| Resumen El tratamiento de la insuficiencia cardíaca es complejo y está en continua evolución. El American College of Cardiology y la American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) publicaron recomendaciones basadas en la evidencia en 2013 y desde entonces se crearon nuevos medicamentos y dispositivos. En este artículo se presenta un enfoque basado en la evidencia para el tratamiento actual de la insuficiencia cardíaca. |
A
► Afección grave y común
► Angiotensina
► Aldosterona
► Afección grave y común
La insuficiencia cardíaca es un síndrome debilitante frecuente que produce deterioro físico y mental y es la principal causa de hospitalizaciones. En los EEUU Se estima que 5,1 millones de estadounidenses sufren insuficiencia cardíaca y se diagnostican 900.000 nuevos casos por año.2
Para describir la gravedad de la insuficiencia cardíaca se puede emplear la clasificación funcional de la New York Heart Association (NYHA; cuadro 1) o las etapas definidas por la ACC y la AHA.1,3
|
Cuadro 1 NYHA clase I NYHA clase II No hay limitaciones físicas Limitación leve de la actividad física NYHA clase III NYHA clase IV Limitación notable de la actividad física Síntomas en reposo Etapa A Etapa B Pacientes con riesgo de insuficiencia cardíaca Enfermedad estructural Sin enfermedad estructural Sin síntomas de insuficiencia cardíaca Etapa C Etapa D Enfermedad estructural Enfermedad terminal Síntomas de insuficiencia cardíaca |
► Inhibidores de la enzima convertidora de angiotensina (ECA)
En la insuficiencia cardíaca con disminución de la fracción de eyección el sistema renina-angiotensina-aldosterona aumenta su acción como mecanismo adaptativo para mantener la homeostasis hemodinámica. 6–8 . La activación prolongada de este sistema puede producir efectos cardiovasculares perjudiciales, como hipertrofia de los miocitos, fibrosis miocárdica, retención del sodio y sobrecarga de líquidos.8,9
La angiotensina II es un potente vasoconstrictor y es importante para el remodelado cardiovascular, generando la progresión de la insuficiencia cardíaca.6
Las recomendaciones aconsejan los inhibidores de la ECA para todos los pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca con disminución de la fracción de eyección
CONSENSUS (Cooperative North Scandinavian Enalapril Survival Study) es un estudio que analizó el efecto del inhibidor de la ECA enalapril sobre la supervivencia en 253 pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca clase IV de la NYHA. Se aleatorizó a los participantes a recibir enalapril o placebo. A 6 meses, la tasa de mortalidad fue del 26% en el grupo enalapril vs 44% en el grupo placebo; se verificó una reducción del riesgo absoluto del 18% y del riesgo relativo del 41%. A 12 meses la reducción del riesgo relativo de mortalidad fue del 30%.10
El estudio SOLVD (Study of Left Ventricular Dysfunction) amplió el empleo de inhibidores de la ECA en todos los pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca, no sólo aquellos con clase IV de la NYHA. Aleatorizó a 1284 pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca de cualquier clase de la NYHA y fracción de eyección menor del 35% a recibir enalapril o placebo y demostró la reducción del 16% del riesgo relativo de mortalidad en el grupo enalapril, con tasas de mortalidad del 36% vs 39,7%.11
Recomendaciones. Los beneficios de la inhibición de la ECA se demostraron en pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca leve, moderada y grave. Por consiguiente, las recomendaciones aconsejan los inhibidores de la ECA para todos los pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca con disminución de la fracción de eyección.1
► Bloqueantes de los receptores de angiotensina II
Los bloqueantes del receptor de angiotensina II (BRA) son otros medicamentos adecuados para los pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca con disminución de la fracción de eyección que no toleran los inhibidores de la ECA.
