Introducción
La esplenectomía laparoscópica (EL) se ha convertido en el estándar para la remoción del bazo en las condiciones hematológicas benignas y el espectro de las indicaciones está en constante expansión. Los beneficios observados de la EL sobre la esplenectomía abierta (EA) han sido tema de varios estudios, que demostraron que los pacientes sometidos a EL tienen generalmente tasas más bajas de complicaciones postoperatorias [1-8], una estadía hospitalaria más corta [1,2,4,7-16] y una imagen corporal y estética más favorable [1].
Sin embargo, la mayoría de los estudios disponibles fueron realizados en grupos pequeños de pacientes, evaluando sólo un único tipo de enfermedad, medidos con muy pocos resultados postoperatorios, o fracasados en el ajuste por factores de confusión clínicamente relevantes, que podrían haber desviado la selección de la técnica de la esplenectomía.
Con esas limitaciones en mente, el propósito de este estudio fue evaluar la incidencia de muerte y de 8 morbilidades mayores, dentro de los 30 días postoperatorios, en pacientes sometidos a EL, comparada con EA, utilizando una base grande de datos del American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (ACS NSQIP).
Métodos
Pacientes
Fue un estudio observacional de cohorte, utilizando datos de la base de datos del ACS NSQIP. Los detalles del ACS NSQIP (www.acsnqip.org) han sido recientemente descritos [17]. Es un registro validado de resultados, diseñado para brindar una retroalimentación a los miembros del hospital, sobre la mortalidad y morbilidad quirúrgicas, ajustadas por riesgo, dentro de los 30 días [18,19].
La base de datos incluye datos no identificados sobre demografía, estado funcional, origen de admisión, factores preoperatorios de riesgo y estudios de laboratorio, variables perioperatorias y resultados postoperatorios dentro de los 30 días, de pacientes adultos (≥ 18 años) sometidos a cirugía mayor en hospitales participantes de la administración, no de veteranos [18].
Revisores entrenados en clínica quirúrgica recolectaron los datos de los pacientes, desde la admisión, de la historia clínica, protocolo operatorio, registro de anestesia, entrevistas con el cirujano actuante y entrevistas telefónicas con el paciente [18]. La calidad de los datos es asegurada a través de un entrenamiento comprehensivo del personal revisor de enfermería, una auditoria de fiabilidad de los sitios participantes, llamadas de conferencia regulares y una reunión anual [20].
Para este estudio, fueron recuperados los Participants Use Files del ACS NSQIP disponibles, de los años 2008 (271.3868 casos de 211 lugares) y 2009 (336.190 casos de 237 sitios), de todas las cirugías mayores realizadas en los centros médicos participantes del programa ACS NSQIP, en los Estados Unidos, Canadá y varios sitios internacionales, incluyendo el Líbano y los Emiratos Árabes Unidos.
Para este estudio, se identificaron los casos de esplenectomía utilizando los códigos de la Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) 38120 para la EL y 38100-38102 para la EA. La base de datos del ACS NSQIP no incluye casos de trauma. Todo paciente admitido en el hospital con un trauma agudo y que tenía operaciones por ese trauma, era excluido. Cualquier operación realizada después de que el paciente ha egresado de trauma, era incluida.
Por lo tanto, el análisis en este estudio incluye esplenectomías realizadas exclusivamente en un escenario no de trauma, dado que la base de datos NSQIP no incluye a pacientes que son sometidos a tratamiento quirúrgico como resultado de un traumatismo mayor. De acuerdo con las guías de la American University of Beirut (que siguen el US Code of Federal Regulations for the Protection of Human Subjects), no fue necesaria la aprobación del comité de revisión institucional para este análisis, porque los datos fueron recolectados como parte de una actividad de aseguramiento de la calidad.
