Uno de los grandes desafíos clínicos del control de la DM es que la enfermedad rara vez ocurre aisladamente.
Introducción
La atención de los pacientes mayores con diabetes mellitus (DM) es un desafío importante para las políticas de salud pública. La edad a la que alguien está identificado como "mayor" ha evolucionado con los avances de la medicina, pero actualmente, la edad aceptada por la mayoría de los países desarrollados es 65 años.
La prevalencia de la DM es elevada; más del 20% de los adultos > 65 años tiene diagnóstico de DM. En comparación con sus pares no diabéticos, los adultos mayores con DM tienen un riesgo más elevado de enfermedades microvasculares y cardiovasculares, condiciones geriátricas (tales como caídas y demencia) e hipoglucemia. A pesar de la considerable carga de la DM en los adultos mayores, el manejo de la enfermedad ha sido motivo de controversia; en esta población han tenido lugar debates periódicos sobre la intensidad adecuada del control de la glucosa y el papel de los hipoglucemiantes.
Atención de la diabetes
Actualmente, las guías para la atención de la DM de muchas organizaciones clínicas hacen hincapié en el concepto de individualizar la fijación de los objetivos y el plan terapéutico, y maximizar la calidad de vida cotidiana. Un objetivo primario de esta revisión es asegurar que los médicos tengan en cuenta estas guías, las cuales han sido poco adoptadas, como puede observarse en los estudios nacionales de atención de la DM. El segundo objetivo de la revisión es identificar las lagunas en la evidencia y delinear una agenda de investigación para el campo de la diabetes geriátrica, que sigue siendo relativamente poco estudiada.
Fuentes y criterios de selección
Para establecer la base de la evidencia para el control intensivo de la glucosa se identificaron ensayos aleatorizados y controlados publicados en Inglés en revistas médicas que incluyeron a adultos mayores (>65 años) con DM tipo 2, así como se tuvo en cuenta la evaluación de los efectos clínicos del control intensivo de la glucosa con el uso ambulatorio de fármacos. A tal efecto, el autor realizó una exhaustiva búsqueda bibliográfica, incluyendo las recomendaciones de importantes sociedades y organizaciones médicas.
Prevalencia y fisiopatología
La DM es una enfermedad crónica del envejecimiento. Su prevalencia aumenta marcadamente con la edad, afectando al 1,6% de las personas <45 años; 12,2% de los adultos de 45-64 años y, 21,8% de los adultos de 65-74 años. En la gran mayoría de los adultos mayores diabéticos, la DM es de tipo 2 (96%) debido a una combinación del aumento de la resistencia a la insulina y la alteración de la secreción de insulina. Se cree que la resistencia a la insulina asociada a la edad avanzada se debe a una combinación de adiposidad, sarcopenia (disminución de la masa muscular) e inactividad física.
La prevalencia de la DM en los adultos mayores es un reflejo del crecimiento general de la DM observado en todos los grupos etarios a los largo de 3 décadas. Con el envejecimiento de la generación del baby boom y los índices elevados de obesidad, se espera que en las próximas 2 décadas, en EE. UU. se duplique la subpoblación de personas mayores con DM. Se supone que esta morbilidad va a contribuir a triplicar los costos de Medicare para la atención de la DM en los próximos 25 años. EE. UU. no está solo en su lucha contra esta creciente epidemia. La International Diabetes Federation prevé que la prevalencia global de la DM sufrirá un aumento, ya que de 415 millones de habitantes que tiene el planeta en 2015 pasará a tener 642 millones en 2040, de los cuales casi el 50% tendrá más de 65 años.
Diabetes y comorbilidades
Uno de los grandes desafíos clínicos del control de la DM es que la enfermedad rara vez ocurre aisladamente. Casi el 60% de los adultos mayores con DM tiene al menos una comorbilidad crónica y hasta el 40% tienen ≥4 enfermedades. La creciente prevalencia de las personas mayores con múltiples enfermedades crónicas puede ser atribuida a los progresos en la salud pública y la medicina, que han permitido que aumente el número de personas de la de población que alcanza edades más avanzadas y, el mejoramiento del control de de las enfermedades crónicas, de modo que se ha extendido el tiempo que las personas sobreviven con su enfermedad crónica.
A menudo, las condiciones comórbidas ocurren combinadas.
Un ensayo que estudió el conjunto natural de condiciones comórbidas utilizó el análisis de clases latentes para identificar a los subgrupos de una muestra representativa nacional (National Social Life, Health, and Aging Project [NSHAP]) de adultos residentes en la comunidad (de 57-85 años) con DM (n = 750), considerando 14 condiciones comórbidas altamente prevalentes en la población más envejecida. Se eligió un modelo de 3 clases según criterios ajustados al modelo especificado.
Todas las clases tenían probabilidades estimadas de obesidad, hipertensión y artritis ≥40%. La Clase 1 (67%) tenía la probabilidad más baja de tener la mayoría de las condiciones. La Clase 2 (29%) tenía la mayor probabilidad de incontinencia, enfermedad renal y cáncer. La Clase 3 (9%) tenía la mayor probabilidad de insuficiencia cardíaca congestiva e infarto de miocardio (> 95%). Solo los encuestados en las clases 2 y 3 tenían ≥6 condiciones comórbidas.
Los encuestados de las clases 2 (17%) y 3 (33%) tenían tasas de mortalidad a los 5 años marcadamente mayores que los encuestados de la Clase 1 (9%). La clasificación de la población de más edad con DM que tiene en cuenta las condiciones comórbidas incluye 3 subgrupos diferentes. La historia de la enfermedad cardiovascular y el conteo de las condiciones comórbidas pueden distinguir a los subgrupos con menor probabilidad de beneficiarse de un control intensivo de la glucosa.
