|
Resumen La hiperglucemia durante la internación es una condición frecuente que se asocia al aumento de complicaciones y resulta en un mal pronóstico para quienes la padecen. La estrategia para su tratamiento es la insulinoterapia. Un adecuado control glucémico se asocia a mejor evolución y pronóstico. Sin embargo, el nivel adecuado de glucemia se encuentra aún en debate, ya que aquellos ensayos en los cuales se fijaron metas estrictas demostraron incrementar las tasas de hipoglucemia y eventos clínicos adversos. La diabetes mellitus es la principal causa de enfermedad renal crónica en nuestro país. El tratamiento en ese contexto merece un análisis especial, ya que la vida media de la insulina puede resultar prolongada. Las opciones de insulinización en pacientes con enfermedad renal crónica e insuficiencia asociada provienen de recomendacio- nes de expertos en las cuales se jerarquizan esquemas que utilizan insulina de acción intermedia o prolongada asociadas a insulina regular o análogos de acción rápida. Durante el embarazo, las insulinas NPH y regular han demostrado seguridad y eficacia. Sin embargo, el desarrollo de nuevas moléculas de acción lenta y rápida permitió reducir la variabilidad glucémica, mejorar el control de la glucemia postprandial y reducir la tasa de hipoglucemias. El objetivo del presente trabajo es proporcionar una revisión sobre el adecuado uso de insulina en estas tres situaciones especiales. |
► Insulinoterapia en el paciente internado
Los pacientes diabéticos tienen tres veces más chance de ser hospitalizados comparados con aquellos que no lo son1, 2. Se estima que el 20% de los que egresan de un hospital tienen diabetes mellitus (DM) y que el 30% requiere dos o más internaciones por año. La presencia de hiperglucemia en internados es muy frecuente (38-80%), varía según la gravedad del caso y se asocia con peor pronóstico3-6.
Un adecuado control glucémico mediante diferentes regímenes de insulinización reduce la morbimortalidad, tanto en unidad de cuidados intensivos, como en internación general7. No obstante, estudios recientes han demostrado que el tratamiento intensivo con insulina incrementa el riesgo de hipoglucemias, lo que se asoció de manera independiente con mayor mortalidad en pacientes hospitalizados8-10.
Debido a estos hallazgos y a pesar de que la insulina es la terapéutica más recomendada, desde diferentes ámbitos se plantea cuáles deberían ser los objetivos glucémicos adecuados sin generar mayor morbimortalidad11-13.
♦ Fisiopatología y diagnóstico de la hiperglucemia durante la internación
En pacientes internados, se considera hiperglucemia un valor >140 mg/dl
En condiciones normales, durante el ayuno la glucemia se mantiene entre 70 y 100 mg/dl como consecuencia de un balance entre producción endógena y utilización periférica. En situaciones especiales, como enfermedades agudas o procesos quirúrgicos, se produce un aumento de la gluconeogénesis (hepática y en menor grado renal), incremento en la glucogenolisis y resistencia a la insulina en los tejidos periféricos, generando hiperglucemia sostenida.
Cuantitativamente la producción hepática de glucosa representa el mayor defecto fisiopatológico y está incrementada debido a la elevada disponibilidad de precursores para la gluconeogénesis (alanina y glutamina como resultado del exceso de proteólisis y disminución de síntesis proteica); exceso de lactato debido al aumento de glucogenolisis muscular y elevadas concentraciones de glicerol como consecuencia del incremento en la lipólisis14.
En situaciones de estrés se observa un incremento de la concentración de las hormonas contrarregulatorias (glucagón, cortisol, hormona de crecimiento y catecolaminas) generando insulino-resistencia, incremento en la producción hepática de glucosa e inhibición de la secreción de insulina. La hiperglucemia resultante genera un estado proinflamatorio caracterizado por una elevación de citoquinas y estrés oxidativo. Niveles elevados circulantes de factor de necrosis tumoral, interleuquina (IL) 6, IL 1-β, IL-8, proteína C reactiva generan en conjunto insulino-resistencia y compromiso en la secreción de insulina.
La hiperglucemia resulta en diuresis osmótica con hipovolemia y produce alteraciones tisulares generando injuria mitocondrial, stress oxidativo y disfunción endotelial por compromiso en la síntesis de óxido nítrico. Estos cambios serían los responsables de incrementar el riesgo de infección, compromiso en la cicatrización de heridas, falla orgánica múltiple, prolongación de la internación y muerte15.
En pacientes internados, se considera hiperglucemia un valor >140 mg/dl. Puede presentarse en pacientes con antecedentes de DM, en aquellos sin diagnóstico conocido pero que tienen DM –hemoglobina glicosilada (HbA1c) ≥6.5%– o bien como hiperglucemia transitoria intrahospitalaria (de stress), caracterizada por presentar glucemia >140 mg/dl y HbA1c <6.5%. Sin embargo es importante destacar que alrededor del 60% de estos últimos suelen presentar DM dentro del año posterior al alta12, 16, 17.