Resultados postoperatorios
Los resultados postoperatorios evaluados fueron la mortalidad a los 30 días y 8 morbilidades mayores, incluyendo: (1) cardíaca (infarto agudo de miocardio o paro cardíaco requiriendo resucitación cardiopulmonar); (2) respiratoria (neumonía, apoyo ventilatorio > 48 horas o intubación no planificada); (3) sistema nervioso central (accidente cerebrovascular, coma con duración > 24 horas); (4) renal (insuficiencia renal progresiva o falla renal aguda); (5) herida (infección del sitio quirúrgico incisional profunda, infección del sitio quirúrgico en órgano o espacio o dehiscencia de la herida); (6) sepsis (sepsis o shock séptico); (7) trombosis venosa (trombosis venosa profunda o embolia pulmonar) y (8) sangrado mayor (requiriendo transfusión de más de 4 unidades de paquetes de glóbulos rojos [pGR] dentro de las 72 horas postoperatorias).
Análisis estadístico
Las estadísticas descriptivas son presentadas como medias ± desvío estándar (DE), medianas (rango intercuartilar) o porcentajes. Los datos demográficos de los pacientes y los factores de riesgo preoperatorios, fueron comparados entre los grupos de EL y de EA, usando la prueba de x2 para las variables categóricas y la prueba de t para muestras independientes, para las variables continuas.
La medición del resultado primario del estudio fue la muerte, dentro de los 30 días de la cirugía, en el grupo EL, comparado con el grupo EA. La medición del resultado secundario del estudio fue la ocurrencia de morbilidad mayor, dentro de los 30 días de la cirugía, en el grupo de EL, comparado con el grupo de EA. Se construyeron modelos de regresión logística multivariados separados, para la mortalidad a los 30 días y para cada morbilidad individual, para recuperar los cocientes de probabilidades (odds ratios [OR]) ajustados y los intervalos de confianza del 95% (IC).
Los modelos se construyeron ajustando la asociación entre la técnica de la esplenectomía y los resultados, por potenciales factores de confusión de relevancia clínica. Se usaron 2 niveles de ajuste. El Modelo 1, con un ajuste básico para los factores preoperatorios de riesgo más relevantes, que podrían afectar potencialmente la tasa de resultados y la elección de la EL versus la EA (datos demográficos de los pacientes, indicación para la esplenectomía y mediciones del estado físico general de los pacientes).
En el Modelo 2, se realizó un ajuste más extenso por un número más grande de factores preoperatorios de riesgo, que podrían ser clínicamente relevantes para cada resultado de interés. El análisis (Modelo 2) fue también estratificado por las diferentes indicaciones para la esplenectomía.
Los datos fueron casi completos, con la excepción de valores perdidos de algunos estudios preoperatorios de laboratorio: sodio sérico (n = 159; 8,9%), urea en sangre (n = 197; 11,1%), creatinina sérica (n = 134; 7,5%), albúmina sérica (n = 565; 31,7%), bilirrubina total (n = 467; 26,2%), alanina amino transferasa (n = 472; 36,6%), fosfatasa alcalina (n = 477; 36,9%), hematocrito (n = 44; 2,5%), recuento de glóbulos blancos (n = 76; 4,3%), recuento de plaquetas (n = 60; 3,4%) y RIN (n = 560; 31,4%).
Sólo el nivel del hematocrito fue seleccionado en los modelos multivariados, dado que las alteraciones en los restantes índices de laboratorio estaban ya indicadas, a través de la historia médica de los pacientes. Los datos perdidos en los valores de hematocrito para hombres y mujeres, fueron imputados mediante su reemplazo con los valores medios para hombres y mujeres, respectivamente. Las medianas de la estadía quirúrgica total y de la estadía hospitalaria, también fueron comparadas entre los grupos de EL y EA, empleando la prueba U de Mann-Whitney.
Para evaluar las potenciales ocurrencias intraoperatorias que podrían explicar parcialmente el efecto de la técnica de esplenectomía sobre los resultados postoperatorios, los autores compararon también la media del tiempo operatorio total (prueba t para muestras independientes) y la propensión para el uso intraoperatorio de transfusiones de pGR (como un marcador subrogante para el sangrado intraoperatorio) entre los grupos de EL y EA.
