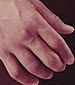
¿Qué es la espasticidad?
1 Martin A, Abogunrin S, Kurth H, Dinet J. Epidemiological, humanistic and economic burden of illness of lower limb spasticity in adults: a systematic review. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 2014:10;111-22.
2 Kheder A, Nair KPS. Spasticity: pathophysiology, evaluation and management. Pract Neurol 2012;12:289-98.
3 Tyry T, Salter A, Largent J, Ann Marrie R. The impact of spasticity severity on healthcare utilization among MS patients: a large-scale six-year follow-up study. J Neurol Sci 2013;333:376-7.
4 Denno MS, Gillard PJ, Graham GD, Dibonaventura MD, Goren A, Varon SF, et al. Anxiety and depression associated with caregiver burden in caregivers of stroke survivors with spasticity. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2013;94:1731-6.
5 Pandyan AD, Gregoric M, Barnes MP, Wood D, Van Wijck F, Burridge J, et al. Spasticity: clinical perceptions, neurological realities and meaningful measurement. Disabil Rehabil 2005;27:2-6.
6 Yelnik AP, Simon O, Parratte B, Gracies JM. How to clinically assess and treat muscle overactivity in spastic paresis. J Rehabil Med 2010;42:801-7.
7 Nielsen JB, Crone C, Hultborn H. The spinal pathophysiology of spasticity from a basic science point of view. Acta Physiol Scand 2007;189:171-80.
8 O’Dwyer NJ, Ada L, Neilson PD. Spasticity and muscle contracture following stroke. Brain 1996:119;1737-49.
9 Daniels J. Catatonia: clinical aspects and neurobiological correlates. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 2009;21:371-80.
10 Phadke CP, Balasubramanian CK, Ismail F, Boulias C. Revisiting physiologic and psychological triggers that increase spasticity. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2013;92:357-69.
11 Morley A, Tod A, Cramp M, Mawson S. The meaning of spasticity to people with multiple sclerosis: what can health professionals learn? Disabil Rehabil 2013;35:1284-92.
12 National Collaborating Centre for Chronic Conditions. Multiple sclerosis: national clinical guideline for diagnosis and management in primary and secondary care. Royal College of Physicians, 2004.
13 Katalinic OM, Harvey LA, Herbert RD, Moseley AM, Lannin NA, Schurr K. Stretch for the treatment and prevention of contractures. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2010;9:CD007455.
14 Jo HM, Song JC, Jang SH. Improvements in spasticity and motor function using a static stretching device for people with chronic hemiparesis following stroke. Neurorehabilitation 2013;32:369-75.
15 Kim EH, Chang MC, Seo JP, Jang SH, Song JC, Jo HM. The effect of a hand stretching device during the management of spasticity in chronic hemiparetic stroke patients. Ann Rehabil Med 2013;37:235-40.
16 Gracies JM, Marosszeky JE, Renton R, Sandanam J, Gandevia SC, Burke D. Short-term effects of dynamic lycra splints on upper limb in hemiplegic patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2000;81:1547-55.
17 Doucet BM, Mettler JA. Effects of a dynamic progressive orthotic intervention for chronic hemiplegia: a case series. J Hand Ther 2013;26:139-46.
18 Ibuki A, Bach T, Rogers D, Bernhardt J. The effect of tone-reducing orthotic devices on soleus muscle reflex excitability while standing in patients with spasticity following stroke. Prosthet Orthot Int 2010;34:46-57.
19 Baker K, Cassidy E, Rone-Adams S. Therapeutic standing for people with multiple sclerosis: efficacy and feasibility. Int J Ther Rehabil 2007;14:104-9.
20 Manella KJ, Field-Fote EC. Modulatory effects of locomotor training on extensor spasticity in individuals with motor-incomplete spinal cord injury. Restor Neurol Neurosci 2013;31:633-46.
21 Ada L, Dorsch S, Canning CG. Strengthening interventions increase strength and improve activity after stroke: a systematic review. Aust J Physiother 2006;52:241-8.
22 Kagawa S, Koyama T, Hosomi M, Takebayashi T, Hanada K, Hashimoto F, et al. Effects of constraint-induced movement therapy on spasticity in patients with hemiparesis after stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2013;22:364-70.
23 Manella KJ, Field-Fote EC. Modulatory effects of locomotor training on extensor spasticity in individuals with motor-incomplete spinal cord injury. Restor Neurol Neurosci 2013;31:633-46.
24 Amatya B, Khan F, La Mantia L, Demetrios M, Wade DT. Non pharmacological interventions for spasticity in multiple sclerosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2013;2:CD009974.
25 Chou R, Peterson K, Helfand M. Comparative efficacy and safety of skeletal muscle relaxants for spasticity and musculoskeletal conditions: a systematic review. J Pain Symptom Manage 2004;28:140-75.
26 Taricco M, Pagliacci MC, Telaro E, Adone R. Pharmacological interventions for spasticity following spinal cord injury: results of a Cochrane systematic review. Eura Medicophys 2006;42:5-15.
27 Montane E, Vallano A, Laporte JR. Oral antispastic drugs in nonprogressive neurologic diseases: a systematic review. Neurology 2004;63:1357-63.