♦ Importancia clínica
Numerosos estudios han demostrado una asociación positiva entre hiperglucemia y complicaciones tales como mortalidad intrahospitalaria, mayor duración de la internación, mayor frecuencia de admisión en unidad de cuidados intensivos, necesidad de internaciones en instituciones de complejidad intermedia, riesgo de infección, compromiso en la cicatrización de heridas y falla orgánica múltiple. Esto ocurre tanto en pacientes que presentan estado crítico como en los que no lo presentan3.
Pacientes en estado crítico internados en unidad de cuidados intensivos con glucemias promedio de 214 mg/dl, presentaron mayor prevalencia de infecciones comparados con los que presentaron glucemias de 177 mg/dl18. Por otra parte, aquellos con niveles >200 mg/dl tuvieron una tasa mayor de mortalidad que los que se mantuvieron debajo de ese nivel19.
♦ Insulinoterapia en pacientes en estado crítico
Diferentes estudios demostraron que el tratamiento intensivo (objetivo glucémico entre 80 y 110 mg/dl) redujo complicaciones agudas, días de internación y mortalidad en pacientes internados en unidad de cuidados intensi- vos20. En contraposición, el tratamiento intensivo genera hipoglucemias graves con mayor riesgo de mortalidad21 y además, cuando se comparan tratamiento intensivo con tratamientos más conservadores no hay diferencia en cuanto a objetivos clínicos finales (puntos duros)22.
El estudio NICESUGAR publicado en 2009 comparó de manera aleatoria pacientes tratados intensivamente con insulina intravenosa vs. aquellos tratados no intensivamente (objetivos glucémicos 81-108 mg/dl vs. < 180 mg/dl). La mortalidad a 90 días fue mayor en el grupo tratado intensivamente (27.5% vs. 24.9%; OR 1.14; IC 95% 1.02-1.28; p = 0.02). Además, se observó incremento del riesgo de hipoglucemias graves (6.8% vs. 0.5%; OR 14, IC 95% 9-25.9; p <0.001)23.
Los principales factores de riesgo de hipoglucemia en pacientes hospitalizados son antecedentes de hipoglucemia previa, mayor edad, enfermedad renal crónica, falla cardíaca congestiva, malnutrición, irregularidad en el ingreso de nutrientes, uso concomitante de ciertos fármacos y tiempo de duración de la enfermedad. Se recomienda comenzar el tratamiento con insulina en unidad de cuidados intensivos cuando los niveles glucémicos superan 180 mg/dl. El objetivo terapéutico es mantener niveles entre 140 y 180 mg/dl. En pacientes en estado no crítico (con alimentación enteral) se recomienda mantener glucemias preprandiales <140 mg/dl al azar <180 mg/ dl12, 13 (Fig. 1).
El tratamiento con insulina por vía endovenosa es la mejor opción terapéutica en pacientes en estado crítico. La insulina regular administrada en forma continua mediante bomba de infusión tiene la ventaja de brindar, dada su corta vida media, gran flexibilidad, ya sea para intensificar o para suspender el tratamiento. Una variedad de protocolos de infusión intravenosa de insulina regular han sido descriptos, incluso existen protocolos computarizados y automatizados, aunque no demostraron superioridad terapéutica24.
No existe un algoritmo ideal. Cada centro debería implementar el esquema que más se ajuste a la disponibilidad de recursos humanos y materiales. A modo de sugerencia, cuando la glucemia supera los 140 mg/dl se debe comenzar monitoreo glucémico capilar cada 4-6 horas y si supera 180 mg/dl se debe iniciar insulinoterapia intravenosa continua con controles horarios de monitoreo glucémico capilar (Fig. 2)25.
En todos los casos es necesario administrar en forma continua, parenteral o enteral, un mínimo de 120 gramos de glucosa diarios (idealmente 140-180 g). La mayoría de los pacientes requerirá 5-10 gramos de glucosa/hora por lo cual sería adecuado infundir solución dextrosada al 5% a razón de 100-200 ml/h. En ciertos pacientes en estado crítico que llegan a la unidad de cuidados intensi- vos por motivos quirúrgicos se puede plantear un control glucémico más estricto (Fig. 3)25.
Antes de comenzar la infusión, en pacientes previamente insulinizados o con glucemias >200 mg/dl, puede administrarse un bolo inicial de insulina. El mismo podría calcularse dividiendo la glucemia inicial por 100. A modo de ejemplo, si la glucemia ingreso es 400 mg/dl, se administra un bolo de 4 UI. El ajuste de la infusión también se puede efectuar siguiendo un esquema modificado que requiere mayor complejidad en su seguimiento y el manejo por parte de especialistas (Tabla 1).
