| Introducción |
La diabetes insípida es una condición rara pero tratable que generalmente se presenta con polidipsia y poliuria. Pero distinguir estos síntomas de los síntomas de la polidipsia primaria, la diabetes mellitus y otras causas de polaquiuria sin poliuria puede ser muy difícil.
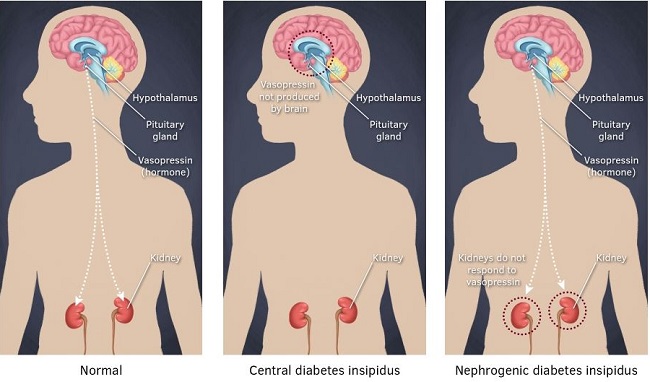
La diabetes insípida está causada por un trastorno en la producción de vasopresina en la glándula pituitaria. (diabetes insípida central) o, por la acción de la vasopresina en los riñones (diabetes insípida nefrogénica).
La administración de desmopresina, un fármaco análogo de la vasopresina, es un tratamiento eficaz para la diabetes insípida central. En Inglaterra, entre 2009 y 2016 hubo 4 casos de muerte debidas a la omisión de desmopresina, y otros 56 incidentes debidos a errores en la dosificación de desmopresina, con resultados dañinos.
|
Lo que es necesario saber • Es poco probable que un paciente con poliuria y osmolaridad urinaria >700 mOsmol/kg sufra diabetes insípida. • Los pacientes con diabetes insípida central que ingresan en el hospital deben contar con información y garantías especializadas para asegurar la administración de desmopresina • La enfermedad intercurrente con hipernatremia en un paciente con diabetes insípida debe ser manejada como una emergencia médica. |
| ¿Qué es la diabetes insípida? |
La diabetes insípida es rara siendo su prevalencia de 1 en 25.000.
La diabetes insípida central suele estar provocada por patologías de la hipófisis, ya sea como resultado de procesos infiltrativos o inflamatorios o, posteriores a la cirugía de un tumor hipofisario, pero también puede deberse a un defecto congénito en la producción de arginina vasopresina (hormona antidiurética).
La diabetes insípida nefrógena suele estar causada por alteraciones electrolíticas, nefropatía o nefrotoxicidad farmacológica (comúnmente litio).
La arginina vasopresina provoca la reabsorción de agua en los tubos colectores del riñón. La deficiencia de la hormona o la resistencia a la misma, como sucede en la diabetes insípida, conducen a un exceso de pérdida de agua por el riñón (poliuria).
Típicamente, el impulso compensatorio es la sed, que proporcionará una rehidratación adecuada, pero en casos graves, cuando no hay acceso al agua, la persona con diabetes insípida puede deshidratarse rápidamente, lo que puede conducir a hiperosmolalidad, hipernatremia y, potencialmente, muerte.
| ¿Cómo se diagnostica la diabetes insípida? |
> Presentación de los síntomas
La sed extrema y la emisión de grandes cantidades de orina clara son síntomas típicos de diabetes insípida, pero puede ser difícil hacer un diagnóstico diferencial con estos síntomas, aunque se pueden hallar indicadores en los antecedentes y los estudios, que pueden ayudar.
