Introducción
El neumotórax espontáneo primario (NEP) es una enfermedad relativamente común en pacientes jóvenes, con una incidencia anual de 18 a 28/100.000 en hombres y de 1,2 a 6,0/100.000 en mujeres [1]. El NEP usualmente requiere hospitalización y a menudo necesita tratamiento quirúrgico y, en ocasiones, puede esperarse un tratamiento conservador prolongado, con un efecto socioeconómico significativo. El aspecto clínico característico del NEP es el riesgo de recidivas en los pacientes que son sometidos sólo a tratamiento conservador, que es del 16% al 52% después del primer episodio, aumentando al 65% después de un segundo episodio ipsilateral [2]. Por lo tanto, la prevención de la recidiva es de la mayor importancia en el manejo de esa condición y sigue siendo, en relación con ciertos aspectos, un tema de debate.
Indubitablemente, la intervención quirúrgica representa la manera más efectiva de prevenir la recidiva. Se ha alcanzado un consenso mundial recomendando la intervención quirúrgica después de la primera recidiva ipsilateral o contralateral, como ha sido reportado en 4 guías publicadas [3-6]. Sin embargo, no hay un acuerdo definitivo sobre la indicación para la prevención de la recidiva después del primer episodio. De acuerdo con el American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) y la British Thoracic Society (BTS), las indicaciones para la intervención quirúrgica después de un primer episodio de NEP están limitadas a la presencia o la persistencia de una fístula aérea, hemoneumotórax o pacientes con alto riesgo por razones ocupacionales, tales como buzos y pilotos [3,4]. En circunstancias distintas a esas condiciones, el uso de la pleurodesis después de un primer episodio de NEP no es generalmente recomendado. La identificación de los factores predictivos de recidiva puede hacer posible la selección, dentro de la población de pacientes que presentan un primer episodio de NEP, de aquellos que están en riesgo alto de recidiva y los que, en consecuencia, pueden beneficiarse con la intervención quirúrgica para prevenirla, aún después de un primer episodio.
Dado que se considera que la rotura de las ampollas (blebs) o bullas representa la causa principal de NEP, la presencia de esas lesiones en una tomografía computada de alta definición (TCAD) ha sido investigada como un predictor de la recidiva [7]. No obstante, esa hipótesis patogénica no puede explicar todos los casos de NEP [8] y, contrariamente, no todas las lesiones pulmonares pueden ser detectadas definitivamente con la TCAD [9]. Por esas razones, el valor de la TCAD para predecir las recidivas permanece controversial. Las guías disponibles no establecen con claridad el rol de la tomografía computada (TC) en ese escenario [3,4]. El objetivo de este estudio retrospectivo fue evaluar la posibilidad de recidiva ipsilateral o contralateral, a través de la presencia de ampollas y bullas detectadas en la TCAD, en una población de pacientes con un primer episodio de NEP, que fueron sometidos a tratamiento conservador con drenaje torácico o sólo con “reposo en cama”.
Material y métodos
Este estudio fue aprobado por el Comité de Ética de la Universidad de Módena y Reggio y se obtuvo un consentimiento individual, para participar en el estudio, de todos los pacientes.
Cohorte del estudio
Se revisaron retrospectivamente los registros clínicos de todos los pacientes admitidos por un primer episodio de NEP y a los que se les realizó una TCAD en la División de Cirugía Torácica de la Universidad de Módena y Reggio Emilia, entre enero de 2000 y diciembre de 2009. Los pacientes de más de 50 años de edad fueron excluidos. Se recolectaron datos sobre edad, sexo, antecedentes de tabaquismo, índice de masa corporal (IMC), lado del neumotórax y abordaje terapéutico, para cada paciente.