♦ Tratamiento de la hipoglucemia
Ante la presencia de hipoglucemia, se sugiere discontinuar la infusión de insulina y administrar solución glucosada hipertónica (dextrosa 50%) endovenosa según los siguientes niveles glucémicos: 40 a 60 mg/dl: 12.5 g (1/2 ampolla) y < 40 mg/dl: 25 g (1 ampolla). Se deberá reevaluar la glucemia plasmática cada 15-30 minutos y repetir la infusión de dextrosa 50% si fuera necesario. Reiniciar la infusión de insulina cuando la glucemia supera los 80 mg/dl en dos determinaciones con 30 minutos de diferencia, utilizando el 50% de la dosis anterior.
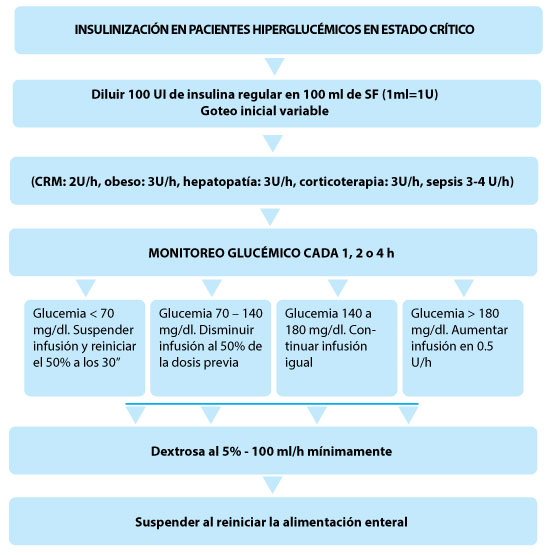
Fig. 2.– Insulinización en pacientes hiperglucémicos en estado crítico25

Fig. 3.– Insulinización en pacientes hiperglucémicos en estado crítico con objetivo de control más estricto25
TABLA 1.– Algoritmo de ajuste de la infusión en tratamiento intravenoso con insulina24
| Algoritmo 1 | Algoritmo 2 | Algoritmo 3 | Algoritmo 4 | ||||
| Glucemia < 110 | U/h Suspender | Glucemia < 110 | U/h Suspender | Glucemia < 110 | U/h Suspender | Glucemia < 110 | U/h Suspender |
| 110-119 | 0.5 | 110-119 | 1 | 110-119 | 2 | 110-119 | 3 |
| 120-149 | 1 | 120-149 | 1.5 | 120-149 | 3 | 120-149 | 5 |
| 150-179 | 1.5 | 150-179 | 2 | 150-179 | 4 | 150-179 | 7 |
| 180-209 | 2 | 180-209 | 3 | 180-209 | 5 | 180-209 | 9 |
| 210-239 | 2 | 210-239 | 4 | 210-239 | 6 | 210-239 | 12 |
| 240-269 | 3 | 240-269 | 5 | 240-269 | 8 | 240-269 | 16 |
| 270-299 | 3 | 270-299 | 6 | 270-299 | 10 | 270-299 | 20 |
| 300-329 | 4 | 300-329 | 7 | 300-329 | 12 | 300-329 | 24 |
| 330-359 | 4 | 330-359 | 8 | 330-359 | 14 | 330-359 | 28 |
| > 360 | 6 | > 360 | 12 | > 360 | 16 | > 360 | 32 |
♦ Transición a insulina subcutánea e insulinoterapia en áreas no críticas
El monitoreo glucémico capilar en sala general varía según si los pacientes se alimenten oralmente o estén en ayuno (o con alimentación enteral o parenteral). Se aconseja realizarlo precomidas y antes de dormir en el primer caso, y cada 4-6 horas en el segundo.
La insulinoterapia subcutánea es el tratamiento indicado independientemente de la etiología de la hiperglucemia. En la mayoría de los pacientes con DM2 internados por una patología aguda, se deberán discontinuar los agentes orales. Se recomienda utilizar una dosis de insulina de acción prolongada para cubrir los requerimientos basales, y varias dosis de insulina de acción corta para contemplar los requerimientos debidos a “escapes glucémicos” (corrección) y/o el aporte alimentario (aporte prandial). Esquemas utilizando insulina tales como NPH/detemir en dos dosis o glargina una vez al día solas o combinadas con insulina regular o análogos rápidos (lispro, aspártica o glulisina) han demostrado su efectividad (Tabla 2)26-28.
No se recomienda el esquema de “correcciones escalonadas” (sliding-scale en la literatura inglesa) de las hiperglucemias con insulina rápida sin aplicar insulina basal más allá de las primeras 24 horas en pacientes con glucemias >180 mg/dl sin diagnóstico previo de DM29.