El estudio Val-HefT (Valsartan HF Trial)12 , doble ciego aleatorizó a 5010 pacientes a recibir valsartan o placebo, con antecedentes de haber recibido betabloqueantes, digoxina, diuréticos e inhibidores de la ECA, entre otros. El criterio de valoración combinado de mortalidad y morbilidad disminuyó el 13% y las hospitalizaciones por insuficiencia cardíaca disminuyeron el 24% en el grupo valsartan.12
El análisis de subgrupos comparó a los pacientes sobre la base del empleo de inhibidores de la ECA y betabloqueantes al inicio del estudio. El valsartan tuvo efecto favorable en los subgrupos que recibían betabloqueantes solos, inhibidores de la ECA solos y ninguno de los dos. Sin embargo, cuando los pacientes recibieron los tres medicamentos la tasa de mortalidad aumentó significativamente (P = 0,009).12 Este dato fue discordante con los de otros estudios, que hallaron que la asociación de un inhibidor de la ECA y un BRA brindaba un pequeño beneficio.
CHARM-Added (Candesartan in HF Assessment of Reduction in Mortality and Morbidity) 13 estudió si el agregado del BRA candesartan a un inhibidor de la ECA mejoraba la evolución de los pacientes. Se aleatorizó a 2548 pacientes de clase II, II o IV de la NYHA con fracción de eyección ventricular izquierda menor del 40% que recibían inhibidores de la ECA a recibir candesartan o placebo. El agregado de candesartan disminuyó significativamente la mortalidad cardiovascular y las hospitalizaciones por insuficiencia cardíaca, pero con la desventaja de tasas más altas de hiperpotasiemia y aumento de la creatininemia.13
Recomendaciones. El empleo conjunto de BRA, inhibidores de la ECA y antagonistas de la aldosterona no se recomienda y puede ser perjudicial.1
► Antagonistas del receptor de aldosterona
El aumento de la concentración de aldosterona produce retención de líquidos, pérdida de magnesio y potasio y fibrosis miocárdica.
RALES (Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study)14 probó la hipótesis de que el antagonista del receptor de aldosterona espironolactona (25 mg diarios) disminuiría las muertes por todas las causas en pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca grave que recibían los medicamentos habituales, entre otros un inhibidor de la ECA. RALES aleatorizó a 1663 pacientes clase III o IV de la NYHA con fracción de eyección ventricular izquierda del 35% o menos a recibir 25 mg de espironolactona o placebo. El estudio halló una reducción del 30% del riesgo relativo y del 11% del riesgo absoluto de la mortalidad por todas las causas, una reducción del 31% del riesgo relativo y del 10% del riesgo absoluto de la mortalidad cardíaca y un 30% menos de hospitalizaciones por cardiopatías en el grupo espironolactona.14
La eplerenona, un antagonista del receptor de aldosterona que carece de los efectos antiandrogénicos de la espironolactona, también es beneficiosa.
EMPHASIS-HF (Eplerenone in Mild Patients Hospitalized and Survival Study
in Heart Failure)16 amplió la aplicación de la eplerenona (y de los antagonistas de la aldosterona en general), al investigar sus efectos en 2737 pacientes clase II de la NYHA, independientemente de la etiología isquémica. El criterio de valoración de muerte cardiovascular u hospitalización por insuficiencia cardíaca se produjo en el 18,3% del grupo eplerenona vs el 25,9% del grupo placebo (P < 0,001). El 12,5% de los pacientes del grupo eplerenona murieron, en relación con el 15,5% del grupo placebo.
Recomendaciones. Las recomendaciones de 2013 aconsejan los antagonistas del receptor de aldosterona para pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca clase II, II o IV de la NYHA con fracción de eyección del 35% o menos, pera disminuir la morbimortalidad.1 También aconsejan no emplear estos fármacos para pacientes con insuficiencia renal.1
► Inihibidor de angiotensina-neprilisina (el futuro)
La neprilisina se identificó como otro blanco posible en el tratamiento de la insuficiencia cardíaca y se buscó asociar la inhibición de la angiotensina y la neprilisina.
La neprilisina, una endopeptidasa neutra, se asocia con la degradación de varios péptidos vasoactivos naturales, como el péptido natriurético, la bradicinina y la adrenomedulina. La inhibición de la neprilisina aumenta estas sustancias y contrarresta la sobreactivación neurohormonal que produce vasoconstricción, retención de sodio y remodelado cardíaco.17
El BRA valsartan se asoció con el inhibidor de neprilisina sacubitril para crear el primer inhibidor de angiotensina-neprilisina (ARNI).