Para este último, la asociación fue evaluada utilizando un modelo de regresión logística multivariado, con ajuste para los factores preoperatorios de riesgo que podrían llevar naturalmente a un uso más liberal de transfusiones de pGR (por ej., edad avanzada, pobre estado clínico, anemia preoperatoria, antecedentes de enfermedad cardíaca y tendencia al sangrado). Todos los valores de P fueron de 2 lados, con un nivel de significación ajustado a < 0,05. El manejo de los datos y los análisis se realizaron usando el programa estadístico SAS (versión 9.1; SAS Institute Inc., NC).
Resultados
Características de los pacientes
Se identificaron 1.781 casos de esplenectomía, de los que 874 (49,1%) fueron EL y 907 (50,9%) EA. La edad media de la muestra total del estudio fue de 54,7 ± 17,6 años, con 826 pacientes (46,4%) de sexo masculino. Las comparaciones de los datos demográficos de los pacientes y de las variables preoperatorias entre los sometidos a EL o EA, se resumen en la Tabla 1.
Comparados con los pacientes sometidos a EA, los pacientes con EL fueron más jóvenes y tuvieron más probabilidad de ser mujeres. La EA fue el procedimiento de elección para casos con enfermedad abdominal benigna o maligna y aquellos con lesión accidental intraoperatoria del bazo, mientras que la EL fue realizada más comúnmente en casos de anemia hemolítica o trombocitopenia primaria.
La EA fue realizada más frecuentemente en los casos de urgencia. En general, los pacientes sometidos a EA tuvieron una prevalencia más alta de factores sistémicos preoperatorios de riesgo y alteraciones de laboratorio. Tuvieron una mayor probabilidad de tener una clase más alta en la clasificación de la American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) y un estado funcional no independiente (Tabla 1).
• TABLA 1: Características basales de los pacientes
Técnica de la esplenectomía y resultados postoperatorios
El análisis no ajustado halló que los pacientes sometidos a EL tuvieron una incidencia acumulativa significativamente menor de mortalidad a los 30 días (OR: 0,29; 95% IC: 0,14-0,55) y de varias morbilidades mayores, incluyendo cardíacas (OR; 0,29; 95% IC: 0,12-0,72), respiratorias (OR: 0,27; 95% IC: 0,18-0,40), renales (OR: 0,22; 95% IC; 0,08-0,58), de la herida (OR: 0,24; 95% IC: 0,12-0,46), sepsis (OR: 0,35; 95% IC: 0,23-0,56) y sangrado mayor (OR: 0,40; 95% IC: 0,22-0,76), que los pacientes sometidos a EA.
Después del ajuste por todos los potenciales factores de confusión en el Modelo 2 (factores de riesgo con efecto potencial sobre los resultados y que pudieron haber llevado a una selección no randomizada de la técnica de esplenectomía), el efecto favorable de la EL sobre la EA fue aun observado para la mortalidad dentro de los 30 días (OR: 0,39; 95% IC: 0,18-0,84) y para las ocurrencias respiratorias postoperatorias (OR: 0,45; 95% IC: 0,28-0,73), las ocurrencias en las heridas (OR: 0,33; 95% IC: 0,15-0,74) y sepsis (OR: 0,50; 95% IC: 0,29-0,86), cuando se comparó con la EA (Tabla 2).
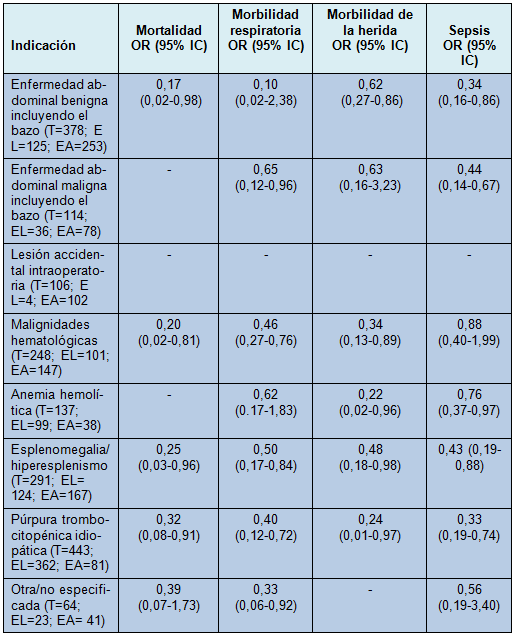
El efecto favorable de la EL sobre la EA para las ocurrencias cardíacas, renales y sangrado mayor, también fue notado, pero con mayor incertidumbre (Tabla 2). La Tabla 3 muestra los efectos estimados para el mismo análisis cuando se estratificó por indicaciones para la esplenectomía.