Por otra parte, en individuos insulinizados, se deberá ajustar la dosis para evitar episodios de hiper o hipoglucemia durante la internación. En los que se iniciará el tratamiento con insulina, se propone una dosis total diaria basada en el peso real: 0.2-0.4 UI/kg.
A modo de ejemplo, para una persona de 80 kg la dosis total diaria inicial mínima sería de 20 UI. Esta dosis se dividirá como basal y prandial, en proporciones de 50/50 o 60/40, utilizándose 12 UI de insulina basal (NPH, glargina o detemir), y 8 UI como bolos preprandiales con insulina regular o análogos de acción rápida. Al comenzar la alimentación oral se debe discontinuar la infusión de insulina dos horas después de aplicar la primera dosis de insulina basal y se ajustará diariamente en base a las glucemias de ayuno y preprandiales.
Se deberá calcular la dosis de corrección con insulina regular o con análogos rápidos en base a los monitoreos glucémico capilar preprandiales y de acuerdo con el grado de sensibilidad a la insulina de cada paciente. Ésta se puede establecer en base al fenotipo, al antecedente de uso previo de insulina o al uso de fármacos como los corticoides que determinen insulino-resistencia (Tabla 3)8. En pacientes previamente insulinizados se recomienda reducir la dosis en un 20-25%. La Tabla 2 describe las distintas insulinas para utilizar durante la internación.
♦ Indicaciones para el alta
La internación es una oportunidad única para profundizar conceptos relacionados al manejo de la diabetes junto con el paciente30. Se pueden repasar pautas alimentarias, de monitoreo glucémico y reforzar entrenamiento en el uso apropiado de la insulina. La interconsulta debe ser temprana, para permitir a la educadora o al equipo médico realizar el ajuste terapéutico adecuado.
Las indicaciones terapéuticas al alta dependerán de la evolución durante la internación y de la HbA1c de ingreso que se utiliza para hacer diagnóstico de diabetes en quienes desconocían padecer esta enfermedad y para programar el tratamiento al momento del alta (Tabla 4)31.
TABLA 2.– Farmacocinética de distintas insulinas28
| Insulinas | Inicio | Pico (horas) | Duración efectiva (horas) |
| Lispro / aspart / glulisina | 5-10 min | 1-2 | 3-5 |
| Cristalina, neutra o corriente | 30-60 min | 2-3 | 3-6 |
| NPH | 2-4 h | 4-10 | 10-18 |
| Detemir | 1-2 h | Lineal | 16-24 |
| Glargina | 1-2 h | Lineal | 20-24 |
TABLA 3.– Tratamiento con insulina según fenotipo8
| Glucemia | Insulino-sensible | Usual | Insulino-resistente |
| > 141-180 | 2 | 4 | 6 |
| 181-220 | 4 | 6 | 8 |
| 221-260 | 6 | 8 | 10 |
| 261-300 | 8 | 10 | 12 |
| 301-350 | 10 | 12 | 14 |
| 351-400 | 12 | 14 | 16 |
| > 400 | 14 | 16 | 18 |
TABLA 4.– Indicaciones terapéuticas al alta
| HbA1c | Indicación |
| 6.5%-7.5% | Opciones: • Aumentar dosis de agentes no insulínicos • Agregar un tercer agente • Agregar insulina basal antes de acostarse |
| 7.6%-9.0% | Si el paciente se encuentra con dos agentes no insulínicos, agregar insulina basal antes de acostarse |
| ≥ 9% | Dar de alta con un régimen basal-bolos • Igual dosis de insulina intrahospitalaria (glargina o detemir una vez al día o NPH dos veces al día) • Bolos de insulina preprandiales (regular, lispro, aspártica o glulisina) • Dos veces al día de premezclas de insulina principalmente en adultos mayores |
TABLA 5.– Parámetros de control glucémico en pacientes diabéticos con enfermedad renal 35
| HAb1c % | Glucemia en ayunas | Glucemia postprandial (2h) | ||||
| mg/dl | mmol/l | mg/dl | mmol/l | |||
| Nefropatía diabética | < 6.5 | 80-120 | 4.4-6.7 |
| < 7.8 | |
| Pre-diálisis | < 7.5 | 100-120 | 5.6-6.7 | < 140-160 | < 7.8-8.9 | |
| Diálisis | < 7.5-8.0 | 100-140 | 5.6-7.8 | < 200 | < 11.1 | |
| Trasplante renal | < 6.5 | 80-120 | 4.4-6.7 | < 140 | < 7.8 | |
♦ Insulinoterapia en pacientes con DM y enfermedad renal crónica
En nuestro medio se ha comunicado que la DM fue una de las principales causas de enfermedad renal crónica en 2004-2013, según señala el Registro Argentino de Diálisis Crónica. Cuatro de cada diez personas que ingresan a diálisis en Argentina tienen DM (proporción similar a las cifras informadas en países como EE.UU.32), siendo la nefropatía diabética la primera causa de ingreso a la misma33. El manejo de la hiperglucemia en la enfermedad renal crónica constituye aún hoy un gran desafío.