PARADIGM-HF (Prospective Comparison of ARNI With ACEI to Determine
Impact on Global Mortality and Morbidity in Heart Failure trial) 17 estudió si la inhibición asociada de angiotensina-neprilisina era superior a la inhibición sólo de la ECA con enalapril en pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca crónica. Se aleatorizó a 10521 pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca clase II, II o IV de la NYHA para recibir sacubitril-valsartan o enalapril. El grupo que recibió sacubitril- valsartan tuvo significativamente menos muertes por causas cardiovasculares y menos hospitalizaciones por insuficiencia cardíaca.17 También se observó en ese grupo mejoría de la calidad de vida y de la clase funcional de la NYHA.17
Actualmente el sacubitril-valsartan está indicado para tratar la insuficiencia cardíaca con disminución de la fracción de eyección y síntomas de clase II, II o IV de la NYHA. Se lo debe evitar en pacientes que sufrieron angioedema con un inhibidor de la ECA o un BRA, en pacientes que reciben aliskiren para la diabetes y en pacientes con hipersensibilidad a cualquiera de sus componentes. Se debe evitar el empleo simultáneo de sacubitril-valsartan y un inhibidor de la ECA y se recomienda un período de eliminación del medicamento cuando se pasa de un inhibidor de la ECA a este fármaco combinado.
B
► Betabloqueantes
► BNP
► Betabloqueantes
En la insuficiencia cardíaca aumenta la activación simpática, con aumentos asociados de la noradrenalina, que pueden generar efectos perjudiciales a largo plazo sobre la función y la estructura cardíaca. Actualmente se sabe que el bloqueo del receptor betaadrenérgico es cardioprotector, pero antes los betabloqueantes estaban contraindicados para los pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca.
El primer estudio que indicó los beneficios del tratamiento de la insuficiencia cardíaca con un betabloqueante se publicó en 1979.20 Estudios posteriores demostraron un inmenso efecto favorable para la supervivencia con los betabloqueantes en la insuficiencia cardíaca, específicamente con el carvedilol, el metoprolol de liberación prolongada y el bisoprolol.
El estudio US Carvedilol Heart Failure Study Group 22 evaluó si el empleo de un betabloqueante en pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca disminuía la morbimortalidad.22 El estudio incorporó a 1094 pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca sintomática durante por un mínimo de 3 meses y fracción de eyección ventricular izquierda del 35% o menos con tratamiento anterior que incluía vasodilatadores, inhibidores de la ECA y digoxina. Se aleatorizó a los pacientes a recibir carvedilol o placebo. El carvedilol se asoció con considerable reducción del riesgo de mortalidad (7,8% con placebo vs 3,2% con carvedilol, P < 0,001) y del riesgo de hospitalizaciones (19,6% vs 14,1%, P = 0,036), lo que llevó a la finalización anticipada del estudio.
CIBIS-II (Cardiac Insufficiency Bisoprolol Study II) 23 investigó los efectos de los betabloqueantes sobre la supervivencia y la morbilidad. Incorporó a 2647 pacientes clase III o IV de la NYHA con fracción de eyección ventricular izquierda < 35% con antecedentes de medicación con diuréticos e inhibidores de la ECA. Este estudio también se dio por terminado anticipadamente tras demostrar un efecto favorable significativo de supervivencia con el bisoprolol.
MERIT-HF (Metoprolol Extended Release Randomized Intervention Trial in
Congestive Heart Failure) 24 evaluó si con metoprolol una vez al día descendía la mortalidad en pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca sintomática. Se estudiaron 3991 pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca crónica clase II-IV de la NYHA y fracción de eyección ventricular izquierda del 40% o menos. MERIT-HF también se dio por terminado anticipadamente, ya que se demostró una disminución del 34% de la mortalidad por todas las causas.
COMET (Carvedilol or Metoprolol European Trial) 25 fue el único estudio aleatorizado controlado comparativo con tratamiento activo que evaluó los resultados clínicos en pacientes que recibieron carvedilol o tartrato de metoprolol. Se aleatorizó a 1511 pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca clase II, II o IV de la NYHA y fracción de eyección ventricular izquierda del 35% o menos a recibir carvedilol o tartrato de metoprolol. El criterio principal de valoración de mortalidad por todas las causas se produjo en el 34% del grupo carvedilol y en el 40% del grupo tartrato de metoprolol (P = 0,0017).