• TABLA 2: Efecto de la técnica de esplenectomía sobre la mortalidad y morbilidad a 30 días

• TABLA 3: Efecto de la técnica de esplenectomía sobre la mortalidad y morbilidad a 30 días, estratificado por indicación
Además, los pacientes sometidos a EL tuvieron una duración significativamente más corta de la estadía quirúrgica [mediana (rango intercuartilar): 3 (3) días vs 6 (6) días; P < 0,001] y de la estadía hospitalaria [3 (3) días vs 7 (7) días: P < 0,001] que aquellos sometidos a EA.
Una mirada más cercana al efecto de la técnica de la esplenectomía
Para explorar adicionalmente el rol de la técnica operatoria en la determinación de la tasa de resultados postoperatorios adversos, los autores analizaron los datos intraoperatorios disponibles. La media del tiempo operatorio total fue más larga en los pacientes sometidos a EL que en aquellos con EA (138,3 ± 58,7 minutos vs 125,8 ± 85,4 minutos; P < 0,001).
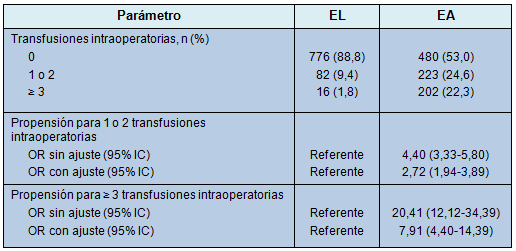
No obstante, los pacientes sometidos a EA tuvieron mayor probabilidad de recibir pGR intraoperatorios que los pacientes sometidos a EL (Tabla 4). Esa asociación se observó aún después de ajustar por otros factores relacionados con los pacientes, que podrían comúnmente necesitar el uso de transfusiones de pGR (Tabla 4). Los pacientes sometidos a EA tuvieron mayor probabilidad de recibir 1 ó 2 transfusiones intraoperatorias de pGR (OR: 2,72; 95% IC: 1,94-3,89) y más probabilidad de recibir 3 ó más transfusiones intraoperatorias de pGR (OR: 7,91; 95% IC: 4,40-14,39) que los pacientes sometidos a EL.
En esta cohorte, el uso de cada transfusión intraoperatoria se asoció con un aumento del riesgo de muerte postoperatoria den-tro de los 30 días (OR: 1,35; 95% IC: 1,25-1,44) y más morbilidades mayores: cardíaca (OR: 1,14; 95% IC: 1,06-1,24), respiratoria (OR: 1,19; 95% IC: 1,12-1,26), renal (OR: 1,17; 95% IC: 1,08-1,27), de la herida (OR: 1,14; 95% IC: 1.06-1,22), sepsis (OR: 1,17; 95% IC: 1,10-1,24) y sangrado mayor (OR: 1,20; 95% IC: 1,12-1,29).
• TABLA 4: Efecto de la técnica de la esplenectomía sobre el uso de la transfusión intraoperatoria
Discusión
Contando con datos de una cohorte grande de pacientes, este estudio demostró que la EL se asocia con una reducción significativa en la mortalidad operatoria dentro de los 30 días, una estadía hospitalaria más corta y significativamente menores complicaciones pulmonares, de la herida e infecciosas, independientemente de la indicación para la esplenectomía o el estado clínico del paciente.
