con hipovolemia en curso).
La sobrecarga de fluidos es el mecanismo básico en diversas complicaciones del dengue grave como la dificultad respiratoria o el fracaso debido al derrame pleural o el edema pulmonar; el shock refractario debido al aumento del trabajo del miocardio o a la isquemia miocárdica y la acidosis persistente y la hemorragia intratable debido al síndrome compartimental abdominal. Por lo tanto estos pacientes requieren investigaciones adicionales y monitoreo como radiografía de tórax, electrocardiograma, ecocardiograma, análisis de enzimas cardíacas y la medición de la presión intraabdominal.
El manejo de la sobrecarga de fluidos de acuerdo con los parámetros clínicos incluye oxigenoterapia o ventilación con presión positiva, disminución o suspensión de los líquidos intravenosos y orales o furosemida intravenosa a 0,1-0,5 mg/kg/dosis o una infusión continua de furosemida a 0,1 mg/kg/hora.
El paciente en estado de shock con signos de sobrecarga de líquidos puede tener hemorragia oculta. Debe administrarse transfusión de sangre entera fresca a la mayor brevedad posible. La diálisis peritoneal es raramente indicada en la diuresis resistente. El drenaje rápido del líquido pleural y ascítico puede causar inestabilidad hemodinámica repentina y hemorragia catastrófica.
Comentario: El dengue es una de las patologías emergentes que provoca mayor preocupación sanitaria a nivel mundial. Las nuevas guías clasifican el dengue en tres categorías, dengue, dengue con signos de alarma y dengue severo a partir de las cuales se proponen diferentes manejos ya sea ambulatorios o de internación. La sospecha clínica rápida, el conocimiento de las fases de la enfermedad (febril, crítica y de recuperación), los métodos diagnósticos adecuados y el tratamiento oportuno según la gravedad del caso permitirá mejorar el pronóstico de los pacientes afectados.
Resumen y comentario objetivo: Dra. Alejandra Coarasa