Manejo del NEP
A lo largo del período investigado, se estandarizó el manejo del primer episodio de NEP. Un paciente asintomático (ausencia de disnea) con un neumotórax pequeño, (definido como de menos de 3 cm entre el ápex del pulmón y la porción apical de la pared torácica o menos de 2 cm entre el margen lateral del pulmón y la pared torácica a nivel del hilio pulmonar), fue tratado con reposo en cama. Un neumotórax pequeño en un paciente sintomático y un neumotórax de cualquier otro tamaño, independientemente de los síntomas, fueron tratados mediante la colocación de un drenaje torácico. De acuerdo con las guías [3-6], el tratamiento quirúrgico del primer episodio fue efectuado sólo en los pacientes con fístula aérea prolongada de más de 4 ó 5 días, hemoneumotórax, o por razones ocupacionales. Todos los procedimientos quirúrgicos consistieron en una resección, con engrampadora, de las ampollas o bullas pulmonares y abrasión pleural, usando un abordaje toracoscópico video asistido.
Los pacientes que fueron sometidos a tratamiento quirúrgico fueron excluidos del análisis, porque la intervención quirúrgica tiene un fuerte efecto sobre la reducción del riesgo de recidiva [3,4]. Sólo los pacientes manejados conservadoramente (drenaje torácico o reposo en cama) fueron incluidos en el análisis.
Exámenes de TC
Los exámenes de TC efectuados antes de mayo de 2003 fueron realizados con adquisición axial y los parámetros típicos fueron: 120 Kvp; 160 a 200 mAs (dependiendo del tamaño del paciente); grosor de los cortes, 1,25 mm; e intervalo de los cortes, 3 a 5 mm a nivel apical y 10 mm en otros niveles, con algoritmo para la reconstrucción ósea. Todos los exámenes de TC posteriores a mayo de 2003 fueron realizados con adquisición espiral y los ajustes típicos fueron: 120 Kvp; 160 a 240 mAs (dependiendo del tamaño del paciente); grosor de los cortes, 1,25 mm; y corte, 1,25 mm, aplicando algoritmo para la reconstrucción ósea.
Las ampollas fueron definidas como espacios con paredes finas, de 1 cm o menos, conteniendo aire y las bullas como aquellas que excedían 1 cm de diámetro. El tipo, número y distribución (por lado) de las lesiones pulmonares conteniendo aire detectadas con la TCAD, fueron registrados para cada paciente. Para los propósitos de este estudio, se adoptó un sistema de puntuación para evaluar mejor la severidad de las lesiones pulmonares, como ya fue propuesto por otros autores [10]. Esa puntuación de gravedad distrófica fue calculada para cada paciente con las TCAD de la siguiente manera: se asignaron valores diferentes para las lesiones pulmonares conteniendo aire, de acuerdo con: el tipo (1 o 2 puntos para ampollas o bullas, respectivamente), el número (1 o 2 puntos para lesiones simples o múltiples, respectivamente) y la distribución (1 o 2 puntos para lesiones unilaterales y bilaterales, respectivamente). El resultado final podía variar desde un mínimo de 3 puntos (grado bajo: una ampolla unilateral) a un máximo de 6 puntos (grado alto: múltiples bullas bilaterales).
Los grados 4 y 5 fueron considerados también en conjunto como un grado intermedio (Fig. 1).
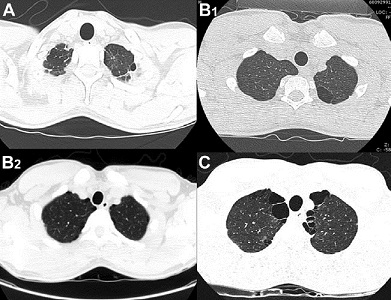
• FIGURA 1: Imágenes de TC que muestran lesiones conteniendo aire relacionadas con NEP, de acuerdo con la puntuación de gravedad distrófica. (A) Bajo grado: ampolla única monolateral. (B) Grado intermedio: B1 bulla única unilateral y B2 ampollas múltiples bilaterales. (C) Alto grado: bullas múltiples bilaterales.