La fortaleza de los datos en este trabajo, proviene del gran número de pacientes que fue incluido en la base de datos del ACS NSQIP y de la extensa lista de variables preoperatorias disponibles, que fue recolectada en todos esos pacientes. Esa extensa lista de variables recolectadas (Tabla 2), permitió el ajuste de varios factores potenciales de confusión que podían haber afectado el resultado, independientemente de la técnica quirúrgica elegida.
Estos hallazgos apoyan fuertemente los hallazgos del único meta-análisis disponible sobre este tema, realizado en el 2003, sobre 2.940 pacientes de 51 series publicadas (EL: 2.119 pacientes; EA: 821 pacientes), apareados por edad, sexo y clase ASA [21]. La observación de los autores es explicada parcialmente por una probabilidad disminuida de transfusión intraoperatoria de pGR asociada con la EL.
La EL ha evolucionado rápidamente como la técnica de elección, comparada con la EA, para las enfermedades hematológicas benignas, a causa de las ventajas del abordaje mínimamente invasivo. No obstante, se han presentado dudas en relación con la idoneidad de la EL para pacientes con esplenomegalia, debido a la exposición limitada y el control vascular complejo, que podría potencialmente conducir a un riesgo aumentado de sangrado intraoperatorio y uso de transfusiones [5,8,22,23].
Sin embargo, estudios recientes continúan confirmando la comparatividad [9,14,24,25] e incluso la superioridad [4-8] de la EL sobre la EA en pacientes con bazos masivos o supramasivos. El presente estudio confirma esos hallazgos, mediante la demostración de que la EL se asoció con resultados postoperatorios más favorables, en pacientes con enfermedades hematológicas benignas o esplenomegalia, recomendando su uso en esos escenarios, aunque dichos datos podrían no explicar las variaciones en el diagnóstico subyacente que lleva a la esplenomegalia o la extensión del agrandamiento esplénico en ambos grupos.
Es más probable que los pacientes con enfermedad maligna sean sometidos a EA [26], como se observó en esta cohorte, lo que puede ser atribuido a una enfermedad extendida que requiera laparotomía. Sin embargo, cuando la EL es el procedimiento de elección, los estudios han demostrado que no existe diferencia significativa en el tiempo operatorio [26], requerimientos de transfusión [26,27], tasas de morbilidad [26,27] o de mortalidad [26], entre los pacientes con enfermedad benigna y maligna, aunque algunos estudios reportaron que el diagnóstico de malignidad se asocia con tasas más altas de complicaciones durante la EL, atribuidas al estado clínico de los pacientes [28,29].
El presente estudio mostró que cuando se la realizó, los beneficios de la EL sobre la EA se observaron independientemente de la condición clínica general de los pacientes, tanto en las indicaciones benignas como malignas.
La EL puede incrementar el riesgo de desarrollar trombosis venosa esplénica o portal [30], porque reduce el flujo sanguíneo en el sistema portal a causa del neumoperitoneo, pero – por el contrario – podría asociarse con menos modificaciones postoperatorias de los parámetros de coagulación que la EA, previniendo – en consecuencia – la trombosis esplénica o portal.
En 1 ensayo controlado y randomizado para investigar el impacto de la anticoagulación sobre la incidencia de trombosis venosa esplénica o portal, en 35 pacientes sometidos a EL, el riesgo global fue menor en ambas ramas del tratamiento [31]. Varios otros estudios confirmaron también que la tasa de trombosis venosa postoperatoria, incluyendo la esplénica o portal, permanece similar en la EL comparada con la EA, tanto en los pacientes que recibieron anticoagulación, como en los que no la recibieron [32-35]. Similarmente, en el presente estudio no se observó aumento en el riesgo de trombosis venosa en los pacientes con EL comparado con los de EA.
Varios reportes han mostrado que la EL se asocia con menor pérdida de sangre y de requerimientos de transfusión intraoperatorios, que la EA, en distintas condiciones [7,36-38], aún en pacientes con esplenomegalia masiva y supramasiva [4.9]. La EL utilizando la tecnología Ligasure (Covidien, CO) en combinación con la maniobra del “colgado” del hilio esplénico, demostró también una reducción adicional de la pérdida de sangre intraoperatoria [39]. La transfusión se asocia con una mayor mortalidad y morbilidad, aun cuando sólo se ha administrado 1 unidad de pGR intraoperatoriamente [40-43].