Un análisis separado de Health and Retirement Study avala el concepto de que los pacientes mayores con DM entran dentro de esas 3 únicas clases. Las personas con DM se clasificaron según la presencia y el número de comorbilidades o impedimentos funcionales.
Este enfoque prescriptivo dio lugar a 3 clases principales de pacientes mayores:
a) pacientes relativamente saludables
b) pacientes con historias clínicas complejas para quienes la atención personalizada puede ser difícil
c) los pacientes con enfermedades comórbidas muy importantes y deterioro funcional.
Mientras que la mayoría de los pacientes pertenecía al grupo relativamente sano, casi el 22% de los adultos con DM (alrededor de 3 millones de personas) tenía características de salud que podrían hacer difícil el automanejo. Otro 10% (1,4 millones) mostró un beneficio limitado del manejo de la DM. Como con el análisis NSHAP, las 3 clases correspondían al aumento de los niveles del riesgo de mortalidad.
Aparte de estos esfuerzos para clasificar a los pacientes de edad avanzada con DM existen varias clasificaciones de comorbilidad bien establecidas. Estos sistemas predicen el riesgo de mortalidad en los adultos mayores e incluyen el índice de comorbilidad de Charlson, el índice de comorbilidad de Elixhauser, desarrollado como base para los reclamos administrativos y, el índice de carga total de la enfermedad (TIBI [del inglés]).
Los investigadores también han encontrado que las alteraciones en las actividades de la vida diaria (AVD) son predictores independientes de mortalidad. Esto ha llevado al desarrollo y la validación de modelos de predicción de mortalidad que incluyen la edad, el sexo, las condiciones comórbidas y las medidas funcionales, que permiten calcular el puntaje del índice de mortalidad.
Desde hace tiempo, los geriatras también han reconocido que algunos pacientes de mayor edad parecen ser particularmente vulnerables a las agresiones externas y han definido a este síndrome clínico como fragilidad. Se considera que la fragilidad se debe a la disminución fisiológica acumulada a lo largo del tiempo, a través de múltiples sistemas. Los marcadores de fragilidad son la disminución de la masa corporal magra, la fuerza, la resistencia, el equilibrio, el rendimiento de la marcha y la actividad, relacionados con la edad. Los pacientes mayores frágiles tienen mayor riesgo de caídas, peor movilidad o discapacidad en las AVD, internaciones hospitalarias y muerte.
Evidencias sobre el control de la glucosa en los ancianos
Ensayos aleatorizados y controlados
Los pacientes mayores con DM y comorbilidades siempre han sido excluidos de los trabajos clínicos sobre la atención de la DM. El importante estudio United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) excluyó a las personas >65 años. Los grandes trabajos posteriores, como el ACCORD (Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes), el ADVANCE (Action in Diabetes and Vascular Disease: Preterax and Diamicron MR Controlled Evaluation) y el VADT (Veterans Affairs Diabetes Trial) incluyeron a adultos > 65 años pero no a muchas personas que tuvieran más de 75 años en el momento del enrolamiento.
Otra limitación de esos trabajos es que tienen objetivos seleccionados, como las complicaciones cardiovasculares y la mortalidad, lo que puede no abarcar por completo la experiencia de los pacientes con tratamiento. A pesar de estas limitaciones, estos estudios igual siguen brindando datos importantes sobre el momento, la magnitud y el resultado de los efectos del descenso de la glucosa en los pacientes mayores. Los trabajos brindan resultados heterogéneos que pueden deberse a diferencias entre la población de pacientes, los tratamientos disponibles, los protocolos terapéuticos y los objetivos glucémicos.
El UKPDS brinda algunas observaciones importantes en cuanto a la variación del momento y la heterogeneidad de los efectos del control intensivo de la glucosa (hemoglobina glicosilada [HbA1c], 7,9% vs- 7,0%) en los pacientes de edad mediana con DM de reciente comienzo.
Durante el período de observación original de 10 años, el control intensivo de la glucosa descendió significativamente las tasas de enfermedad microvascular (reducción del riesgo 25%) pero el gráfico de Kaplan-Meier solo hizo la distinción en forma significativa después de 9 años de seguimiento.
Durante el seguimiento adicional post ensayo de 10 años aparecieron los beneficios del control glucémico intensivo sobre las complicaciones microvasculares y, la reducción de la mortalidad y los infartos de miocardio. Estos hallazgos han sido denominados efecto legado (N. del T: o de memoria metabólica) e indican que los resultados de los efectos de la hiperglucemia sobre la DM pueden diferir de acuerdo con la historia del control de la HbA1c. Con un seguimiento de casi 20 años, los pacientes que sobrevivieron, en promedio, tenían poco más de 70 años.
El ensayo se terminó precozmente después de un seguimiento medio de 3,5 años debido a que el grupo de terapia intensiva tuvo una tasa de mortalidad más elevada que el grupo de tratamiento estándar
En el ensayo ACCORD, 10.251 participantes con DM tipo 2 fueron asignados aleatoriamente a al tratamiento intensivo de la glucosa (HbA1c <6,0%) o al tratamiento estándar (HbA1c 7,0-7,9%). En comparación con el UKPDS, los pacientes mayores tenían mayor duración de la DM (duración media 10 años), y un riesgo elevado de enfermedad cardiovascular. En promedio, el grupo de tratamiento intensivo alcanzó una HbA1c de 6,4% y el grupo de tratamiento estándar una HbA1c de 7,5%. El ensayo se terminó precozmente después de un seguimiento medio de 3,5 años debido a que el grupo de terapia intensiva tuvo una tasa de mortalidad más elevada que el grupo de tratamiento estándar (cociente de riesgo instantáneo 1,22).