Recomendaciones. Las recomendaciones de 2013 otorgan clase IA al consejo de comenzar con un betabloqueante (carvedilol, bisoprolol, o succinato de metoprolol en pacientes con síntomas actuales o pasados de insuficiencia cardíaca.1 Los betabloqueantes se deben iniciar con cautela o evitar en pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca aguda descompensada con sobrecarga de líquidos.
► Péptido natriurético tipo cerebral
La recomendación de la ACC/AHA es clase IA para el empleo de BNP para apoyar la toma de decisiones, especialmente en casos de duda
El péptido natriurético tipo cerebral (BNP por las siglas del inglés) o su producto de escisión amino- terminal (NT-proBNP) se origina en los cardiomiocitos y es liberado por varios disparadores, con más frecuencia el estiramiento de los cardiomiocitos frente a la sobrecarga de volumen o de presión.26 Las funciones biológicas del BNP comprenden la natriuresis y la vasodilatación, la inhibición del sistema renina-angiotensina y la modulación del sistema nervioso simpático. 26
El estudioTIME-CHF (Trial of Intensified vs. Standard Medical Therapy in Elderly Patients With Congestive HF) 27 investigó si los resultados a 18 meses serían mejores si el tratamiento se orientaba según los valores del BNP N-terminal más que por los síntomas. Esta estrategia no dio resultado.
BATTLESCARRED (NT-proBNPAssisted Treatment to Lessen Serial Cardiac
Readmissions and Death trial) 28 en 2009 mostró que el tratamiento orientado por el BNP reducía significativamente la mortalidad en pacientes menores de 75 años en relación con el tratamiento habitual.
PROTECT (Use of NT-proBNP Testing to Guide HF Therapy in the Outpatient
Setting study) 29 también mostró las ventajas de una estrategia orientada por el BNP: disminución de los episodios cardiovasculares y mejoría de la calidad de vida.29
GUIDE IT-HF (Guiding Evidence Based Therapy Using Biomarker Intensified
Treatment in Heart Failure), un estudio en marcha, evalúa la seguridad, eficacia y costo-eficacia de una estrategia orientada por biomarcadores en 1100 pacientes de alto riesgo con insuficiencia cardíaca con disminución de la fracción de eyección.
Recomendaciones. La recomendación de la ACC/AHA es clase IA para el empleo de BNP para apoyar la toma de decisiones, especialmente en casos de duda. El BNP también se puede emplear para determinar el pronóstico o la gravedad en la insuficiencia cardíaca crónica y para lograr la dosis terapéutica óptima para pacientes euvolémicos controlados en un programa estructurado de insuficiencia cardíaca.1
C
► Consultorios
► Cronotropismo
► Consultorios de insuficiencia cardíaca
Los pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca ahora se pueden atender en estos consultorios, cuyo objetivo es mejorar la atención médica orientada por las recomendaciones, educar al paciente y disminuir las hospitalizaciones por insuficiencia cardíaca.
Estudios mostraron que estos consultorios se asocian con mejor dosificación de los medicamentos, menos hospitalizaciones y menor costo de la atención médica.30–32
► Cronotropismo: inhibición de If
El aumento de la frecuencia cardíaca en reposo se asocia con aumento de la morbimortalidad cardiovascular.33 El descenso de la frecuencia cardíaca mejora la contracción del miocardio y la provisión de energía y disminuye el gasto de energía.34 La ivabradina, un inhibidor selectivo de los canales If, reduce la frecuencia cardíaca sin otros efectos cardiovasculares.
SHIFT (Systolic Heart Failure Treatment With the If Inhibitor Ivabradine Trial) 35 investigó si la reducción aislada de la frecuencia cardíaca disminuía los resultados adversos en pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca sintomática. SHIFT aleatorizó a 6505 pacientes con fracción de eyección del ventrículo izquierdo del 35% o menos, ritmo sinusal, frecuencia cardíaca de por lo menos 70 latidos/ minuto, tratamiento médico óptimo y hospitalizados dentro de los 12 meses de su incorporación a recibir ivabradina o placebo. El criterio principal de valoración fue la combinación de mortalidad cardiovascular y hospitalización por empeoramiento de la insuficiencia cardíaca. Los mejores resultados fueron para los pacientes con menor frecuencia cardíaca al término del estudio.