Las imágenes de TCAD fueron evaluadas por 2 radiólogos (G.L y P.T) y 2 cirujanos torácicos (C.C y P.N) bajo condiciones ciegas. El acuerdo fue alcanzado por consenso.
Seguimiento
Todos los pacientes fueron estudiados y tratados por el primer episodio de NEP en la institución en donde se desempeñan los autores. La mayoría de los pacientes que presentaron recidivas fueron derivados a la institución; en los pacientes que nunca tuvieron recidivas o que las tuvieron pero fueron derivados a otro centro asistencial, la información del seguimiento se obtuvo mediante entrevistas telefónicas o de los registros médicos. La primera recidiva fue registrada y definida como ipsilateral o contralateral. La recidiva contralateral también incluyó episodios desarrollados después de una recidiva ipsilateral (o tercer neumotórax). Para los pacientes que no experimentaron recidiva, se estableció un seguimiento alejado mínimo de 12 meses; los pacientes con seguimiento menor de 12 meses fueron considerados como perdidos y fueron excluidos del análisis de recidiva.
Análisis estadístico
El análisis descriptivo fue expresado en frecuencias y medias con desvío estándar (DE). Las frecuencias fueron comparadas usando la prueba de 2 para las variables categóricas y las variables continuas fueron comparadas usando la prueba de t y el análisis de la varianza. El objetivo final primario fue investigar el riesgo de recidiva, después de un primer episodio de NEP, en relación con los hallazgos en la TCAD. Se investigaron las recidivas ipsilaterales y contralaterales. Los valores predictivos positivos y negativos (VPP y VPN) para la recidiva de las lesiones pulmonares detectadas en la TCAD, también fueron calculados. El rol de otras variables clínicas en el desarrollo de la recidiva fue investigado usando análisis univariado y multivariado, realizado por regresión de Cox. La sobrevida libre de recidiva ipsilateral y contralateral (Ipsi-SLR y Contra-SLR, respectivamente) de acuerdo con la puntuación de gravedad distrófica (grados bajo, intermedio y alto, como ya fuera descrito), fueron calculadas según el análisis de Kaplan-Meier. Las curvas de SLR fueron comparadas usando la prueba de log-rank. Una probabilidad menor de 0,05 fue considerada como significativa.
Resultados
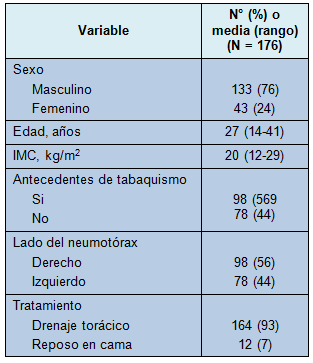
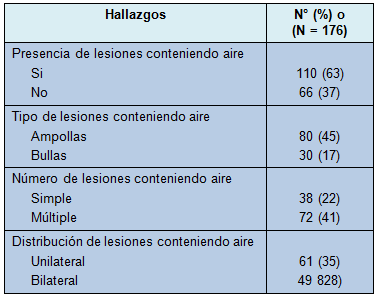
Se registraron los datos de 199 pacientes. De ellos, 8 se perdieron durante el seguimiento y 15 fueron sometidos a intervención quirúrgica después del primer NEP y fueron excluidos del análisis. Por lo tanto, la población en estudio comprendió 176 pacientes. Sus características clínicas se reportan en la Tabla 1 y los hallazgos de la TCAD en la Tabla 2.
• TABLA 1: Características clínicas de los 176 pacientes
• TABLA 2: Hallazgos en las TCAD de los 176 pacientes
El tiempo medio hasta la recidiva ipsilateral fue de 12,8 meses (rango, 1 a 64 meses). El tiempo medio hasta la recidiva contralateral fue de 41,7 meses (rango, 6 a 97 meses). Para los pacientes que no experimentaron recidiva, la media del seguimiento alejado fue de 58 meses (rango, 12 a 128 meses).