La estimación puntual del resultado combinado cardiovascular primario mostró un beneficio del control intensivo de la glucosa, pero el hallazgo no fue significativo (cociente de riesgo 0,90). A los 5 años de seguimiento, el ensayo ACCORD reconfirmó una tasa más elevada de mortalidad en el grupo de tratamiento intensivo de la glucosa (relación de riesgo 1,19) y una tasa más baja de infarto de miocardio no mortal (0,82).
En los análisis estratificados por edad, los investigadores del ACCORD hallaron que el exceso de mortalidad asociada a la terapia intensiva se produjo principalmente en los pacientes <65 años. El estudio ADVANCE incluyó a 11.140 participantes con DM tipo 2 >55 años, quienes fueron elegidos al azar para recibir el tratamiento intensivo de la glucosa (HbA1c <6,5%) o el control glucémico estándar. Al igual que el estudio ACCORD, el ADVANCE incluyó a pacientes con un riesgo elevado de eventos cardiovasculares y a pacientes con antecedentes establecidos de DM (duración media 8 años).
Los grupos asignados a la terapia intensiva y estándar del estudio AVANCE alcanzaron niveles de HbA1c de 6,5% y 7,3%, respectivamente, en un seguimiento de 5 años. Sin embargo, al contrario que en el ensayo ACCORD, el grupo de terapia intensiva de la glucosa tuvo una reducción relativa del 10% en el resultado combinado de eventos macrovasculares y microvasculares importantes (cociente de riesgo 0,90) debido principalmente a un 21% de reducción relativa de la nefropatía (0,79), y no se observaron efectos significativos en los eventos macrovasculares principales o la muerte. Durante los 6 años de seguimiento posteriores al ensayo no aparecieron efectos significativos en las complicaciones macrovasculares o la muerte.
El VADT asignó al azar a 1.791 veteranos al tratamiento intensivo de la glucosa (con una reducción absoluta del 1,5% en la HbA1c) versus la terapia estándar. Los pacientes tenían una duración media de la DM de 11,5 años y el 40% tenía antecedentes de enfermedad cardiovascular. El grupo de terapia intensiva alcanzó una HbA1c media de 6,9%, y el grupo de terapia normal, una HbA1c media de 8,4%.
En una mediana de 5,6 años de seguimiento, el resultado primario de eventos cardiovasculares mayores no fue significativamente menor en el grupo de tratamiento intensivo (razón de riesgo 0,88). No se observaron diferencias significativas en la tasa de muerte entre ambos grupos. En una fe de erratas, los investigadores informaron que la progresión de la albuminuria fue menor en el grupo de terapia de intervención que en el grupo de terapia estándar. En el seguimiento post-ensayo (un total de observación de 10 años), el grupo de terapia intensiva tuvo un riesgo de eventos cardiovasculares mayores significativamente más bajo (razón de riesgo 0,83), pero no obtuvo beneficios en la mortalidad.
Los resultados de los ensayos ACCORD, ADVANCE y VADT son más aplicables a los pacientes de las décadas de los 60 y 70 años. Los investigadores de los trabajos que estudian el manejo intensivo de la DM han intentado incorporar a pacientes de 80 años, pero se encontraron con dificultades inesperadas.
El ensayo ACCORD trató de reclutar pacientes >80 años, pero se encontró con que los pacientes de este grupo de edad tenían tasas de hipoglucemia muy elevadas cuando fueron asignados al azar al grupo de intervención. Más tarde, se revisó el protocolo del estudio para excluir a los pacientes >80 años. En el Japan Elderly Diabetes Intervention Trial, los investigadores intentaron evaluar una intervención múltiple de los factores de riesgo en pacientes de 65 a 85 años. Se asignaron al azar 1,173 para recibir el tratamiento intensivo o el convencional. A pesar de un protocolo estructurado, los investigadores no consiguieron separar las HbA1c logradas en todos los grupos del estudio, lo que fue atribuido a los temores por la hipoglucemia relacionada con el tratamiento en los pacientes de mayor edad.
Ensayos simulados
Debido a los estrictos criterios de exclusión de los ensayos controlados, los investigadores han utilizado modelos de microsimulación y métodos de observación para ganar más conocimiento del efecto esperado del control intensivo de la glucosa en los pacientes más viejos y enfermos.
En los modelos de simulación, la predicción de de los resultados en los pacientes se calculan sobre la base de las probabilidades de transición generadas en los resultados de los ensayos aleatorizados y controlados, estudios epidemiológicos y metaanálisis.
Uno de los modelos de microsimulación evaluó cómo las comorbilidades y el deterioro funcional afectan los beneficios potenciales del control intensivo de la glucosa alcanzados en el UKPDS (HbA1c 7,0% vs 7,9%). Este estudio analítico de decisión utilizó una población hipotética de adultos de 60 a 80 años con DM tipo 2 sin antecedentes de complicaciones diabéticas. Para este análisis, se revisó el modelo del UKPDS, reemplazando el modelo de antecedentes de mortalidad por un modelo de predicción de mortalidad geriátrica desarrollado previamente.
El modelo de DM mostró que los beneficios esperados del control intensivo estaban inversamente relacionados con el nivel de comorbilidad y deterioro funcional en los grupos de todas las edades. Por ejemplo, para loa adultos de 60 a 64 años con DM de reciente comienzo, los beneficios declinaron de 106 (95%) días de buena salud ajustados por la calidad iniciales a 44 (38 a 50) días, con 3 puntos adicionales del índice de mortalidad y 8 (5-10) días con 7 puntos adicionales de dicho índice.