| Claves para distinguir la diabetes insípida de la polidipsia primaria | |||
| Polidipsia primaria | Diabetes insípida central | Diabetes insípida nefrogénica | |
| Comorbilidades | Historia de enfermedad psiquiátrica | Historia de enfermedad hipofisaria, lesión cerebral o terapia con litio o nefropatía; neurocirugía | Historia de tratamiento con litio o enfermedad renal |
| Momento de los síntomas | Síntomas de larga data Síntomas empeoran durante el día El paciente se despierta más con sed que con gamas de orinar | Comienzo rápido Síntomas mal día y noche El paciente se despierta más con ganas de orinar que con sed | Inicio insidioso Síntomas día y noche, y puede haber estado presente por meses o años |
| Respuesta a la reducción de la ingesta de líquidos | Poliuria mejora reduciendo la ingesta de líquidos | La poliuria no mejora con la reducción de la ingesta de líquidos | La poliuria no mejora con la reducción de la ingesta de líquidos |
Un desafío particular es la polidipsia primaria, la cual se refiere a un aumento psicológico de la ingesta de líquidos y no a una alteración de la regulación de la vasopresina; a menudo se observa en pacientes con enfermedades mentales graves y/o discapacidad del desarrollo, aunque puede ser simplemente una alteración del comportamiento y ocurrir en personas sanas, sin enfermedad psiquiátrica. La poliuria debe distinguirse de la polaquiuria por los antecedentes, ya que esta última sugiere un problema urológico.
En la diabetes insípida central, el antecedente de poliuria y polidipsia suele ser de aparición repentina, presentándose a las semanas o meses de inicio. En la diabetes insípida nefrogénica, el inicio es más insidioso y los pacientes suelen haber tenido síntomas durante meses o años antes del diagnóstico.
Los síntomas que sugieren enfermedad pituitaria son fatiga, mareos, ciclos menstruarles irregulares y galactorrea en las mujeres o y, pérdida de la libido y reducción de las características sexuales secundarias en los hombres.
Interrogar acerca de antecedentes de enfermedad pituitaria, lesión cefálica mayor o neurocirugía, los cuales son factores de riesgo de diabetes insípida central. En esta condición se han identificado varias mutaciones genéticas, por lo que una historia familiar de diabetes insípida central o nefrogénica puede ser muy importante.
Se debe analizar cuidadosamente el historial de medicamentos que toman los pacientes. Aquellos que toman diuréticos de asa y fármacos nefrotóxicos están en riesgo de desarrollar diabetes insípida nefrogénica. La diabetes insípida nefrogénica ocurre en casi el 15% de los pacientes que toman litio.
| Investigación inicial |
> Diabetes mellitus
Se debe excluir la diabetes mellitus, ya sea mediante el análisis de orina o pruebas en el punto de atención, confirmadas por la medición formal de la glucemia en ayunas o al azar.
> Alteración electrolítica
Extraer sangre para excluir la hipercalcemia y la hipopotasemia, ya que pueden causar diabetes insípida nefrogénica.
> Diuresis
Si la diuresis de 24 horas es <2,5 litros, es muy improbable que se deba a la diabetes insípida, y hay que buscar otras causas urinarias de los síntomas. El paciente mismo puede medir el volumen de orina o recogerla y enviarla al laboratorio para su medición.
> Osmolalidad pareada de orina y plasma
Si la diuresis de 24 horas es >2,5 litros, las osmolalidades pareadas de suero y orina pueden ayudar a distinguir entre la diabetes insípida y la poliuria secundaria a la polidipsia primaria.
Si la osmolalidad urinaria basal es >700 mOsmol/kg, es muy poco probable que se trate de la diabetes insípida ya que esta osmolaridad demuestra la capacidad de concentración urinaria.
La diabetes insípida es probable si la osmolalidad sérica es elevada (>295 mOsmol/kg) y la osmolalidad de la orina es baja (<300 mOsmol/kg).
Debido a que los pacientes con diabetes insípida se compensan bebiendo para calmar la sed, puede ser difícil distinguir a la diabetes insípida de la polidipsia primaria basándose en una sola medición de la osmolalidad urinaria y plasmática. En esta situación puede ser necesario realizar investigaciones más especializadas.
| Consultoría y manejo especializado |
Los pacientes con sospecha de diabetes insípida deben ser derivados al especialista para más estudios y el tratamiento. La urgencia de la derivación depende de la gravedad de los síntomas.