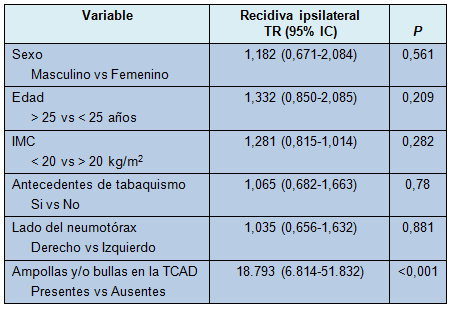
La recidiva ipsilateral ocurrió en 79 pacientes (44,8%). De ellos, 19 (24%) experimentaron también una recidiva contralateral, como un tercer episodio de neumotórax, después de la primera recidiva ipsilateral. Sólo 2 pacientes (1,1%) presentaron una recidiva contralateral como un segundo episodio de neumotórax. Globalmente, 21 pacientes (12%) experimentaron un episodio contralateral de neumotórax durante el seguimiento alejado. El análisis univariado mostró que la edad, sexo IMC y antecedentes de tabaquismo, no afectaron significativamente la tasa de recidiva global.
El riesgo de recidiva estuvo significativamente relacionado con la presencia de ampollas o bullas o ambas en la TCAD. De los 79 pacientes que experimentaron recidiva ipsilateral, 75 tenían lesiones conteniendo aire, mientras que sólo 4 pacientes no las tenían. En los 110 pacientes con lesiones conteniendo aire, se desarrollaron recidivas en 75, mientras que en 35 no ocurrieron. Eso significa que el riesgo de recidiva ipsilateral para los pacientes con lesiones conteniendo aire fue de 68,1%. Esa tasa representa el VPP de la TCAD. No obstante, el riesgo de recidiva ipsilateral para los pacientes sin lesiones conteniendo aire fue del 6,1%, con un VPN de 93,9% para la recidiva de la TCAD.
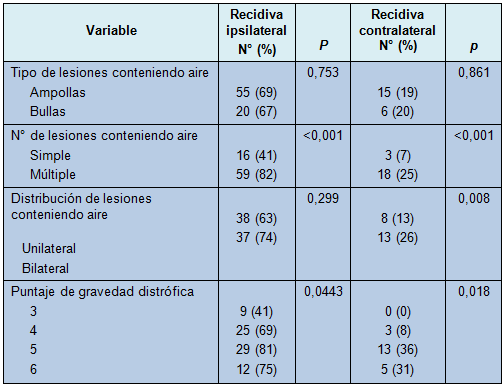
La recidiva contralateral se desarrolló en 21 pacientes con lesiones conteniendo aire, mientras que no lo hizo en pacientes sin dichas lesiones. El riesgo de recidiva contralateral para los pacientes con o sin lesiones conteniendo aire fue de 19% y 0%, respectivamente, con un 100% de VPN en la TCAD para la recidiva contralateral. El análisis univariado para la recidiva ipsilateral y contralateral de acuerdo con el tipo, número y distribución de las lesiones y la puntuación de gravedad distrófica, se reportan en la Tabla 3.
• TABLA 3: Análisis univariado de la recidiva ipsilateral y contralateral del neumotórax, de acuerdo con los hallazgos en la TCAD
El rol de las ampollas y bullas y del puntaje de gravedad distrófica en la predicción de la recidiva fue investigado temporalmente. La Ipsi-SLR a 3 años disminuyó significativamente desde los pacientes con ampollas y bullas (93%) hasta los pacientes con un puntaje de gravedad distrófica bajo (54%; P < 0,001), al igual que desde el grado bajo (54%) al grado intermedio (31%) (P = 0,023). No se halló diferencia en la Ipsi-SLR a 3 años entre el grado intermedio (31%) y el grado alto (22%; P = 0,864). En relación con la Contra-SLR a 3 años, ningún paciente presentó recidiva en ausencia de ampollas y bullas o con un índice bajo de gravedad distrófica en la TCAD (Contra-SLR del 100%). La Contra-SLR a 3 años disminuyó significativamente desde los pacientes con un grado bajo (100%) a un grado intermedio (89%; P < 0,039). La Contra-SLR a 3 años no fue significativamente diferente para el grado intermedio (89%) y para el grado alto (80%) (P = 0.567).