Para los pacientes con mayor duración de la DM, los beneficios esperados del control intensivo de la glucosa también se asociaron negativamente con la esperanza de vida. Para los adultos de 60 a 64 años con DM de 10-15 años de duración, el beneficio esperado del control intensivo de la glucosa disminuyó de 116 (103 a 129) días ajustados por la calidad a 36 días (29 a 43), con 4 puntos adicionales del índice y 8 (6 a 11) días con 8 puntos adicionales del índice.
Un estudio de observación ulterior de 3.074 pacientes con DM tipo 2 clasificó a los participantes en grupos de comorbilidad elevada y mortalidad baja a moderada, (puntaje TIBI) al inicio del estudio y durante los 5 años de seguimiento. Los pacientes del grupo de comorbilidad baja a moderada con niveles de HbA1c <6,5% tuvieron menor incidencia de eventos cardiovasculares a los 5 años (razón de riesgo ajustada 0,60).
Sin embargo, los pacientes del grupo de comorbilidad elevada no obtuvieron ningún beneficio significativo de los niveles de HbA1c ≤6,5%. Del mismo modo, solo el grupo de comorbilidad baja a moderada tuvo menos eventos cardiovasculares como consecuencia de una HbA1c de 7,0% (razón de riesgo ajustada 0,61). En conjunto, estos estudios indican que en los pacientes diabéticos con esperanza de vida limitada, pueden ser razonables los objetivos glucémicos menos estrictos.
Calidad de vida
Un reto importante en la investigación fue determinar cuál era la correcta evaluación que debía hacerse en los pacientes de edad avanzada con múltiples enfermedades crónicas. Los resultados de las biomediciones a corto plazo utilizados en los ensayos de medicamentos a corto plazo y dispositivos para la DM (tales como la HbA1c) son convenientes y más fácilmente modificables por los tratamientos, pero pueden no tener relevancia clínica inmediata en los pacientes.
Los resultados clínicos como la mortalidad y las complicaciones microvasculares y cardiovasculares son importantes para los pacientes pero pueden no ser modificables en el corto plazo y no captar el espectro pleno de lo que experimentan los pacientes. Los líderes de opinión en la investigación del envejecimiento han recomendado que los investigadores comiencen utilizando las mediciones de la calidad de vida relacionadas con la salud tales como los ítems Short Form Survey 8 y 36 del Medical Outcomes Study y el ítem Health Profile Health Profile del Patient Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System.
Lamentablemente, dice el autor, una revisión reciente de ensayos clínicos de DM halló que son pocos los estudios que incluyeron resultados importantes para los pacientes. Partiendo de los resultados clínicos tradicionales y cambiando los resultados importantes para los pacientes surgen preguntas sobre cuáles son las intervenciones o condiciones con mayores efectos sobre los resultados centrados en el paciente. Un estudio evaluó las asociaciones entre la calidad de vida relacionada con la salud (CVRS) y los síndromes geriátricos (dolor crónico, depresión, incontinencia urinaria, bajo peso y caídas), las complicaciones diabéticas y la hipoglucemia en los adultos mayores con DM.
La información proviene de muestras estratificadas al azar de adultos de 60 a 75 años con DM tipo 2 o tipo 1 que completaron una encuesta que incluyó un el instrumento de CVRS basado en el SF-8 (n = 6317). En los modelos de exposición combinados, los síndromes geriátricos y las complicaciones de la DM se asociaron con una CVRS física menor.
La CVRS mental más baja se asoció con depresión, peso inferior al normal (índice de masa corporal <18), amputación e hipoglucemia. En los modelos de exposición combinados solo la hipoglucemia se asoció con una CVRS mental más baja. Los síndromes geriátricos y la hipoglucemia se asocian con peor calidad de vida en un grado comparable a las complicaciones tradicionales de la DM. Estos resultados sugieren que el abordaje de los síndromes geriátricos y la evitación de la hipoglucemia deben ser considerados con una prioridad tan elevada como la prevención de las complicaciones de la DM en los adultos mayores con DM.
Figura 3: Beneficios para la calidad de vida esperada del control intensivo de la glucosa en pacientes de 60-64 años y de 75-79 años con DM de reciente comienzo, con niveles crecientes de enfermedades comórbidas y deterioro funcional.
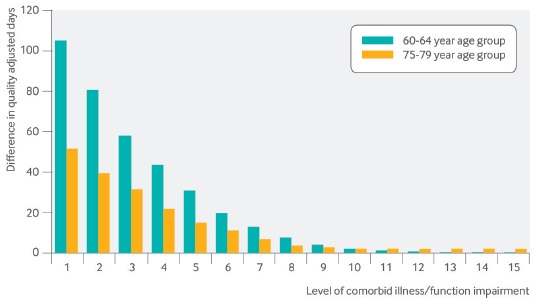
A pesar de que este estudio pone de relieve la importancia de los síndromes geriátricos, no incluye el deterioro cognitivo y la demencia. Estas condiciones, que se asocian estrechamente con la DM, suelen conducir a la pérdida de la independencia en las AVD y de las AVD instrumentales, elementos importantes de la calidad de vida.