Si hay sed y poliuria extremos y la osmolalidad sérica es >295 mOsmol/kg, la derivación debe hacerse en unos días o unas pocas semanas como máximo.
Los pacientes con diabetes insípida conocida que tiene hipernatremia deben ser considerados en estado de emergencia, que debe ser resuelto mismo día.
| Investigaciones especializadas |
> Prueba de privación de agua
Actualmente, en casos dudosos en los que el diagnóstico de diabetes insípida no está bien definido, esta prueba es el test confirmatorio más común utilizado en el ámbito de la atención especializada. En esta prueba, la persona está privada de agua durante varias horas, mientras que su diuresis y la osmolalidad urinaria y sérica se controlan a lo largo del tiempo.
En los pacientes con diabetes insípida grave, la privación de agua puede ser altamente desagradable y debe ser supervisada por el equipo de endocrinología midiendo continuamente la osmolalidad sérica y urinaria, la diuresis y el peso.
Si durante la restricción hídrica el paciente está angustiado o hay evidencia clara de una diuresis muy elevada de orina diluida o, hay un excesivo aumento de la osmolalidad sérica y pérdida excesiva de peso, la prueba debe ser detenida.
En las personas con diabetes insípida hay poliuria continua con osmolalidad urinaria baja a pesar de la privación de agua.
Si la diuresis disminuye y la osmolalidad urinaria es >750 mOsmol/kg, queda excluida la diabetes insípida. En estos casos, el diagnóstico más probable es la polidipsia primaria. En la segunda parte de la prueba de privación de agua, los pacientes en los que se ha confirmado la diabetes insípida debe administrarse desmopresina.
Los pacientes con diabetes insípida central responden a la desmopresina con aumento de la osmolalidad urinaria y descenso del volumen de orina. Los pacientes con diabetes insípida nefrogénica no responden a la desmopresina.
> Otras investigaciones especializadas
Actualmente está muy difundida la medición de la copeptina, un marcador de los niveles de arginina vasopresina luego de la infusión de solución salina hipertónica. En individuos normales, el líquido hipertónico provoca mayor liberación de vasopresina y, por lo tanto, un aumento de los niveles de copeptina.
En la diabetes insípida central la copeptina muestra una aumento modesto, y probablemente sea una prueba diagnóstica más sensible y específica que la prueba de privación de agua.
Las imágenes de la hipófisis, como las de la resonancia magnética y la tomografía por emisión de positrones pueden ayudar a diferenciar los trastornos hipofisarios inflamatorios de los infiltrativos.
| Tratamiento |
> Diabetes insípida central
Los pilares terapéuticos son el reemplazo adecuado de líquidos, el tratamiento de la patología subyacente y la administración de desmopresina. Este análogo de la hormona antidiurética puede administrarse por vía oral o mediante un spray intranasal.
En general, la diabetes insípida central responde inmediatamente a la desmopresina, y los pacientes notan una reducción importante de la poliuria y la sed. Los síntomas del aporte insuficiente de desmopresina son la sed y la poliuria, mientras que los síntomas de un reemplazo excesivo son cefalea y confusión leve (debido a la hiponatremia), y disminución de la diuresis.
Una parte importante del tratamiento es capacitar a los pacientes para el manejo de su enfermedad, mientras que la enfermera especializada desempeña un papel clave en este sentido.
Un área importante del auto manejo es prevenir la hiponatremia, de presentación habitual, la cual es una complicación del tratamiento con desmopresina porque el exceso de ingesta líquida en presencia de desmopresina continua puede llevar a la dilución excesiva de la sangre, por reabsorción excesiva de agua.
Es una buena práctica para el paciente mantener una diuresis regular omitiendo la dosis de desmopresina 1-2 veces/semana o, esperar a orinar antes de tomar su medicación. La Pituitary Foundation diseñó una tarjeta de diabetes insípida y folletos para que los pacientes los lleven consigo, para conocimiento del médico tratante en caso de emergencia.