En el análisis multivariado, sólo la presencia de ampollas o bullas en la TCAD estuvo relacionada significativamente con el desarrollo de recidiva ipsilateral (Tabla 4). Los pacientes con lesiones conteniendo aire tuvieron una tasa de riesgo (TR) de recidiva ipsilateral de 18.
• TABLA 4: Análisis de regresión de Cox de la sobrevida libre de recidiva ipsilateral
Comentarios
La terapia quirúrgica, consistente en la resección de las ampollas y pleurodesis, representa actualmente el método más efectivo para prevenir la recidiva [3,4]. Aunque el procedimiento toracoscópico video asistido muestra una incidencia 4 veces mayor en la tasa de recidiva, comparado con la operación abierta [11], es preferido en la actualidad por sobre el abordaje abierto tradicional, debido a la estadía hospitalaria más corta, menor dolor y relación costo-beneficio más favorable [11-13].
En la actualidad, la necesidad de prevenir la recidiva después de un primer episodio de NEP, sigue siendo un tema controversial. La identificación de los factores predictivos de recidiva podría ser útil para seleccionar a los pacientes que pueden beneficiarse con el tratamiento quirúrgico para la prevención de la recidiva después del primer episodio, por fuera de la situación clínica descrita por las guías actuales. Desafortunadamente, hasta ahora, ninguna característica clínica confiable o prueba diagnóstica han probado ser efectivas para identificar pacientes con riesgo aumentado de recidiva. La presencia de lesiones conteniendo aire en la TCAD representa el indicador clínico más extensamente investigado. Sin embargo, estudios previos sobre este tema difieren en relación con su diseño, número de pacientes, técnicas de TC, duración del seguimiento alejado y reporte de los resultados. Debido a esa heterogeneidad, los resultados en la literatura son difíciles de evaluar y las guías actuales no pueden establecer claramente el papel de la TCAD después del primer episodio de NEP [3-6].
Smith y col. [14], reportaron un estudio de casos controlados en el que compararon la prevalencia de las lesiones conteniendo aire en la TCAD, en pacientes después de un primer episodio de NEP versus pacientes después de la recidiva. No encontraron diferencias y concluyeron que los hallazgos de la TCAD no predicen la recidiva. Esa es una conclusión cuestionable en un estudio de casos controlados, en donde no hay análisis del seguimiento alejado. Por esa razón, la subsiguiente discusión en el presente reporte se restringirá a estudios longitudinales en los que los valores de riesgo de recidiva, sobre la base de los hallazgos de la TCAD, fueron reportados directamente o pueden ser calculados usando los datos publicados. Hasta ahora, un único estudio retrospectivo grande [15] y 4 estudios longitudinales prospectivos [10,16-18] han sido realizados sobre este tema. Los mismos sugirieron que un posible rol de la TCAD para la predicción de los episodios de recidiva contralateral del NEP, mientras que aparentemente la presencia de ampollas o bullas puede no estar relacionada con la recidiva ipsilateral.
El presente estudio no confirma esa última presunción. En efecto, los autores encontraron que la presencia de ampollas o bullas detectadas en la TCAD tuvo un alto valor de riesgo de recidiva ipsilateral (68,1%). Además, cuando se detectaron múltiples lesiones conteniendo aire, el riesgo de recidiva ipsilateral después de un primer episodio de NEP aumentó hasta un 82%. Es interesante señalar que el riesgo de desarrollar una recidiva ipsilateral aumentó progresivamente desde una única ampolla unilateral hasta múltiples bullas bilaterales, como se demostró mediante el análisis de los valores de riesgo de la puntuación de gravedad distrófica. Finalmente, como fue confirmado por el análisis multivariado, la presencia de lesiones conteniendo aire estuvo independientemente relacionada con el desarrollo de recidiva ipsilateral, con una tasa de riesgo de desarrollar un segundo episodio de 18 por pacientes con ampollas/bullas.