Hipoglucemia
Durante mucho tiempo la hipoglucemia ha sido considerada un obstáculo para la obtención el control intensivo de la glucemia. En los ensayos sobre el control intensivo de la glucosa, las tasas de hipoglucemia grave que requieren atención médica siempre han sido consistentemente mayores en los grupos de control intensivo. Aunque antes era considerado un resultado secundario, la hipoglucemia se ha convertido en un resultado primario de base y de la investigación clínica de la DM. Desde una perspectiva política, la hipoglucemia se ha propuesto como un evento adverso clave y la medida de la ejecución de los sistemas de asistencia sanitaria.
Varios estudios recientes avalan la creciente importancia de la hipoglucemia en relación con las complicaciones tradicionales de la DM. Un estudio de la historia natural de una cohorte actual de pacientes diabéticos de más edad evaluó cómo la incidencia y la clasificación de las complicaciones fueron diferentes según la edad y la duración de la DM. Entre los adultos mayores con DM de corta duración, las complicaciones cardiovasculares seguidas de hipoglucemia fueron las complicaciones no mortales más comunes.
Entre los pacientes de 70 a 79 años con DM de corta duración, las tasas de coronariopatía e hipoglucemia fueron mayores (11,47/1.000 personas años y 5,03/1.000 personas años, respectivamente) que las tasas de nefropatía terminal (2,60/1.000 personas años), amputación de miembros inferiores (1,28/1.000 personas años) y, episodios hiperglucémicos agudos (0,82/1.000 personas años).
Las clasificaciones actuales de las complicaciones relacionadas con la DM en los adultos mayores son un reflejo de las tendencias seculares en el manejo de la DM.
Un estudio de observación retrospectivo utilizó datos de 33.952.331 beneficiarios de consultas pagas de Medicare ≥65 años, desde 1999 hasta 2011. Durante este período, las tasas de internación por hiperglucemia se redujeron un 38,6% (de 114 a 70 internaciones/100.000 personas), mientras que las internaciones por hipoglucemia se incrementaron en un 11,7% (de 94 a 105 internaciones/100.000 personas años). En la actualidad, las tasas de internación hospitalaria por hipoglucemia en los adultos mayores superan a las tasas de internación por hiperglucemia.
Los resultados de estos dos estudios indican que a medida que la supervivencia de los diabéticos aumenta y la población envejece serán necesarios más esfuerzos de investigación y de salud pública para reducir la hipoglucemia y complementar los esfuerzos en curso para reducir las complicaciones cardiovasculares y microvasculares.
Carga de los tratamientos cotidianos
La carga de los tratamientos cotidianos está relacionada con la hipoglucemia, un aspecto subestimado de la calidad de vida. La acumulación de tareas para tomar los medicamentos, el cumplimiento de las dietas y de los programas de ejercicios y el control de la glucemia, al mismo tiempo que se deben cumplir las recomendaciones para otras comorbilidades, puede ser abrumadora. Aunque este concepto es importante, ha sido difícil de cuantificar mediante las medidas tradicionales de la calidad de vida.
Un estudio estatal de servicios públicos de salud usó métodos (una medida de preferencia) para determinar la relación de la carga de las complicaciones relacionadas con la DM y los tratamientos. Esto obtuvo utilidades (puntajes de 0-1 en una escala en la que 0 representa la muerte y 1 la perfecta salud) para 9 estadios de complicaciones y 10 estadios de tratamientos en 701 pacientes con DM. La etapa final de las complicaciones tuvo una media más baja de utilidades que las complicaciones intermedias (por ej., ceguera 0,38 (SD 0,35) vs. retinopatía 0,53 (SD 0,36); y las complicaciones en su etapa final tuvieron calificaciones más bajas en todos los estados de salud.
El tratamiento intensivo tuvo una media más baja de utilidades que los tratamientos convencionales (por ej., control intensivo de la glucosa 0,67 (0,34) vs. control convencional de la glucosa 0,76 (0,31) y el estado de tratamiento calificado como el más bajo fue la atención integral de la DM. En promedio, los pacientes en el grupo de tratamiento integral fueron calificados en forma similar al grupo de pacientes con complicaciones intermedias.
El autor sostiene que es importante destacar que las calificaciones de los estados de salud de los pacientes fueron muy heterogéneas: algunos pacientes que tenían un estado de salud casi perfecto continuaban con la atención integral de la DM mientras que una minoría significativa (18%) que siguió el mismo tratamiento tuvo un resultado fatal.
La carga de los tratamientos tiene consecuencias importantes para la determinación de las metas y los tratamientos de la DM en los pacientes mayores. En los análisis de rentabilidad, la incorporación de las preferencias de los pacientes con respecto a su vida con tratamiento ha demostrado que el valor del control intensivo de la glucosa en los pacientes de edad avanzada depende mucho de las hipótesis acerca de la calidad de vida con tratamiento. Esto se debe a que los efectos terapéutico sobre la calidad de vida que son experimentados por todos pacientes expuestos en forma rutinaria al tratamiento pueden exceder fácilmente los beneficios esperados a largo plazo del control de la glucemia, que son experimentados por una minoría de los pacientes.
Guías
Durante los últimos 15 años, las guías sobre la atención de la DM de muchas organizaciones clínicas han adoptado conceptos para la fijación de objetivos y el manejo de la atención individualizada, con el fin de maximizar la calidad de vida, pero difieren en los detalles de sus recomendaciones.