La ivabradina está indicada para pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca sintomática con fracción de eyección del ventrículo izquierdo menor del 35%, en ritmo sinusal, con las demás características mencionadas más arriba que reciben un betaboqueante en la dosis máxima tolerada o que tienen contraindicación para los beta-bloqueantes. La ivabradina se debe evitar en pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca aguda descompensada o que son hipotensos (presión arterial < 90/50 mm Hg), así como en pacientes con una anomalía de conducción significativa, disfunción hepática o bradicardia (frecuencia cardíaca en reposo < 60 latidos /minuto).
D
► Digoxina
► Diuréticos
► Dispositivos
► Digoxina
La digoxina se emplea para el tratamiento de la insuficiencia cardíaca sistólica desde hace más de 70 años.36, 37
► DIG (Digoxin Investigative Group trial) 38 evaluó durante 3 años el efecto a largo plazo de la digoxina sobre la mortalidad y la hospitalización por insuficiencia cardíaca. En pacientes con fracción de eyección del ventrículo izquierdo menor del 45%, la digoxina no tuvo efecto sobre la mortalidad cuando se la asoció con diuréticos e inhibidores de la ECA. Sin embargo, el riesgo de hospitalización por empeoramiento de la insuficiencia cardíaca disminuyó significativamente con el tratamiento con digoxina.38
Recomendaciones. La digoxina se debe considerar cuando los pacientes están tratados según las recomendaciones, pero los síntomas de insuficiencia cardíaca persisten. La dosis inicial es de 0,125 – 0,25 mg. 1La digoxina puede tener efectos tóxicos en pacientes con disfunción renal, hipopotasiemia, hipomagnesemia e hipotiroidismo.
La ACC/AHA considera como recomendación clase IIA a la digoxina en pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca con disminución de la fracción de eyección, para reducir las hospitalizaciones por insuficiencia cardíaca, salvo que esté contraindicada.1
► Diuréticos
Los diuréticos son la base del tratamiento de la insuficiencia cardíaca, que en la mayoría de los pacientes se inicia con la asociación de un diurético del asa y dieta hiposódica.
Las recomendaciones 2013 de la ACC/AHA consideran como recomendación clase I a los diuréticos en pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca con disminución de la fracción de eyección que tienen evidencia de retención de líquidos, salvo contraindicación, para mejorar los síntomas.1
► Dispositivos: Desfibriladores cardioversores implantables (DCI)
Los pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca tienen mayor riesgo de muerte súbita y arritmias ventriculares.39 Antes, los antiarrítmicos eran la norma para la taquicardia ventricular no sostenida tras el infarto de miocardio.
MADIT (Multicenter Automatic Defibrillator Implantation Trial) investigó si la implantación profiláctica de un desfibrilador cardíaco interno mejoraba la supervivencia a 5 años en pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca. Los pacientes idóneos habían sufrido un infarto de miocardio con onda Q o enzimas positivas dentro de las 3 semanas de su incorporación al estudio. También habían sufrido un episodio de taquicardia ventricular no sostenida asintomática no relacionado con el infarto agudo de miocardio. Además su fracción de eyección ventricular izquierda era menor del 35% y tenían taquiarritmia ventricular no suprimible, sostenida, inducible en las pruebas electrofisiológicas.40 Durante el estudio, murieron 15 pacientes en el grupo desfibrilador contra 39 en el grupo de tratamiento tradicional (P = 0,009) 40
MADIT II evaluó el posible efecto favorable sobre la supervivencia de un desfibrilador implantado profilácticamente en ausencia de pruebas electrofisiológicas para inducir arritmias. El estudio incorporó a 1232 pacientes con infartos de miocardio previos y fracción de eyección ventricular izquierda del 30% o menos. Se los aleatorizó a recibir un desfibrilador cardioversor implantado o tratamiento médico tradicional. El criterio principal de valoración fue la muerte por cualquier causa.41
La mortalidad fue del 19,8% en el grupo de tratamiento tradicional vs el 14,2% en el grupo desfibrilador group.41 MADIT-II confirmó los beneficios de un desfibrilador cardioversor implantado profilácticamente observados en el estudio MADIT original MADIT y además eliminó la necesidad de una prueba electrofisiológica previa al implante del dispositivo.
