| Introducción: sarcopenia y fragilidad física en el envejecimiento |
> Contexto clínico
La sarcopenia (SP) es un síndrome geriátrico muy prevalente. La SP primaria está relacionada con la edad; tiene múltiples causas, a menudo desconocidas, y se agrava por enfermedades agudas y crónicas, inflamación, disfunción endocrina, inactividad física y estilo de vida poco saludable.
La masa y el rendimiento muscular disminuyen y puede superponerse con la fragilidad física, aunque son diferentes. Fisiopatológicamente, la fragilidad presenta una gran reducción del rendimiento físico y de la fuerza muscular.
Aunque la causa no se conoce con precisión, en la SP se hallan alteraciones significativas de los parámetros metabólicos endocrinos, bajos niveles del factor de crecimiento símil insulina-1 o de testosterona libre.
- La inflamación subclínica crónica y la resistencia a la insulina también son importantes para la resistencia anabólica en los miocitos, ya que disminuye la síntesis de proteínas musculares.
- También se observa infiltración adiposa muscular, que empeora aún más la función muscular.
> Tratamiento y prevención de la sarcopenia: nutrición y ejercicio
La nutrición adecuada y la actividad física son los pilares de la atención primaria de la SP ya que la composición de la MI depende mucho de ellas y viceversa, también puede influir en la fisiología del huésped, modulando la inflamación sistémica, el anabolismo, la sensibilidad a la insulina y la producción de energía.
En teoría, el metabolismo bacteriano de los nutrientes influye en la función de los miocitos del músculo esquelético, mediante la producción de mediadores que impulsan estos efectos sistémicos. La prevención y el tratamiento de la SP requieren una nutrición adecuada, con la prescripción adecuada de proteínas, vitamina D, antioxidantes y ácidos grasos poliinsaturadas. La ingesta proteica debe ser mayor (1,2-1,5 g/kg/día), para satisfacer los mayores requisitos de energía y superar la pérdida de masa grasa.
En cuanto al ejercicio físico, en el adulto mayor el tratamiento es aumentar la fuerza, porque puede promover la diferenciación y proliferación de los miocitos satélite, la producción de energía y la eficiencia metabólica de las mitocondrias, capilaridad muscular con mejor suministro de O2, inervación y vías de detección metabólica; todo esto mejora el anabolismo y la sensibilidad a la insulina.
> Objetivos
Hallar evidencia en la literatura científica que apoye el concepto de la participación de la MI en la fisiopatología de la SP primaria
| Microbiota intestinal: ¿el actor ignorado en el envejecimiento? |
> Conceptos generales sobre la MI a lo largo de la vida útil
La MI humana está compuesta por bacterias, virus, hongos, protozoos, arqueas, y pesa de 175 g-1,5 kg. La relación con el huésped es simbiótica, de modo que los factores ambientales y genéticos pueden moldear su composición, influyendo en la fisiología del huésped, el cual se adapta a su presencia.
En personas sanas, incluye de1.100 a 2.000 taxones bacterianos, que en su mayoría no se pueden cultivar en forma tradicional. La base de su estudio es el ADN bacteriano extraído de las heces y la identificación de polimorfismos del gen del ARN ribosómico 16S (ARNr), lo cual ha mejorado la investigación en seres humanos.
La composición de la MI se forma en la primera infancia y depende de factores geográficos, tipo de parto, lactancia, edad de destete, exposición a antibióticos y regímenes dietéticos. Hacia los 3 años se estabiliza y así permanece durante la vida útil, aun en circunstancias anormales. El 90% de las especies son Bacteroidetes y Firmicutes, de abundancia inversamente proporcional entre ambos. En la población sana hay una gran variabilidad interindividual.
> La dieta como determinante de la composición de la MI intestinal
Los principales factores ambientales que hacen la diferencia interindividual en la composición de la MI saludable son la ubicación geográfica y la dieta. El cambio brusco a dietas hiperproteicas se asocia con una baja diversidad microbiana, mayor cantidad de bacterias con tolerancia a los ácidos biliares y disminución de las bacterias que metabolizan los polisacáridos vegetales.
En cambio, las dietas veganas se asocian con gran abundancia de Prevotella y diversidad microbiana. Sin embargo, el consumo hiperproteico prolongado se ha asociado con composiciones favorables de MI, más aún si se acompaña de ejercicio físico. Estas dietas suelen modificar la proporción relativa de Bacteroidetes y Firmicutes y favorecen a los patógenos oportunistas.
Estos cambios aumentan la permeabilidad de la mucosa intestinal y promueven la inflamación sistémica, la activación inmune subclínica y las alteraciones metabólicas (resistencia a la insulina).