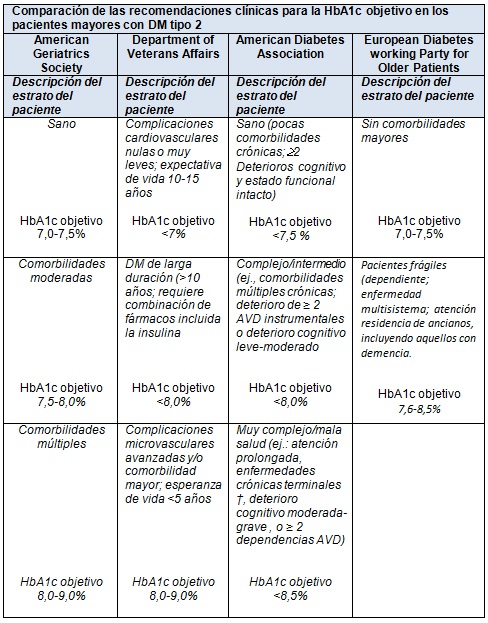
Desde el año 2003, la American Geriatrics Society (AGS) ha respaldado el concepto de la individualización de la atención de la DM, sobre la base de la expectativa de vida. Las guías originales estratificaron a los pacientes mayores en los que tienen una esperanza de vida por encima y por debajo de los 5 años. La AGS actualizó esta guía en 2013 y apoyó un esquema de 3 niveles de estratificación de los objetivos glucémicos ("sano": HbA1c de 7,0 7,5%; comorbilidades "moderadas": de 7,5 a 8,0% y, comorbilidades "múltiples" 8,0 a 9,0%).
En 2010 se actualizaron las guías de diabetes del Department of Veterans Affairs y del Department of Defense. Para los objetivos glucémicos, la guía tiene 3 categorías de pacientes basadas en la duración de la DM, las complicaciones y la esperanza de vida. Los pacientes con o sin complicaciones microvasculares muy leves de la DM que están libres de las principales enfermedades concurrentes y que tienen una esperanza de vida de al menos 10 a 15 años deben tener un objetivo de HbA1c <7%, siempre que pueda lograrse sin riesgos.
Los pacientes con una duración de la DM >10 años o con comorbilidades y que requieren un tratamiento farmacológico combinado, incluyendo la insulina, deben tener un objetivo de HbA1c <8%. Los pacientes con complicaciones microvasculares avanzadas, enfermedades comórbidas importantes y/o una esperanza de vida <5 años es poco probable que se beneficien del control intensivo de la glucosa y deben tener un objetivo de HbA1c de 8-9%. Los objetivos inferiores (<8%) se pueden establecer en forma individual.
En 2011, el European Diabetes Working Party for Older People publicó la guía para tratar a las personas >70 años con DM. En ella se incluyen recomendaciones para llevar a cabo evaluaciones anuales del estado funcional (global/físico, cognitivo, afectivo) utilizando instrumentos validados para evitar el uso de la glibenclamida debido a su alto riesgo de hipoglucemia en esta población, y para calcular el riesgo cardiovascular en todos los pacientes <85 años.
La HbA1c objetivo sugerida se basa en la edad y la comorbilidad. Para los pacientes mayores con DM tipo 2 sin comorbilidades importantes se sugiere un rango de 7-7,5% y para los pacientes frágiles (dependientes, con enfermedad multisistémica, internación en residencia de ancianos, incluyendo aquellos con demencia), cuyo riesgo de hipoglucemia puede ser elevado, con una probabilidad de beneficio relativamente baja, se propone una HbA1 c de 7,6 a 8,5%.
En 2012, la American A Diabetes Association (ADA) publicó una declaración de consenso sobre la atención de los pacientes de mayor edad que recomienda la individualización de la atención de la DM basada en la esperanza de vida, las habilidades para el autocuidado y las preferencias del paciente. Los autores de la declaración hicieron recomendaciones específicas para los objetivos glucémicos y el control de la presión arterial, y proporcionaron un marco para estratificar a los pacientes por el estado de salud en las siguientes clases: "saludable", "complejo" o "muy complejo”, con objetivos de HbA1c <7,5%, 8,0% y 8,5%, respectivamente. Estas 3 clases fueron identificadas según una combinación de condiciones de comorbilidad y discapacidad en las AVD y las ADL instrumentales. En 2014, estas recomendaciones fueron incorporadas formalmente a las normas de atención médica anuales de la ADA.
Estado actual de la atención
A pesar de que desde 2013 se dispone de guías para la atención de la DM geriátrica, existe mucha evidencia de que en la práctica clínica, las recomendaciones para individualizar la atención de la DM no han sido adoptadas. Muchos estudios sobre la atención de pacientes de edad avanzada con DM que utilizaron las bases de datos nacionales han demostrado que la intensidad del tratamiento no varía por el estado de salud.
Un estudio describió la intensidad del tratamiento de la DM en los pacientes de mayor edad clasificados por el estado de salud en la National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) (2001-10). La proporción de pacientes mayores que logró una HbA1c <7,0% fue del 61% en general, y no fue diferente en los 3 niveles del estado de salud. En los pacientes con una HbA1c <7,0%, el 54,9% fue tratado con insulina o con sulfonilureas, y esta proporción fue similar en los 3 niveles del estado de salud.
Integración de las comorbilidades a la atención de la diabetes
La aparente falta de atención individualizada en los estudios nacionales podría deberse al hecho de que muchas de las recomendaciones de las guías nacionales han sido transformadas en protocolos de atención para la práctica clínica. La búsqueda sobre en la literatura y en los ensayos clínicos en curso del manejo de la DM solo halló relativamente pocos estudios dedicados al estudio de los pacientes >65 años (2 de cada 232 ensayos en curso sobre el manejo de la DM).
Los ensayos sobre el autocontrol de la DM han proliferado, pero, con raras excepciones, estas intervenciones no han sido adaptadas a los objetivos o las necesidades especiales de la población geriátrica. Más importante aún es que la mayoría de los ensayos del manejo de la DM sigue siendo motivada por el supuesto de que todos los pacientes comparten los mismos objetivos glucémicos.