SCD-HeFT (Sudden Cardiac Death in Heart Failure Trial) evaluó si la amiodarona o un desfibrilador cardioversor implantado de sólo shock, de una sola derivación disminuía el riesgo de muerte (por todas las causas) en una población con insuficiencia cardíaca de leve a moderada con causas isquémicas y no isquémicas.42 Se aleatorizó a 2521 pacientes con fracción de eyección del 35% o menos, clase II o III de la NYHA y con insuficiencia cardíaca, estable a recibir un desfibrilador cardioversor implantable de una sola cámara, amiodarona o placebo.
Se produjeron 244 muertes en el grupo placebo, 240 en el grupo amiodarona y 182 mueertes en el grupo desfibrilador.42
Recomendaciones. Las recomendaciones 2013 de la ACC/AHA1 otorgan una recomendación clase 1A al desfibrilador implantable para la prevención primaria de la muerte súbita en determinados pacientes con miocardiopatía no isquémica o miocardiopatía isquémica por lo menos 40 días después de un infarto del miocardio y 90 días después de una angioplastia intraluminal coronaria o una derivación aortocoronaria con fracción de eyección del ventrículo izquierdo del 35% o menos; y síntomas de clase II o III de la NYHA con tratamiento médico crónico. Este tratamiento recibe una clasificación clase IB para la prevención primaria de la muerte súbita cardíaca para reducir la mortalidad total en determinados pacientes por lo menos 40 días después del infarto del miocardio con fracción de eyección ventricular izquierda del 30% o menos y síntomas clase I de la NYHA mientras o reciben.
► Dispositivos:
Tratamiento de resincronización cardíaca
El 25% - 30% de los pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca sufren una anomalía de conducción intraventricular, 43,44 que puede producir alteraciones de la función sistólica y diastólica. La estimulación biventricular, donde se coloca un catéter en el seno coronario además de la aurícula y el ventrículo derechos, optimiza la sincronización de la contracción ventricular.43,44
MUSTIC (Multisite Stimulation in Cardiomyopathies study) fue un estudio aleatorizado para evaluar la eficacia de la estimulación biventricular (también conocido como tratamiento de resincronización cardíaca) en pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca .44 Los criterios de incoporación fueron insuficiencia cardíaca clase III de la NYHA por lo menos durante 1 mes, fracción de eyección del ventrículo izquierdo de menos del 35%, diámetro ventricular izquierdo telediastólico > 60 mm y QRS de más de 150 ms. Los pacientes se controlaron hasta 9 y 12 meses.
A 12 meses, los pacientes podían caminar mucho más lejos en 6 minutos y su consumo máximo de oxígeno había aumentado. También refirieron una mejora significativa de la calidad de vida y la clase de la NYHA mejoró en un 25%. MUSTIC fue el primer estudio que mostró resultados favorables en la tolerancia al ejercicio, la calidad de vida, la mejoría del funcionamiento cardíaco y la reducción de los síntomas de insuficiencia cardíaca con el empleo de un marcapaso de estimulación biventricular a 1 año.
MIRACLE (Multicenter InSync Randomized Clinical Evaluation) validó los datos de MUSTIC con el empleo de una mayor población y un método doble ciego. 45
Recomendaciones. La ACC/AHA 2013 otorga al tratamiento de resincronización cardíaca una indicación clase IA/B para los pacientes clase II, III o IV de la NYHA que reciben tratamiento médico ,tienen ritmo sinusal, con fracción de eyección del ventrículo izquierdo del 35% o menos, bloqueo de rama izquierda, y duración del QRS de 150 ms o más.1
► Dispositivos: sensores implantables
El futuro del tratamiento ambulatorio de la insuficiencia cardíaca quizás incluya sensores implantables de la presión de la arteria pulmonar.