En este contexto, se ha propuesto a la relación relativa Bacteroides:Prevotella como un biomarcador de envejecimiento saludable y activo, dieta y estilo de vida. Las dietas hipergrasas son desfavorables para la MI mientras que la dieta Mediterránea ha mostrado brindar beneficios para la MI.
La composición de la MI es mucho más influenciada por patrones dietéticos a largo plazo que por cambios temporales en la ingesta de alimentos (resiliencia de la comunidad bacteriana).
> La microbiota intestinal en el envejecimiento
Después de los 65 años, la resistencia de la MI suele reducirse y su composición es más vulnerable a los cambios en el estilo de vida, tratamientos farmacológicos (antibióticos) y enfermedades. La diversidad de la MI está inversamente correlacionada con la función física y la institucionalización de los ancianos, con gran variación interindividual de la MI. El envejecimiento se asocia con cambios específicos en la MI.
> Microbiota intestinal y fragilidad física
Hay investigaciones que apoyan la hipótesis de que existe un eje "intestino-cerebral" (ya demostrado en enfermedades psiquiátricas y neurológicas), que también está involucrado en la aparición de la fragilidad cognitiva y, posiblemente, la demencia.
En los mayores, hay conexiones fisiopatológicas estrictas entre la función cerebral y muscular, así que suele ser imposible diferenciar la fragilidad física de la cognitiva, En este contexto, la MI podría influir en el rendimiento físico y la función muscular, a través de la mediación del sistema nervioso central.
| Justificación de una posible correlación entre la microbiota intestinal y la sarcopenia |
> Influencia del ejercicio en la microbiota intestinal: estudios en animales
Hay estudios en animales que apoyan el concepto de que la composición de la Mi está modulada por el ejercicio físico. En varios de esos estudios, el ejercicio se asoció con mayor biodiversidad de la MI y modulación de la inflamación intestinal sistémica y local. El ejercicio puede promover estos cambios sinérgicamente con la dieta, es decir, una dieta poco saludable puede antagonizar los efectos beneficiosos del ejercicio y viceversa.
> Influencia del ejercicio en la microbiota intestinal: estudios en seres humanos
Dada la elevada prevalencia de SP en ancianos, y la efectividad del ejercicio para prevenir o tratar la SP, se necesitan más estudios en adultos mayores para aclarar si la MI puede ser un mediador activo de los beneficios del ejercicio físico en la edad avanzada.
> Microbiota intestinal y efectos sistémicos relacionados con la función muscular
La MI sería un "transductor" de señales de nutrientes para el huésped. Se ha comprobado que una MI sana promueve el anabolismo, mientras que la disbiosis se asocia con resistencia anabólica o incluso catabolismo.
Estos hallazgos no son sorprendentes si se tiene en cuenta cuántos nutrientes están biodisponibles para el huésped provenientes del metabolismo de la MI, o son producidos significativamente por la propia MI. También se destaca el papel activo de la MI como modulador metabólico para el huésped.
> Descripción general de mediadores de la MI y su efecto sobre el músculo esquelético
Varios compuestos producidos o modificados por la MI pueden ingresar a la circulación sistémica y finalmente influir en las células del músculo esquelético . Por ejemplo, una MI saludable puede producir cantidades significativas de ácido fólico y vitamina B12, lo que puede mejorar el anabolismo muscular y prevenir el estrés oxidativo inducido por la hiperhomocisteinemia, y el daño endotelial, lo que lleva a la disminución de la función muscular.
Además, la MI es capaz de sintetizar algunos aminoácidos, como el triptófano, un sustrato fundamental para el anabolismo de las proteínas musculares. También se cree que la betaína de la dieta, con la mediación de la MI, tiene gran influencia en los miocitos esqueléticos.
> Efectos musculares de la manipulación de la microbiota intestinal: estudios en animales
En animales, la administración de probiótico con Lactobacillus reuteri ? un modulador conocido del Factor transcripcional Forkhead Box N1 (FoxN1) para modelos de cáncer en ratones ? puede inhibir el desarrollo de caquexia y preservar la masa muscular. Además, algunos probióticos tienen un marcado efecto antiinflamatorio que beneficia el anabolismo muscular.
Otros estudios evaluaron el efecto sistémico de la interrupción de la homeostasis de la Mi inducida por la administración de antibióticos. También se comprobó que la disbiosis disminuye la fuerza y propiedades mecánicas del músculo.
> Efectos musculares de la manipulación de la microbiota intestinal: estudios en seres humanos
Un estudio de intervención realizado en pacientes mayores y dirigido a explorar los efectos de las modificaciones de la MI en los resultados del músculo esquelético implicaron la administración de prebióticos (sustancias promotoras de la sobreexpresión de bacterias beneficiosas).
| Conclusiones: ¿existe un eje intestino-muscular en el envejecimiento? |
Algunos estudios respaldan la hipótesis de que la MI puede intervenir en el inicio y curso clínico de la SP. Dado que la nutrición es fundamental en la composición de la MI y participa en la patogénesis de la SP, puede ser que se halle en la encrucijada fisiopatológica entre estos dos elementos.