La escasez de pruebas de ensayos para esta población puede atribuirse a la fragmentación de la enfermedad realizada por las agencias de financiación de la investigación, la lenta adopción de los resultados importantes para los resultados primarios de los pacientes y el énfasis histórico de la investigación de los servicios de salud y las políticas sanitarias para la atención de la DM para alcanzar los niveles objetivo uniformes para la población (por ej., HbA1c <7,0%).
A pesar de las deficiencias en la literatura existente, los componentes de un programa para el manejo de la atención de los pacientes de edad avanzada con comorbilidades han sido estudiados individualmente y, si son integrados con éxito, podrían mejorar la calidad de vida de estos pacientes. Estos componentes básicos incluyen la soporte para la toma de decisiones personalizada, para fijar objetivos y planificar el tratamiento y el manejo de la atención en forma individual, diseñada para el desarrollo social y las circunstancias clínicas que rodean a los pacientes de mayor edad.
Apoyo a las decisiones
El establecimiento del pronóstico y de las preferencias terapéuticas del paciente para fijar los objetivos requiere un tiempo valioso; los objetivos personalizados pueden ser difíciles de recordar y de cumplir por parte de los pacientes complejos. El cumplimiento y la documentación de estas tareas en forma precisa, rápida y oportuna podría mejorarse mucho con la el apoyo a las decisiones clínicas. Más allá de los aspectos técnicos para tomar las mejores decisiones, el reconocimiento de las comorbilidades en la atención de la DM es fundamentalmente tener en cuenta las realidades de la esperanza de vida en la toma de decisiones médicas. En muchos sentidos, el desafío clínico y ético del manejo de la DM en los pacientes mayores es el mismo que el del final de la vida, con la gran diferencia que se produce mucho antes en el curso de la vida de los pacientes.
Una revisión sistemática ha creado un marco conceptual de la atención personalizada de la DM porque ilustra el grado en que la atención de la DM puede ser personalizada dentro del proceso de la toma de decisiones clínicas. Las dos maneras principales de tomar las decisiones clínicas son: establecer los objetivos para los factores de riesgo (por ej., HbA1c, presión arterial, colesterol) y, seleccionar el tratamiento. Estas dos áreas de toma de decisiones pueden ser personalizadas sobre la base de los factores clínicos (como la farmacogenómica, la comorbilidad, la esperanza de vida, la etapa de la enfermedad) y las preferencias de los pacientes.
Dentro de este marco, existen 4 grandes áreas de superposición en las que se pueden tomar decisiones personalizadas. En las categorías A y C de la siguiente figura, las decisiones clínicas son personalizadas sobre la base de los factores clínicos; para las categorías B y D, las decisiones clínicas son personalizadas sobre la base de las preferencias de los pacientes. El apoyo a la decisión es personalizado cuando en el proceso de toma de decisiones clínicas la ayuda o herramienta de decisión incorpora las características clínicas de los pacientes y/o sus preferencias de tratamiento.
La revisión sistemática halló que entre las 13 herramientas de apoyo a las decisiones solo 3 fueron diseñadas para involucrar al paciente en la toma de decisiones. Estas herramientas intentaron considerar e incorporar las preferencias de los pacientes acerca de la selección de los tratamientos (categoría D) y, en un caso, la selección de los objetivos del manejo (categoría B). En general, estas herramientas mejoran el conocimiento de los pacientes, reducen los conflictos en la toma de decisiones y aumentan la participación de los pacientes en las decisiones.
Figura 4

(Círculo naranja) Factores clínicos
(Círculo verde)Preferencias de los pacientes
(Círculo violeta) Decisiones clínicas: objetivos par factores de riesgo
(Círculo amarillo) Decisiones clínicas: selección del tratamiento
A partir de esta revisión, las intervenciones de apoyo a las decisiones que alientan a los prestadores a tener en cuenta tanto el pronóstico como las preferencias todavía parecen ser pocas. Un ejemplo de integración de las categorías A y B de apoyo a las decisiones implicó una herramienta de soporte para las decisiones basado en la web, diseñada para fomentar el establecimiento de los objetivos sobre la base del pronóstico y las preferencias de los pacientes acerca del tratamiento. Las características únicas de esta herramienta incluyen un modelo de simulación de la DM geriátrica que calcula los índices de esperanza de vida y de complicaciones, y obtiene formalmente las preferencias de los pacientes.
Un estudio piloto en clínicas de la Universidad de Chicago eligió al azar a médicos (n = 28) y sus pacientes (n = 100) para utilizar la herramienta de apoyo a la toma de decisiones, en una relación de reclutamiento de 3 a 1 (75 pacientes para el grupo de intervención; 25 pacientes para el grupo control). Antes de la visita a la clínica, los pacientes del grupo de intervención interactuaron con la herramienta, lo que generó un resumen que su médico incluyó en la estimación individual de la esperanza de vida, las preferencias terapéuticas y los resultados del cribado para las condiciones geriátricas.
Los pacientes del grupo control recibieron un folleto educativo sobre la HbA1c. El 91% de los pacientes había discutido la HbA1 objetivo durante una visita médica en comparación con el 76% de los controles (p = 0,19). Los pacientes de la intervención tuvieron disminuciones más grandes en el Informed Subscale of Decisional Conflict (-20,0 vs. 0). No se observaron diferencias significativas en la proporción de pacientes con cambios en los objetivos (49% vs. 28%), aunque la proporción fue mayor en el grupo de intervención. La mayoría de los pacientes de la intervención informó que la herramienta es fácil de usar (91%) y los ayudó a comunicarse con su médico (84%).