El CardioMEMS es un sistema implantable permanente para medir diariamente la presión de la arteria pulmonar de manera ambulatoria a fin de disminuir las hospitalizaciones relacionadas con la insuficiencia cardíaca. 46,47
CHAMPION (CardioMEMS Heart Sensor Allows Monitoring of Pressure to Improve Outcomes in NYHA Class III Patients trial) fue uno de los primeros estudios que evaluaron la seguridad y la eficacia de los sistemas implantables de monitoreo de la presión arterial pulmonar.46 El dispositivo en estudio se asoció con la disminución significativa de las presiones medias de la arteria pulmonar, menos hospitalizaciones por insuficiencia cardíaca y mejor calidad de vida. También se acortó la duración de las hospitalizaciones por esa causa en el grupo CardioMEMs.46
E
► Ejercicio
► Etapa terminal de la insuficiencia cardíaca
► Ejercicio
Los pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca habitualmente disminuyen su capacidad funcional, lo que se manifiesta como menor tolerancia al ejercicio y mala calidad de vida. Por esta causa el médico recomienda reposo y se produce deterioro físico paradojal y la posible progresión de los síntomas.
Varios estudios mostraron que la rehabilitación cardíaca mejora los resultados para los pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca.48 La rehabilitación cardíaca es un programa supervisado que comprende entrenamiento en ejercicio, hábitos de vida saludables, educación y consejería psicosocial.
HF-ACTION (Heart Failure: A Controlled Trial Investigating Outcomes of Exercise
Training) es el estudio aleatorizado más grande efectuado para determinar si el entrenamiento en ejercicio aeróbico disminuye la mortalidad por todas las causas o la hospitalización por todas las causas y mejora la calidad de vida en pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca estable.49 Aunque la reducción de los criterios de valoración inicialmente no fue estadísticamente significativa, tras ajustar para los factores pronósticos de mala evolución (tiempo de ejercicio cardiopulmonar, fracción de eyección ventricular izquierda, fibrilación auricular y depresión), se halló que el entrenamiento en ejercicio reducía la incidencia de mortalidad por todas las causas o de hospitalización por todas las causas en el 11% (P = 0,03).49
Recomendaciones. Sobre la base de los resultados de este estudio y de varios otros más pequeños, la ACC/AHA otorga una recomendación clase IA al entrenamiento en ejercicio como una actividad segura y eficaz para los pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca que pueden participar, a fin de mejorar su estado funcional. Se otorga una recomendación clase IIA para la rehabilitación cardíaca para mejorar la capacidad funcional, la duración del ejercicio, la calidad de vida y las tasas de mortalidad.1
► Etapa terminal de la insuficiencia cardíaca: Reconocimiento
Una parte de los pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca con disminución de la fracción de eyección finalmente progresan a la etapa D, también llamada insuficiencia cardíaca “avanzada”. La tasa de supervivencia a 5 años para pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca es del 50%, pero la mortalidad a 1 año para aquellos con insuficiencia cardíaca avanzada es mayor del 50%.50
Estas altas tasas de morbimortalidad se pueden disminuir. Por eso es esencial reconocer la progresión de la insuficiencia cardíaca a fin de derivar rápidamente a los pacientes para tratamientos como la infusión de inotrópicos, el apoyo circulatorio mecánico y el trasplante cardíaco, así como para tratamiento paliativo.1
La ACC/AHA1 publicó datos útiles para identificar a los pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca avanzada:
• Dos o más hospitalizaciones o visitas al servicio de urgencias por insuficiencia cardíaca durante el año anterior
• Deterioro progresivo de la función renal (aumento de la creatinina o la urea en sangre)
• Adelgazamiento sin ninguna otra causa
• Intolerancia a los inhibidores de la ECA debido a hipotensión o empeoramiento de la función renal
• Intolerancia a los betabloqueantes debido a empeoramiento de la insuficiencia cardíaca o la hipotensión
• Presión arterial sistólica a menudo <90 mm Hg
• Disnea persistente al bañarse o vestirse, que exige reposo
• Incapacidad para caminar una cuadra en terreno plano debido a disnea o fatiga
• Necesidad reciente de aumentar la dosis de diurético para mantener la volemia, a menudo llegando a dosis diarias equivalentes a furosemida >160 mg/día< o empleo de metolazona complementaria
• Disminución progresiva de la natremia, habitualmente hasta debajo de 133 mmol/l
• Frecuentes shocks del desfibrilador cardíaco implantado.