♦ Clasificación de la enfermedad renal crónica
La enfermedad renal ha sido reclasificada en 2012 por la National Kidney Foundation en 5 estadios considerando el filtrado glomerular y los niveles de albuminuria, lo que permite evaluar el riesgo de progresión y morbimortalidad cardiovascular. Esta nueva clasificación jerarquiza de alguna manera el hecho que la albuminuria y la función renal son factores independientes de riesgo34.
♦ Insulinoterapia en pacientes con DM y enfermedad renal crónica
Se cuenta con escasa información, la mayoría proveniente de estudios no aleatorizados, en cuanto al control glucémico y su implicancia sobre función renal, morbilidad y mortalidad en pacientes con DM y enfermedad renal crónica (estadio 3-4-5) o en terapia de diálisis35.
En un estudio retrospectivo, Chun-ChenYu y col. compararon durante seis meses dos grupos de pacientes con DM en una unidad de diálisis, clasificados según su control glucémico, (nivel de glucosa en sangre y valor de HbA1c). Los pacientes con buen control glucémico tuvieron mayor supervivencia que aquellos con mal control (p < 0.01). En análisis multivariado sólo la edad y el control glucémico tuvieron impacto en la supervivencia36. En base a lo descripto se han propuesto diferentes objetivos de control glucémico según el estadio de la nefropatía (Tabla 5)35.
Los parámetros de control glucémico incluyen HbA1c, glucemia en ayunas, prueba de tolerancia oral a la glucosa, y la prevención de los episodios de hipoglucemia que describimos a continuación:
a) Hemoglobina glicosilada: La HbA1c es el parámetro bioquímico para monitorear el grado de control glucémico en pacientes con DM sin insuficiencia renal y se correlaciona con el riesgo de complicaciones microvasculares. Sin embargo, cabe señalar que los principales ensayos (DCCT37y UKPDS38) que demostraron esta relación excluyeron a pacientes con función renal significativamente alterada.
En los pacientes con enfermedad renal crónica la vida útil de los eritrocitos puede reducirse 30-70%, acortando el tiempo de exposición de los mismos a la glucosa con disminución de los niveles de HbA1c. A su vez, el uso de estimulantes de la eritropoyesis mejora la anemia, en par- te por aumentar el número de glóbulos rojos inmaduros en la circulación, cada uno de ellos con menor susceptibilidad a la glicosilación, por lo que actúa como una variable más que disminuye los valores de HbA1c39. Diferentes factores modifican los valores de HbA1c (Tabla 6). Todo lo mencionado anteriormente resulta en una gran variabilidad de la HbA1c, lo cual dificulta su interpretación, especialmente en los estadios de insuficiencia renal.
b) Glucemia en ayunas: Un estudio realizado en una comunidad india en Arizona (EE.UU.) con un seguimiento de 5 años sugiere que la medición de la glucemia en ayunas predice el desarrollo de retinopatía y nefropatía por diabetes40. Las glucemias de ayuno siguen siendo útiles para establecer criterios diagnósticos y determinar objetivos en los pacientes con DM41.
c) Prueba de tolerancia oral: Se estima que la hiperglucemia postprandial antecede en años a la hiperglucemia en ayunas42. El estudio Honolulu Heart43 realizó un seguimiento durante 12 años de 8006 hombres japoneses entre 45-70 años al inicio del estudio y reveló una correlación lineal entre la prueba de tolerancia oral y el riesgo de enfermedad coronaria. El estudio DECODE44, un análisis retrospectivo de 25 000 pacientes con DM2 en 13 estudios de cohorte europeos, con un seguimiento medio de 7.3 años, demostró asociación entre la glucemia postprandial obtenida por la prueba de tolerancia oral y mortalidad cardiovascular, sin relación con la glucemia de ayuno. De cualquier manera el subgrupo de pacientes con DM y enfermedad renal crónica, está pobremente representado en los mismos, por lo que las principales conductas terapeúticas en este subgrupo se basan en recomendaciones de expertos.
d) Hipoglucemia: En tres ensayos clínicos, (AC-CORD45, ADVANCE46 y VADT47) la hipoglucemia fue más frecuente en las ramas de tratamiento intensivo. En el estudio ADVANCE, la hipoglucemia grave fue casi dos veces más frecuente en el grupo de control intensivo al igual que en el estudio VADT, sin haberse demostrado un beneficio cardiovascular con la estrategia de terapia intensiva, aunque sí una reducción en los eventos microvasculares (retinopatía y nefropatía). Con respecto al riesgo adicional por padecer enfermedad renal crónica, en el análisis del estudio ADVANCE, los altos niveles de creatinina fueron un factor de riesgo independiente para la hipoglucemia grave.