Las discrepancias entre estos hallazgos y los resultados en estudios previos pueden ser atribuidas a muchos factores. Dos estudios que fallaron en demostrar una correlación entre los hallazgos de la TCAD y la recidiva ipsilateral mostraron algunas limitaciones [16,17]: fueron analizados pocos pacientes (35 y 55, respectivamente), el período de seguimiento alejado fue relativamente corto (9,6 y 30,7 meses, respectivamente) y la frecuencia de lesiones conteniendo aire en la TC fue significativamente más baja que lo esperado en un estudio (47%) [17]. Esos hechos pueden explicar la tasa relativamente baja de recidiva ipsilateral reportada en ambos estudios (~ 23%), lo que finalmente puede llevar a una subestimación de los valores de riesgo de recidiva ipsilateral por la presencia de ampollas y bullas.
El estudio de Ouanes-Besbes y col. [10] superó esas limitaciones, pero concluyó que las lesiones distróficas pulmonares vistas frecuentemente en el NEP no están asociadas con un riesgo aumentado de recidiva. Como consecuencia de ello, su puntaje de lesiones distróficas pulmonares no estuvo significativamente relacionado con las recidivas. No obstante, en ese estudio, el 15% de los pacientes con un primer episodio de neumotórax, fue tratado con pleurodesis química, explicando la tasa extremadamente baja de recidiva (16%). La pleurodesis quirúrgica previa, que es altamente eficaz para prevenir la recidiva, es indudablemente una variable de confusión cuando se investiga a un sujeto por recidiva de un NEP. Por esa razón, los autores del presente trabajo prefirieron excluir a los pacientes sometidos a operación después del primer episodio, para investigar una población más homogénea.
Otro tema controversial es la predicción de un episodio contralateral después de un primer episodio de NEP. Un estudio prospectivo y un estudio retrospectivo grande analizaron esa cuestión [15,18]. Sihoe y col. [18], demostraron que la detección de bullas en la TC en el pulmón contralateral después de un primer episodio de NEP se asoció con una tasa más alta de recidiva contralateral. Esos autores concluyeron que la TC puede ser usada para predecir el riesgo de neumotórax contralateral, cuando se seleccionan pacientes para un tratamiento quirúrgico temprano. Hallazgos similares fueron recientemente reportados por Huang y col. [15], en el estudio más grande publicado sobre este tema.
Los resultados del presente trabajo confirman esos hallazgos previos: la mayoría de los pacientes que experimentaron un episodio contralateral de NEP presentaban lesiones bilaterales conteniendo aire en la TCAD. No obstante, el riesgo absoluto para un episodio contralateral en presencia de lesiones conteniendo aire fue significativamente más bajo que el riesgo de recidiva ipsilateral, tanto en este estudio (19%) como en otros (24% y 27%) [15,18]. Eso significa que si todos los pacientes con lesiones bilaterales conteniendo aire fueran a ser operados bilateralmente, aproximadamente el 75% sería sometido a un procedimiento quirúrgico contralateral inútil. Por lo tanto, sobre la base de los resultados del presente estudio y los datos reportados disponibles, los autores consideran que la terapia quirúrgica después de un primer episodio de NEP debería ser propuesta ipsilateralmente en pacientes con múltiples ampollas, bullas o ambas, en la TCAD.
Contrariamente, la detección de lesiones bilaterales conteniendo aire no representa un criterio suficiente para proponer una pleurodesis quirúrgica bilateral.