► Etapa terminal de la insuficiencia cardíaca: Dispositivos de asistencia ventricular izquierda
Para pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca resistente a pesar del tratamiento médico óptimo, tratamientos como el trasplante cardíaco o los dispositivos de asistencia ventricular izquierda son opciones duraderas. 52
REMATCH (Randomized Evaluation of Mechanical Assistance for the Treatment of Congestive HF trial) fue el estudio emblemático que mostró que el implante de un dispositivo de asistencia ventricular izquierda tenía efectos favorables para la supervivencia y la calidad de vida en pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca avanzada no idóneos para trasplante cardíaco, comparado con el tratamiento médico. 50 Este implante se asoció con la reducción absoluta del 27% de la mortalidad a 1 año.50 Sin embargo, la tasa de supervivencia a 2 años fue de sólo el 23%.
El estudio HeartMate II (Thoratec) comparó un dispositivo de flujo continuo de tipo axial vs el dispositivo de asistencia ventricular izquierda pulsátil y observó una supervivencia a 2 años del 58% con el dispositivo de flujo continuo vs el 24% con el dispositivo pulsátil (P =0,008).53
ADVANCE (Evaluation of the HeartWare Left Ventricular Assist Device for the Treatment of Advanced Heart Failure) mostró eficacia similar con el dispositivo de asistencia ventricular (Heartware), de flujo continuo centrífugo.54
La siguiente generación de dispositivos de asistencia ventricular izquierda de flujo continuo está actualmente en estudio.
La identificación temprana de los pacientes con enfermedad avanzada que se pueden beneficiar con estos tratamientos es importante.
► Falla o insuficiencia cardíaca
El tratamiento de la insuficiencia cardíaca evolucionó. En la década de 1960 se trataba con digoxina, diuréticos y reposo. En la actualidad se trata con bloqueo neurohormonal, diuréticos y recomendación de actividad física.55 Desde la publicación de las recomendaciones de 2013, surgieron nuevas opciones clínicas y nuevos dispositivos que mejoran la supervivencia o reducen las hospitalizaciones.
Es importante identificar a los pacientes en riesgo de insuficiencia cardíaca (etapa A) e implementar la modificación de los factores de riesgo. El tratamiento de la hipertensión, la diabetes mellitus y la dislipidemia disminuye el riesgo de insuficiencia cardíaca.1
Para los pacientes con evidencia de cardiopatía estructural con síntomas y sin ellos, la figura 1 resume el enfoque de las recomendaciones para el tratamiento de la insuficiencia cardíaca. Es importante señalar que las recomendaciones son para orientar el tratamiento, pero no reemplazan al criterio clínico.
La insuficiencia cardíaca es la vía final de toda la patología cardíaca y el conocimiento de la respuesta neurohormonal y de la fisiopatología generó la creación de nuevos tratamientos y dispositivos.
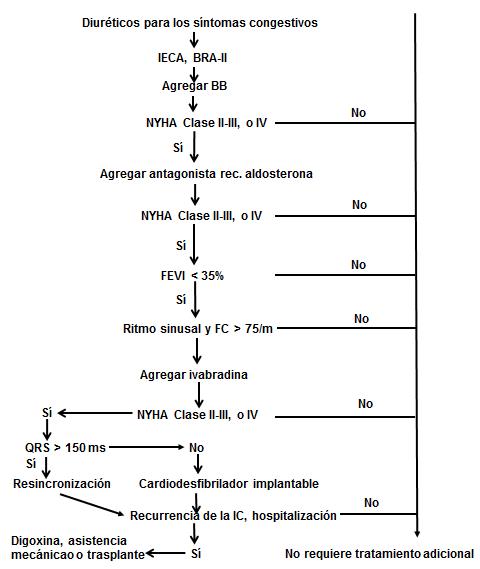
Figura 1. Algoritmo para el tratamiento de la insuficiencia cardíaca con disminución de la fracción de eyección.
Abreviaturas IECA: inhibidor de la enzima convertidora de angiotensina. BRA: bloqueantes del receptor de angiotensina II. BB: beta bloqueantes FEV: fracción de eyección del ventrículo izquierdo IC: insuficiencia cardíaca
Resumen y comentario objetivo: Dr. Ricardo Ferreira