| Introducción |
La obstrucción ateroesclerótica de la arteria fémoro-poplítea (AFP) se asocia con una significativa morbilidad, mortalidad y deterioro de la calidad de vida [1]. La colocación de endoprótesis (stents) en la AFP utilizando las autoexpandibles de nitinol es un procedimiento mínimamente invasivo cada vez más popular, para mejorar la permeabilidad arterial después de la angioplastia, particularmente en casos que involucran lesiones más complejas y disecciones arteriales limitantes del flujo.
A pesar de la significativa experiencia clínica y de la disponibilidad de endoprótesis de nueva generación, los resultados del procedimiento continúan decepcionando, con muchos pacientes desarrollando una falla de la reconstrucción en un período de varios meses o unos pocos años después de la colocación de la endoprótesis [2].
La habilidad de las endoprótesis autoexpandibles para desempeñarse razonablemente bien en otras localizaciones, sugiere que el entorno local de la AFP juega un rol significativo en el fracaso de la misma. Condiciones mecánicas severas en el muslo y la pierna que inducen un importante acortamiento [3,4] (o compresión axial), flexión [3,5], torsión [6] y pellizcamiento [7] de la AFP, probablemente producen interacciones adversas endoprótesis – arteria , que pueden llevar a la reestenosis o a la fractura de la endoprótesis.
Datos recientes [3,5,6] sugieren que esas deformaciones pueden ser significativamente más severas que lo previamente asumido [7]. Asimismo, pruebas importantes de banco, cabeza a cabeza, comparando las endoprótesis de la AFP de diferentes fabricantes, demostraron diferencias apreciables en el comportamiento del dispositivo entre los diseños de las endoprótesis, cuando se las sometió a diferentes modos y magnitudes de deformación.
Dado que las pruebas de banco no pueden actualmente replicar las condiciones de carga in situ, complejas y multidimensionales, que existen en la AFP durante la flexión de la extremidad, esos resultados necesitan ser verificados mediante modelos más realísticos.
Aunque los datos clínicos evaluando la efectividad comparativa de las diferentes endoprótesis son el gold estándar final, esos análisis requieren muestras de gran tamaño, debido a la heterogeneidad de las poblaciones de pacientes con enfermedad arterial periférica (EAP), diferencias anatómicas y variabilidad de las características lesionales.
Además, los aspectos financieros y logísticos del reclutamiento de pacientes y disponibilidad de los dispositivos, hacen que sean desafiantes las comparaciones clínicas cabeza a cabeza de múltiples endoprótesis. Esos análisis a menudo limitan los objetivos finales a simples mediciones y son frecuentemente insuficientes para caracterizar comprehensivamente el comportamiento de los dispositivos, tal como su capacidad para adaptarse a la torsión inducida por la flexión [6].
Los autores de este trabajo hipotetizaron que cada uno de los 7 diseños de endoprótesis podría afectar diferencialmente el acortamiento, flexión, torsión y pellizco de la AFP inducidos por la flexión de la extremidad. Para comprobar esa hipótesis, se utilizó un modelo de cadáver humano perfundido y un método de marcación intraarterial previamente descrito y validado [3,5,6].
Para permitir un tamaño más pequeño de la muestra y reducir la variabilidad entre los cadáveres y las arterias, se utilizaron las mismas arterias para caracterizar las deformaciones basales y por la endoprótesis de la AFP, actuando cada AFP como su propio control.
| Métodos |
> Deformaciones basales con modelo de cadáver humano perfundido
Las deformaciones de la AFP fueron mensuradas con marcadores intraarteriales de nitinol de 4 patas diseñados a medida que se ilustran en la Figura 1C.
Los marcadores fueron diseñados para moverse con la arteria durante la flexión de la extremidad, sin deslizarse por su luz o penetrar en la pared de la AFP. Una de las patas del marcador estaba hecha con material extra en la punta para una identificación fácil en la imagen, lo que permitió la evaluación de la torsión que, de otra manera, sería imposible de medir con la suficiente resolución y precisión.
La cabeza de cada marcador era hueca para permitir la inserción de un cordel para un rápido despliegue y recuperación del marcador. Antes de su uso en el cadáver, la técnica del marcador fue validada en tubos de silicona y se halló que producía mediciones precisas y respetables [6]. En los cadáveres, la validación se efectuó mediante la imagen de las arterias antes y después del despliegue del marcador, sin un efecto medible sobre las deformaciones inducidas por la flexión de la extremidad debidas a la presencia de los marcadores (Fig. 1).