En un metaanálisis que incluyó 5 estudios con 33040 pacientes y en los que se compararon distintos objetivos de control glucémico, se demostró que no existía beneficio en cuanto a eventos macrovasculares, logrando reducciones significativas en la incidencia de retinopatía y nefropatía con aumento de los episodios de hipoglucemia grave (OR: 3.3 IC 95% 2.69 a 4.06)48.
Las normas de la American Diabetes Association (ADA) recomiendan metas menos estrictas de HbA1c para aquellos pacientes con complicaciones avanzadas, múltiples comorbilidades o episodios de hipoglucemias graves49. Dado que los pacientes con enfermedad renal crónica presentan mayor riesgo de hipoglucemias, se los debe considerar como un grupo vulnerable y ser más permisivos en cuanto a los objetivos metabólicos (ver Tabla 5). Con la evidencia actual no es posible recomen- dar un control intensivo de la glucemia como medida de prevención de eventos cardiovasculares y menos aún en el subgrupo de pacientes con enfermedad renal crónica con insuficiencia renal50.
|
• Glucemia en ayunas: 70 a 90 mg/dl |
| Disminuye los valores | Aumenta los valores |
| Alteración de vida media del eritrocito por ER | Carbamilación de la hemoglobina |
| Transfusiones | Salicilatos - opiáceos |
| Ferropenia | Uremia - acidosis |
| Uso de eritropoyetina | Hipertrigliceridemia |
► Estrategias terapéuticas en pacientes con enfermedad renal crónica e insuficiencia renal
La enfermedad renal crónica asociada a la insuficiencia renal así como los tratamientos sustitutivos (hemodiálisis, diálisis peritoneal o trasplante) actúan sobre la secreción de insulina, su acción y metabolismo, generando valores de glucemia impredecibles. La concentración de dextrosa en los preparados para la diálisis puede también afectar el control de la glucemia. En conjunto, contribuyen a una mayor variabilidad glucémica, aumentando el riesgo de episodios hipoglucémicos.
La terapia con insulina en pacientes con insuficiencia renal difiere con respecto a otro grupo de pacientes debido a que las necesidades de insulina pueden ser menores y su acción puede verse prolongada. Cuando la tasa de filtrado glomerular está entre 10 y 50 ml/min, la dosis total de insulina se debería reducir un 25%; con valores de filtrado menores de 10 ml/min, la dosis debiera disminuirse un 50%, pero estas recomendaciones deberían ajustarse a cada paciente de forma individual35.
La mayoría de los esquemas de insulinización provienen de recomendaciones de expertos en guías de práctica clínica, indicando la utilización de insulina de acción intermedia (NPH) o análogos de acción prolongada (glargina, detemir) junto a un análogo de acción rápida en relación a las comidas40. Durante el tratamiento sustitutivo renal se deben agregar más controles glucémicos para ajustar el tratamiento, considerando que en los días del procedimiento, los requerimientos pueden variar.
No hay ensayos clínicos que evalúen diferentes regímenes de insulinización en el paciente renal, ni se han establecido algoritmos de cómo se debe aplicar la insulina en la población en diálisis. Es muy importante consensuar con el paciente y/o su familia el mejor esquema terapéutico que permita una mejor adherencia con reducción del riesgo de hipoglucemia.
La frecuencia del auto monitoreo no está establecida, se sugiere realizarlo según valores y variabilidad de la glucemia, recurrencia y severidad de las hipoglucemias, grado de educación y capacidad de tomar decisiones para modificar el esquema terapéutico. Durante el tratamiento sustitutivo renal, es necesario realizar controles según día y horario del tratamiento para ajustar la dosis de insulina. El baño de hemodiálisis debe ser preparado con una concentración de glucosa de ∼1 g/l.
No se han establecido algoritmos de cómo se debe aplicar la insulina en la población en diálisis. En la Tabla 7 mostramos algunos esquemas que pueden ser utilizados.
TABLA 7.– Ejemplo. Insulinización en insuficiencia renal crónica en tratamiento con hemodiálisis (según horario de hemodiálisis)
| Desayuno | Almuerzo | Merienda | Cena | Antes de dormir |
| Turno mañana (7-11 h) | NPH | NPH | ||
| NPH | ||||
| Determir | Determir | |||
| Glargina | ||||
| NPH | Turno tarde (12-16 h) | Determir | NPH | |
| Determir | Glargina | |||
| Glargina | Glargina | |||
| NPH | Turno noche (16-21 h) | NPH | ||
| Determir | Determir | |||
| Glargina | Glargina |
► Insulinoterapia en el embarazo
La prevalencia de diabetes en el embarazo se ha incrementado notablemente en los últimos años. La mayoría de los casos corresponden a diabetes gestacional y el resto a diabetes pregestacional, la que confiere un riesgo significativamente mayor para el embarazo que la diabetes gestacional51.