Sihoe y col. [18] y Huang y col [15], reportaron que ningún paciente sin ampollas, bullas, o ambas, experimentó una recidiva contralateral. Esto fue confirmado en la presente serie, donde no se desarrolló recidiva contralateral en pacientes sin lesiones conteniendo aire. Eso significa que el VPN de la TCAD para la recidiva contralateral es muy alto. Ese no fue el caso cuando se investigó el valor de riesgo de recidiva ipsilateral para los pacientes con TCAD negativa; de hecho, en este estudio, así como en otros estudios previos [10,16,17], se desarrollaron recidivas en pacientes sin lesiones pulmonares detectables.
Se ha reportado una incidencia más alta de neumotórax recidivado después de la resección quirúrgica de ampollas sin la adición de pleurodesis [19-21]. Esos hallazgos sugieren que otros factores distintos a la rotura de una ampolla o bulla, pueden contribuir al desarrollo de un NEP. Este hecho limita el rol de la TCAD en la selección de pacientes para pleurodesis quirúrgica después de un primer episodio de NEP. No obstante, dado que la recidiva se desarrolla en pocos pacientes sin lesiones conteniendo aire, el rol etiológico de la rotura de la ampolla/bulla sigue siendo el factor más atractivo para explicar la ocurrencia de un NEP. Por lo tanto, sobre la base de estos datos y de aquellos disponibles en la literatura, es razonable establecer que, después de un primer episodio de NEP, en ausencia de ampollas o bullas en la TCAD, no debería proponerse el tratamiento quirúrgico.
Otro tema debatido es la relación entre el cigarrillo y el desarrollo de un NEP recidivado. Recientemente, Cheng y col. [22], evaluaron esa relación en 155 pacientes sometidos a tratamiento quirúrgico por NEP y concluyeron que fumar cigarrillos se asociaba con una extensa bronquiolitis respiratoria, que tiene un efecto significativo sobre la tasa de recidiva del NEP. Ese resultado no fue registrado en el presente estudio, en donde los autores no encontraron una correlación significativa entre el tabaquismo y el riesgo de recidiva después de un primer episodio de NEP. Consideran que el rol del hábito de fumar para predecir la recidiva de un NEP necesita una evaluación adicional.
El principal límite de este estudio fue su diseño retrospectivo, lo que hace inevitable algún desvío en la selección. Sin embargo, el número grande de pacientes, los estrictos criterios de selección y el protocolo terapéutico estandarizado adoptado a todo lo largo del período investigado, hacen que la serie sea bastante homogénea. La presencia de una población en estudio bien definida es confirmada por las características de los pacientes de la serie (Tabla 1), que describe perfectamente al paciente con un NEP (alta prevalencia de hombres jóvenes y delgados).
La puntuación de la gravedad distrófica puede ser una herramienta útil para la toma de decisión clínica. Desafortunadamente, ese puntaje carece aún de validación clínica, la que no pudo obtenerse en este estudio prospectivo. La validación de la puntuación de la gravedad distrófica no fue el objetivo del estudio y debería hacerse prospectivamente, con una muestra independiente de pacientes, lo que podría ser el tema de estudios adicionales.
En conclusión, la presencia de ampollas o bullas o ambas, detectadas en la TCAD después de un primer episodio de NEP, estuvo relacionada significativamente con el desarrollo de una recidiva ipsilateral o de un episodio contralateral de neumotórax. Esa correlación fue particularmente significativa en los casos de múltiples lesiones conteniendo aire. Cuando múltiples ampollas o bullas estaban presentes, los valores de riesgo para la recidiva ipsilateral fueron particularmente altos, pero fueron bastante bajos para los episodios contralaterales. Por lo tanto, los autores de este trabajo creen que después de un primer episodio de NEP tratado sólo conservadoramente, en presencia de múltiples ampollas o bullas en la TCAD, debería considerarse un tratamiento quirúrgico temprano del lado afectado, para reducir el riesgo de una recidiva ipsilateral. Si la puntuación de gravedad distrófica es validada en estudios prospectivos ulteriores, podría ser una herramienta útil para la toma de decisión quirúrgica.
♦ Comentario y resumen objetivo: Dr. Rodolfo D. Altrudi