28 National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Spasticity in children and young people with non- progressive brain disorders. (Clinical Guideline 145.) 2012. http://guidance.nice. org.uk/CG145.
29 Halpern R, Gillard P, Graham GD, Varon SF, Zorowitz RD. Adherence associated with oral medications in the treatment of spasticity. PM R 2013;5:747-56.
30 Simon O, Yelnik AP. Managing spasticity with drugs. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med 2010;46:401-10.
31 Ghidini A, Healey A, Andreani M, Simonson MR. Pregnancy and women with spinal cord injuries. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2008;87:1006-10.
32 Moran LR, Almeida PG, Worden S, Huttner KM. Intrauterine baclofen exposure: a multidisciplinary approach. Paediatrics 2004;114:267-9.
33 Koppel BS, Brust JCM, Fife T, Bronstein J, Youssof S, Gronseth G, et al. Systematic review: efficacy and safety of medical marijuana in selected neurological disorders: Report of the guideline development subcommittee of the American Academy of neurology. Neurology 2014;82:1556-63.
34 Wade DT, Collin C, Stott C, Duncombe P. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of Sativex (nabiximols), on spasticity in people with multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 2010;16:707-14.
35 Lakhan SE, Rowland M. Whole plant cannabis extracts in the treatment of spasticity in multiple sclerosis: a systematic review. BMC Neurol 2009;9:59.
36 McCrory P, Turner-Stokes L, Baguley IJ, De Graff S, Katrak P, Sandanam J et al. Botulinum toxin for treatment of upper limb spasticity following stroke: a multi-centre randomized placebo-controlled study of effects on quality of life and other person centred outcomes. J Rehabil Med 2009;41:536-44.
37 Shaw L, Rodgers H, Price C, van Wijck F, Shackley P, Steen N, et al. BoTULS: a multicentre randomised controlled trial to evaluate the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of treating upper limb spasticity due to stroke with botulinum toxin type A. Health Technol Assess 2010;14(6).
38 Royal College of Physicians, British Society of Rehabilitation Medicine, Chartered Society of Physiotherapy, Association of Chartered Physiotherapists Interested in Neurology. Spasticity in adults: management using botulinum toxin. National guidelines. RCP, 2009.
39 Wissel J, Ward AB, Erztgaard P, Bensmail D, Hecht MJ, Lejune TM, et al. European consensus table on the use of botulinum toxin type A in adult spasticity. J Rehabil Med 2009;41:13-25.
40 Simpson DM, Gracies JM, Graham HK, Miyasaki JM, Naumann M, Russmann B, et al. Assessment: botulinum neurotoxin for the treatment of spasticity (an evidence based review): report of the therapeutics and technology assessment subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 2008;70:1691-8.
41 Lee SJ Sung IY, Jang DH, Yi JH, Lee JH, Ryu JS. The effect and complication of botulinum toxin type A injection with serial casting. Ann Rehabil Med 2011;35:344-53.
42 Zahavi A, Geertzen JH, Middel B, Staal M, Rietman JS. Long term effect of intrathecal baclofen on impairment, disability and quality of life in patients with severe spasticity of spinal origin J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2004;75:1553-7.
43 Schiess MC, Oh IJ, Stimming EF, Lucke J, Acosta F, Fisher S, et al. Prospective 12-month study of intrathecal baclofen therapy for post stroke spastic upper and lower extremity motor control and functional improvement. Neuromodulation 2011;14:38-45.
44 Bensmail D, Peskine A, Roche N, Mailhan L, Thiebaut JB, Bussel B. Intrathecal baclofen for treatment of spasticity of multiple sclerosis patients. Mult Scler 2006;12:101-3.
45 McIntyre A, Mays R, Mehta R, Janzen S, Townson A, Hsieh J, et al. Examining the effectiveness of intrathecal baclofen on spasticity in individuals with chronic spinal cord injury: a systematic review. J Spinal Cord Med 2014;37:11-8.
46 Stetkarova I, Yabion SA, Kofler M, Stokic DS. Procedure and device related complications of intrathecal baclofen administration for management of adult muscle hypertonia: a review. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 2010:24; 609-19.
47 Ross JC, Cook AM, Stewart GL, Fahy BG. Acute intrathecal baclofen withdrawal: a brief review of treatment options. Neurocrit Care 2011;14:103-8.
48 Kocabas H, Salli A, Demir AH, Ozerbil OM. Comparison of phenol and alcohol neurolysis of tibial nerve motor branches to the gastrocnemius muscle for treatment of spastic foot after stroke: a randomized controlled pilot study. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med 2010;46:5-10.
49 Yasar E, Tok F, Taskaynatan MA, Yilmaz B, Balaban B, Alaca R. The effects of phenol neurolysis of the obturator nerve on distribution of buttock seat interface pressure in spinal cord injury patients with hip adductor spasticity. Spinal Cord 2010;48:828-31.
50 Pinder C, Bhakta B, Kodavali K. Intrathecal phenol: an old treatment revisited. Disabil Rehabil 2008;30:381-6.
Comentarios
Para ver los comentarios de sus colegas o para expresar su opinión debe ingresar con su cuenta de IntraMed.