Algunos taxones microbianos clave pueden ser determinantes de la estructura y función muscular, al producir mediadores metabólicos que influyen en la fisiología del huésped, después de la absorción en la mucosa intestinal.
Glicina betaína, triptófano, ácidos biliares y ácidos grasos de cadena corta, como el butirato, son los más prometedores de estas selecciones. Teóricamente estas moléculas y las bacterias que las producen en la microbiota fecal podrían ser biomarcadores de SP, cuya detección es reconocida mundialmente como una prioridad clave en el campo de la investigación de la SP.
Sin embargo, faltan estudios que evalúen específicamente la composición de la MI en la fragilidad física y la SP. Los estudios de intervención que evalúan los efectos de la administración de prebióticos o probióticos en el músculo esquelético han sido realizados principalmente en modelos animales, siendo incierta la aplicación de sus resultados a los seres humanos.
Por otro lado, los probióticos que hay en el comercio no suelen estar dirigidos a las alteraciones de la MI. El desarrollo de nuevos probióticos de "próxima generación" parece muy prometedor en este campo.
En este contexto, se deberán realizar estudios para probar la presencia, funcionalidad y relevancia clínica del supuesto eje intestino-muscular, correlacionando la composición de la MI con la nutrición, el rendimiento muscular y la estructura.
Los efectos de las manipulaciones dietéticas, incluidos los beneficios de una dieta de Mediterránea y el uso de prebióticos y probióticos, también deben evaluarse en personas mayores, tomando como resultados la funcionalidad del músculo esquelético y las variables clínicas. Es decir, una transición clínica de los antecedentes de la ciencia básica que une la MI con el músculo. La fisiología debe ser una de las prioridades de la investigación sobre el envejecimiento, la fragilidad y la sarcopenia.
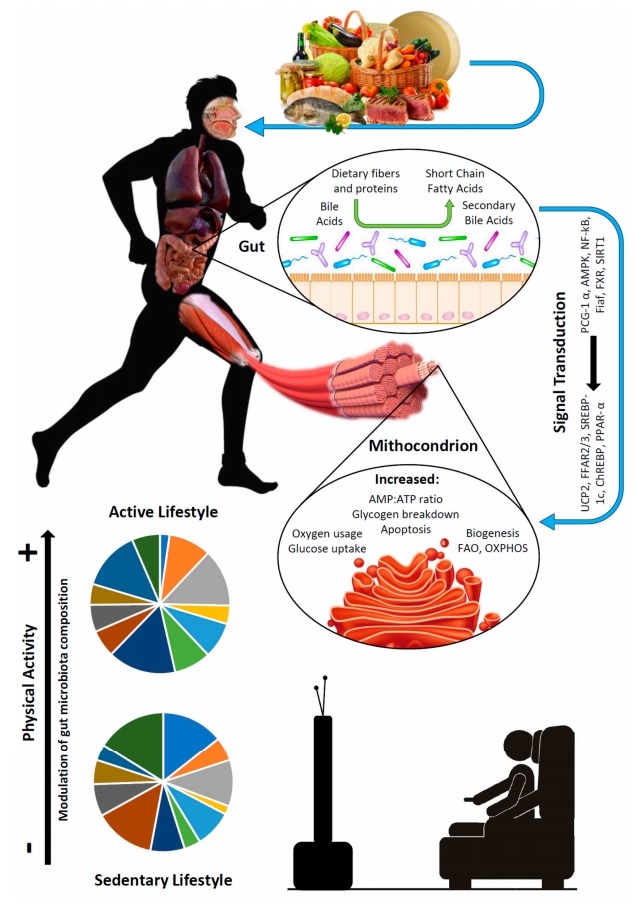 |
| Descripción general de los supuestos mecanismos fisiopatológicos que colocan a la composición de la MI en la encrucijada entre la nutrición y la función muscular. La dieta influye en la composición de la MI; a su vez, la MI metaboliza algunos nutrientes, incluidas las fibras y las proteínas, en mediadores, como los ácidos grasos de cadena corta, que ingresan a la circulación sistémica. Estos mediadores tienen una influencia conocida en los miocitos, y especialmente en sus mitocondrias, a través de múltiples vías de señalización que resultan de la modulación de la inflamación y la promoción de la sensibilidad a la insulina. La parte inferior de la figura también muestra que el ejercicio físico en sí mismo puede modular la composición de la MI y representar un actor importante en estos fenómenos. |
Resumen y comentario objetivo: Dra. Marta Papponetti