Se considera diabetes gestacional a cualquier grado de intolerancia a la glucosa con inicio en el embarazo; complica 2-10% de los mismos y se caracteriza por aumento de resistencia a la insulina e incapacidad de las células β para compensarlo. Se diagnostica al final del segundo trimestre (24-28 semanas de gestación) y aumenta el riesgo de complicaciones en la madre, el feto y el recién nacido. Luego del parto, el 35-60% de las mujeres con diabetes gestacional podrían desarrollar DM2 en los 10 a 20 años posteriores al embarazo52, 53.
♦ Fisiopatología
Durante el embarazo la transferencia de glucosa al feto se realiza por difusión facilitada, determinada por el gradiente materno fetal de la misma, siendo la glucemia fetal 10 a 20 miligramos menor que la materna. La transferencia excesiva de glucosa altera la embriogénesis54, 55.
Durante el primer y segundo trimestre hay un in- cremento marcado de los niveles de leptina e insulina séricas, se produce aumento de peso, del depósito de grasa y del índice de masa magra en la madre. Además, la sensibilidad a la insulina en los tejidos es normal o se encuentra ligeramente aumentada y, debido al consumo de glucosa por la placenta y al crecimiento fetal, la madre se encuentra predispuesta a episodios de hipoglucemia en ayunas.
A partir de la mitad del segundo trimestre del embarazo, la sensibilidad de los tejidos maternos a la insulina disminuye (insulino-resistencia fisiológica), la utilización periférica de glucosa es menor, lo que estimula la producción y secreción de insulina. Esto aumenta el requerimiento insulínico para lograr el objetivo glucémico en esta etapa del embarazo55. Cuando no se logra, se desarrolla la diabetes gestacional.
Luego del parto y el alumbramiento, los requerimientos de insulina caen abruptamente, situación que debe tenerse en cuenta, a fin de evitar el desarrollo de hipoglucemias55.
♦ Consecuencias de la hiperglucemia en el embarazo
Estudios observacionales muestran una relación directa entre la HbA1c elevada en el período embriogénico y el riesgo incrementado de embriopatía diabética (especial- mente de déficit de cierre de tubo neural y cardiopatías congénitas). También se ha demostrado la importancia de un medio intrauterino adecuado para evitar el riesgo del imprinting negativo en el niño que favorecerá enfermedades cardio-metabólicas en la edad adulta. La hiperglucemia materna se asocia con hipoglucemia neonatal, síndrome de dificultad respiratoria, macrosomía, hiperbilirrubinemia, infecciones del tracto urinario y trastornos hipertensivos del embarazo56.
La insulina es el agente terapéutico elegido para el manejo de la diabetes en el embarazo, ya que no existe evidencia suficiente sobre la utilización de otros fármacos a largo plazo.
♦ Diagnóstico y objetivos terapéuticos
A todas las embarazadas se le solicitará una glucemia en ayunas en la primera consulta. Se diagnostica diabetes gestacional cuando se constata57:
⇒ Dos o más glucemias en ayunas iguales o superiores a 100 mg/dl (5.5 mmol/l) asegurando un ayuno de 8 horas
⇒ Prueba de tolerancia oral a la glucosa realizada en las semanas 24-28 con un valor a las 2 horas ≥ 140 mg/dl (7.8 mmol/l)
Los factores de riesgo para el desarrollo de diabetes gestacional son los siguientes57:
⇒ Edad mayor o igual a 30 años.
⇒ Índice de masa corporal ≥ 27 al comienzo del embarazo.
⇒ Glucemia en ayunas > 85 mg/dl.
⇒ Síndrome de poliquistosis ovárica.
⇒ Preeclampsia.
⇒ Multiparidad.
⇒ Utilización de drogas hiperglucemiantes (corticoides, antiretrovirales, betamiméticos, etc.).
⇒ Antecedente de diabetes gestacional en embarazo anterior, diabetes en familiares de primer grado, macrosomía fetal (peso al nacer de un hijo ≥ 4 000 g), mortalidad perinatal inexplicada y alto o bajo peso al nacer en la madre.
♦ Insulinoterapia en diabetes pregestacional
El tratamiento con insulina durante el embarazo conlleva el riesgo de generar estimulación mitogénica, teratogenicidad y embriotoxicidad por atravesar la barrera hematoplacentaria. Se dispone de evidencia proveniente de estudios observacionales y aleatorizados que permiten establecer diferentes recomendaciones para la insulinización de mujeres con DM previa57.