El mecanismo exacto por el que la transfusión de sangre empeora el resultado quirúrgico es desconocido. La transfusión de eritrocitos resulta en una inmunomodulación inducida por la transfusión, a causa de la infusión de citosinas, lípidos y otras sustancias bioactivas solubles, muy probablemente debido a leucocitos alogénicos [44,45]. La inmunomodulación puede conducir a una activación inmunológica, resultando en una injuria pulmonar relacionada con la transfusión, o en una inmunosupresión, aumentando la susceptibilidad a las complicaciones infecciosas [44].
La leuco reducción se asocia con disminución de la mortalidad, pero no con cambios en la incidencia de infecciones graves nosocomiales [46]. El almacenamiento de eritrocitos lleva a una disminución en la deformabilidad celular y a un aumento en la adherencia al endotelio vascular [47], resultando en un flujo microvascular deteriorado y un descenso en la liberación de oxígeno [44,48]. Un trabajo reciente mostró que los pacientes quirúrgicos que reciben eritrocitos que han estado almacenados por más de 2 semanas, tienen un riesgo más alto de mortalidad intrahospitalaria y de complicaciones postoperatorias [49].
El presente estudio tiene varias limitaciones. La principal es que fue realizado como un estudio observacional para una intervención terapéutica, lo que implica que los factores de confusión por la indicación y las características de los pacientes, no pudieron ser descartados totalmente, a pesar del ajuste estadístico, pudiendo persistir algunos factores de confusión.
Los autores tampoco pudieron determinar si la EL fue convencional o asistida con la mano, para permitir una estratificación de los resultados. La EL asistida con la mano, ha sido considerada como una opción más favorable en casos de esplenomegalia, dado que ofrece las ventajas potenciales de la laparoscopía, con el añadido de la seguridad de tener la mano del cirujano en el abdomen durante la operación [5,50].
Sin embargo, en un análisis comparativo de la experiencia de un único cirujano con 43 pacientes sometidos a EL asistida con la mano y 42 pacientes con EL convencional, la tasa de mortalidad operatoria fue similar, sin diferencia en la duración de la estadía hospitalaria [51]. Otros estudios también confirmaron resultados comparables usando ambas técnicas [52].
Los autores tampoco pudieron determinar la tasa de conversión, porque los pacientes y las características están identificados por el código final de procedimiento de la CPT. No obstante, esperaron una tasa baja en esta base de datos describiendo cirugías de años recientes, después de mejoras en la técnica laparoscópica y la acumulación de experiencia laparoscópica, aún en casos considerados como difíciles y en aquellos con bazos extra grandes [53,54].
La base de datos del ACS NSQIP no registra el uso preoperatorio de terapia anticoagulante, transfusión de plaquetas o antibióticos y terapia inmunosupresora en lugar de esteroides. Eso pudo haber afectado la tasa verdadera de incidencia de trombosis venosa postoperatoria, sangrado mayor o infecciones, respectivamente. Esas drogas pueden haber sido usadas más comúnmente en algunas indicaciones que otras.
Conclusiones
En conclusión, este estudio muestra que la selección de la EL sobre la EA se asocia con resultados postoperatorios más favorables. Este estudio observó esos beneficios, independientemente de la enfermedad subyacente de los pacientes y del estado clínico, haciéndose eco de trabajos recientes que muestran que la EL puede ser aplicada en una amplia variedad de escenarios.
Estos hallazgos deberían ayudar al cirujano a hacer una mejor evaluación del riesgo/beneficio para el paciente individual, aunque la experiencia del cirujano con la técnica desempeña el papel más importante. Ensayos adicionales controlados y randomizados podrían ser necesarios, para lograr recomendaciones con mayor base en la evidencia.
♦ Comentario y resumen objetivo: Dr. Rodolfo D. Altrudi