Manejo de la atención
Junto con la fijación de objetivos personalizados, la prestación de apoyo para el autocuidado es importante para mejorar los resultados clínicos, ya que para los pacientes no es suficiente simplemente establecer los objetivos a alcanzar. Un ensayo aleatorizado y controlado evaluó si las barreras para el autocuidado y las estrategias para contrarrestar estas barreras, implementadas telefónicamente por un educador de DM, fueron superiores a la atención habitual con el control durante el momento de la atención. El grupo de intervención recibió un modelo de atención en el que un equipo de DM evaluó las barreras geriátricas y las estrategias desarrolladas para ayudar a los pacientes a contrarrestar las barreras.
El programa incluyó el abordaje de las condiciones comórbidas en los pacientes de edad avanzada, tales como el deterioro cognitivo, la depresión, la discapacidad visual, los problemas de movilidad/destreza y los problemas deglutorios. Las estrategias se llevaron a cabo a través de llamadas telefónicas a los pacientes realizadas por un educador de DM. La intervención activa fue implementada durante los primeros 6 meses, con un período posterior de seguimiento "sin contacto” (un total de 12 meses). La duración de la atención del grupo control fue la misma.
Después del período de intervención activa, la HbA1c disminuyó un 0,45% en el grupo de intervención comparado con 0,31% en el grupo control. A los 12 meses, la HbA1c disminuyó aún más en el grupo de intervención (0,21%) en comparación con el 0% en el grupo control. El grupo intervenido mostró beneficios adicionales estadísticamente significativos en los puntajes del autocuidado (Self-Care Inventory-R), marcha, equilibrio (Tinetti) y resistencia (prueba de la caminata de 6 minutos) en comparación con los controles.
Un enfoque potencial para mejorar la atención y los resultados en los pacientes de la tercera edad con DM es mejorar tanto la fijación de los objetivos como el manejo de la atención, usando técnicas para el manejo de la población a nivel clínico. Un uso clínico potencial podría ser el registro médico electrónico, para establecer objetivos de la atención de la DM mediante calculadoras de pronóstico automatizadas, utilizando los datos existentes de la demografía, las comorbilidades y las alteraciones funcionales.
La historia clínica electrónica también podría ayudar a fomentar a las clínicas y los médicos a documentar los objetivos de la atención de la DM en forma anual. Estos objetivos documentados podrían influir en las decisiones terapéuticas posteriores y ayudar a mejorar la coordinación de la atención entre varios prestadores. Sin embargo, una vez establecidos los objetivos para una población, algunos pacientes requieren apoyo para alcanzar sus objetivos. Las clínicas podrían tener programas especializados para el manejo de la atención de los pacientes de mayor edad que no alcanzan sus objetivos personales y tienen un riesgo elevado de encontrar barreras para el autocuidado. En concordancia con estos esfuerzos, estos programas especializados podrán aplicarse a los pacientes mayores que puedan estar con un tratamiento excesivo y que podrían beneficiarse de una disminución de la intensidad de la atención.
Conclusiones
Un segmento importante de la epidemia mundial de obesidad/diabetes es la creciente población de personas mayores con DM. A pesar de la considerable carga clínica y económica de esta subpoblación diabética, los ensayos clínicos han excluido históricamente a los pacientes más viejos y a aquellos con comorbilidades. Los ensayos aleatorizados y controlados más importantes del control intensivo de glucosa, relevantes para los pacientes mayores, indican que el tratamiento brinda beneficios microvasculares y cardiovasculares, pero normalmente después de largos períodos de tratamiento (5-9 años) y con exposición a riesgos a corto plazo como la mortalidad (en un ensayo) y la hipoglucemia).
Estos datos de los ensayos y la investigación complementaria a partir del análisis de decisión, la economía de la salud y los estudios de observación han formado parte de las guías de atención clínica actuales. Casi todas estas guías recomiendan que los médicos y los pacientes personalicen la intensidad del control de la glucosa y los tratamientos sobre la base del pronóstico y las preferencias de los pacientes de más edad. Aunque en general existe un acuerdo sobre estos conceptos amplios, muy pocos ensayos han intentado estudiarlos formalmente en la práctica clínica. Sin un estudio formal, los efectos clínicos a largo plazo del establecimiento de los objetivos y los tratamientos personalizados seguirán siendo desconocidos.
Para satisfacer mejor las necesidades terapéuticas de los pacientes de edad avanzada con DM se necesita más investigación para determinar los riesgos y los beneficios de la intensificación, el mantenimiento o la disminución de la intensidad del tratamiento en los pacientes más ancianos con múltiples enfermedades crónicas. Estos riesgos y beneficios pueden ser alterados por la disponibilidad de nuevas clases de agentes hipoglucemiantes (inhibidores de la 4 dipeptidil peptidasa, agonistas del péptido 1 símil glucagón, inhibidores del cotransportador 2 sodio-glucosa).
Debido a las dificultades que se hallan al realizar ensayos en pacientes mayores con múltiples enfermedades, esperanza de vida más corta y/o deterioro cognitivo, se necesitan tanto estudios de observación como ensayos controlados que permitan responder las preguntas básicas para esta población. Este esfuerzo de investigación debe extenderse al desarrollo y estudio de las herramientas para el apoyo a las decisiones así como para los programas de administración de atención específica. La integración de ambas funciones a la práctica clínica puede mejorar los resultados en la salud de esta población.
Comentario y resumen objetivo: Dra. Marta Papponetti