Las insulinas humanas de acción intermedia (NPH) y de acción rápida (insulina regular) han demostrado su eficacia, seguridad y costo-efectividad durante el embarazo incluyendo su administración con infusores de insulina58. No siempre se logra el control de las variaciones glucémicas postprandiales, y si se alcanza, aún pueden ocurrir episodios de hipoglucemia de gravedad variable. En los últimos años se ha incorporado el uso de análogos de insulina que han demostrado ciertas ventajas con respecto a las insulinas humanas59.
El desarrollo de análogos de acción rápida ha permitido lograr objetivos muy importantes tales como mejorar el control de la glucemia postprandial comparados con insulina regular humana, disminuir la tasa de hipoglucemias tardías y reducir la variabilidad glucémica cuando se asocian a una insulina basal60, 61.
En cuanto a la evaluación de las insulinas según las categorías farmacológicas según la Food and Drug Administration de los EE.UU., la mayoría se encuentran en categoría B, es decir, sin evidencia de riesgo en la especie humana, pero con escasos estudios controlados en mujeres embarazadas.
En cuanto a la utilización del análogo de acción prolongada glargina durante el embarazo, se han comunicado hasta la fecha estudios observacionales retrospectivos. En un estudio multicéntrico, Lepercq y col. no observaron mayor tasa de malformaciones congénitas ni mayor mortalidad perinatal en 102 mujeres embarazadas tratadas con insulina glargina62. Otro estudio realizado en 20 centros obstétricos del Reino Unido analizó a 115 mujeres que recibieron insulina glargina durante el embarazo, evidenciando que su uso no se asoció con complicaciones maternas, abortos, anomalías congénitas, mortalidad ni morbilidad perinatal63. Es considerada categoría C por la Food and Drug Administration.
En una comparación aleatoria y controlada en 310 mujeres con DM1, Mathiesen y col. demostraron que el análogo lento detemir no es inferior a la insulina NPH en el descenso de HbA1c a las a las 36 semanas de gestación. La glucemia en ayunas fue menor en el grupo detemir sin aumento de los episodios de hipoglucemia64. Detemir se encuentra en la categoría B en las recomendaciones de la Food and Drug Administration para su uso en el embarazo.
Dada la gran variedad de regímenes de insulinización existentes y las distintas formas de presentación de la enfermedad, se aconseja la individualización del tratamiento y el control por un equipo especializado. Esto minimiza- ría la ocurrencia de episodios de hipoglucemia, los que constituyen la mayor barrera para el adecuado control metabólico, principalmente en pacientes con DM157.
♦ Insulinoterapia en diabetes gestacional
La mayoría de las recomendaciones provienen de estudios que evaluaron la utilización de insulina en embarazadas con DM1 y se apoyan en recomendaciones de expertos. Se sugiere indicar insulinoterapia en pacientes con diabetes gestacional cuando, luego de 7 días con plan de alimentación, no alcancen los objetivos glucémicos en el 80% de los controles solicitados (Fig. 4).
Si los valores de glucemia son muy elevados, se podrá acortar dicho plazo o insulinizar desde el comienzo57. Se sugiere comenzar con 0.1-0.2 UI/kg peso actual/día de insulina NPH con el objetivo de lograr glucemias de ayuno adecuadas. Si con ello no se logran controlar los perfiles durante el resto del día es necesario comenzar con insulina preprandial (regular o análogos ultrarrápidos), buscando personalizar los esquemas en base a los automonitoreos glucémicos.
La insulinoterapia deberá ser personalizada, y lo ideal es combinar una insulina de acción rápida con una de acción intermedia o prolongada, basándose en los esquemas de insulinización para pacientes con DM157.
♦ Estrategias de insulinización en diabetes pregestacional
Sigue los mismos lineamientos que en las mujeres no embarazadas con DM1. Se recomienda un régimen basal-prandial, recordando que los objetivos glucémicos son más bajos que en la población no embarazada. Para alcanzar los mismos se deberán realizar un promedio de 4-6 autocontroles de glucosa diarios entre pre y postprandiales.
En conclusión, en la actualidad, y a pesar de los numerosos trabajos publicados, existen diversas situaciones especiales en las cuales la insulinización de pacientes con DM aún mantiene muchas características artesanales y subjetivas. Hemos intentado transmitir con la mayor objetividad y claridad posible la información disponible con diferentes niveles de evidencia, unida a nuestra experiencia clínica en las áreas descriptas para su posible aplicación en la práctica diaria. Es muy importante seguir investigando diferentes esquemas de insulinización en estas situaciones para establecer guías prácticas basadas en los más altos grados de evidencia para lograr adecuados resultados en nuestros pacientes.
 Usted puede ingresar a todos los artículos del número de la revista Medicina Bs. As. Volumen 77 Año 2017 – Nº 5 índice haciendo click aquí
Usted puede ingresar a todos los artículos del número de la revista Medicina Bs. As. Volumen 77 Año 2017 – Nº 5 índice haciendo click aquí