Esto garantiza que si un paciente está demasiado mal para responder al interrogatorio, el primer médico que entra en escena conozca el diagnóstico de diabetes insípida y la importancia de administrar líquidos y desmopresina.
Actualmente se están desarrollando trabajos para producir folletos de información para el paciente, similares a las reglas para la hidrocortisona durante los días de enfermedad de los pacientes con hipoadrenalismo.
> Diabetes insípida nefrogénica
Se trata con aporte de líquido y tratamiento etiológico específico, bajo la atención de un nefrólogo. Otros tratamientos incluyen dietas hiposódicas e hhipoproteicas, diuréticos y antiinflamatorios no esteroides.
| Manejo de la diabetes insípida para médicos no especialistas |
> Cuidado del paciente hospitalizado
La Society for Endocrinology recientemente ha desarrollado recomendaciones para el tratamiento hospitalario de los pacientes con diabetes insípida que padecen una enfermedad aguda. Estas pautas recomiendan que todos los pacientes hospitalizados con diabetes insípida central sean identificados al ingreso y se avise al equipo de endocrinología o clínico correspondiente.
Cualquier paciente con diabetes insípida central que ingresa a un hospital necesita un cuidadoso monitoreo del reemplazo de líquidos, así como la administración apropiada de desmopresina. En la evaluación prequirúrgica de todos los pacientes que van a ser sometidos a una cirugía electiva se debe establecer un plan perioperatorio claro.
Se recomienda que los hospitales desarrollen un sistema de alerta para identificar a todos los pacientes que requieren tratamiento con desmopresina, con el fin de garantizar que no se omita la medicación.
Una encuesta de la Society for Endocrinology en el Reino Unido, realizada a los endocrinólogos indica que el problema del retardo en la administración de desmopresina y líquidos de los pacientes que se hospitalizan está muy extendido.
El 55% de los encuestados tenía dudas sobre el manejo de los pacientes con diabetes insípida en su hospital, y el 47% reportó que al menos 1 paciente sufre daño debido a la administración retrasada de desmopresina o la sustitución insuficiente de líquidos.
Una alerta de seguridad para el paciente del NHS (del inglés: National Health Service) ha reportado una serie de incidentes críticos en pacientes con diabetes insípida central. Entre 2009 y 2016, en Inglaterra se produjeron 4 muertes hospitalarias causadas por la omisión de desmopresina. Uno era un hombre de 22 años con un tumor hipofisario benigno que murió después de un procedimiento ortopédico de rutina.
Esta alerta de seguridad identificó varios errores en estos incidentes, como la falta de conciencia de la importancia de la desmopresina entre el personal médico, farmacéutico y de enfermería; la escasa disponibilidad de desmopresina en las áreas de internación clínica y la falta de aporte de líquidos orales debido a la premisa de “nada por boca” o a la presencia de un enfermedad aguda.
Una pequeña encuesta en el personal de enfermería no especializado halló que algunos no sabían que la diabetes insípida era una condición diferente. de la diabetes mellitus.
> Enfermedad intercurrente
Diabetes insípida central: en aquellos que se encuentran mal debido a una enfermedad intercurrente, es importante evaluar con precisión el estado hidroelectrolítico. Los pacientes con hipernatremia deben tratarse como una emergencia médica, con un estrecho monitoreo.
Durante la reanimación con líquidos se debe monitorear el sodio sérico cada 4 has. En los pacientes con alteración de la conciencia, administrar desmopresina por vía intravenosa, subcutánea o intramuscular.
Diabetes insípida nefrogénica: los pacientes tienen un riesgo similar de hipernatremia y deshidratación grave. Solicitar la interconsulta con un nefrólogo. Tratar la causa de la enfermedad intercurrente, suspender los medicamentos que pueden estar causando la diabetes insípida, y hacer la reanimación con líquidos.
Resumen y comentario objetivo: Dra. Marta Papponetti.