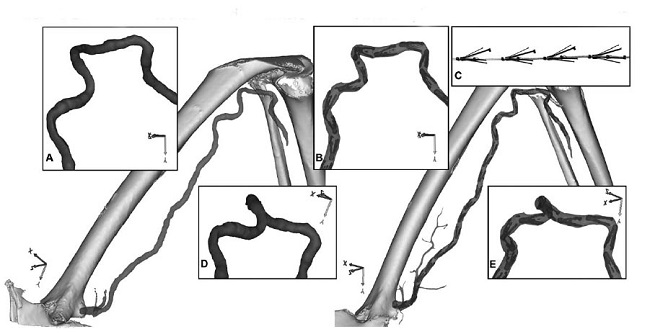
FIGURA 1. Imagen representativa de la AFP en postura de jardinería, antes (A, D) y después (B, E) del despliegue de los marcadores intraarteriales (C). Las inserciones muestran vistas ampliadas de la AFP en diferentes proyecciones ilustrando que los marcadores no influencian las deformaciones naturales de la arteria con la flexión de la extremidad.
Un total de 28 extremidades de 15 cadáveres ligeramente embalsamados (edad promedio 81 ± 9 años; rango: 60-93; 9 mujeres y 6 hombres sin intervenciones arteriales previas, no enfermedad aneurismática, y sin prótesis metálicas que pudieran interferir con las imágenes de la tomografía computada [TC]), fueron utilizados para evaluar las deformaciones de la AFP con la flexión de la extremidad.
El uso de cadáveres levemente embalsamados con una solución basada en glutaraldehido, en oposición a aquellos completamente embalsamados con una solución basada en formaldehido, permitió una mejor preservación de la elasticidad natural de los tejidos [9].
Cuando se las comparó con los cadáveres frescos humanos, las arterias levemente embalsamadas se asemejaban al comportamiento mecánico de las AFP viejas y enfermas, lo que fue verificado realizando una prueba de extensión planar biaxial [10-12], y comparando los resultados con datos previamente publicados para AFP frescas [13].
Al menos 10 horas antes del experimento, las extremidades se envolvieron con almohadillas eléctricas, lo que permitió que toda la extremidad se calentara. Durante el procedimiento, se insertó un catéter angulado en la arteria tibial posterior o en la arteria peronea que se usó luego para punzar la arteria y los tejidos blandos circundantes, para establecer un acceso para la liberación y difusión del marcador.
Los marcadores intraarteriales fueron comprimidos y cargados dentro de tubos plásticos de 6F para una colocación mínimamente invasiva dentro de la AFP bajo guía endoscópica desde un sitio de acceso en la arteria ilíaca externa. Eso permitió el mantenimiento de la integridad de las estructuras anatómicas alrededor de la AFP, mientras que brindó un número suficiente de puntos de referencia para la caracterización precisa de las deformaciones. En publicaciones previas de los autores se describen mayores detalles de este método [3,5,6].
Después de la liberación del marcador, las AFP fueron presurizadas utilizando una bomba (Harvard Apparatus Large Animals; Harvard Apparatus, Holliston, MA) por la que circulaba un fluido radioopaco a 37ºC conteniendo carbonato de calcio, para evitar la hinchazón del tejido. La temperatura del fluido de perfusión fue medida a su salida por el extremo distal de la arteria, para asegurar su consistencia a lo largo de toda la arteria.
Las imágenes de TC (GE Light Speed VCTXT scanner, GE Healthcare, Waukesha, WI) de las extremidades en posturas de pie, (180º), caminando (110º), sentado (90º) y de jardinería (60º) fueron tomadas con una resolución axial de 0,625 mm, para medir las deformaciones basales de la AFP con la flexión de la extremidad (Fig. 2).
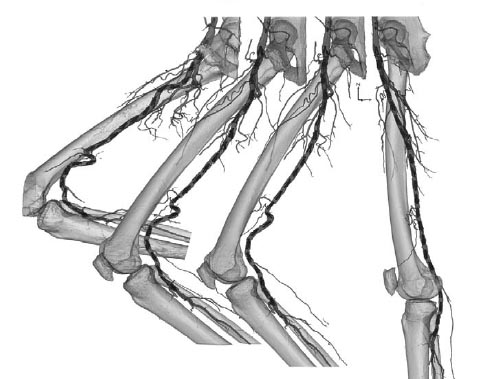
FIGURA 2: Reconstrucciones tridimensionales de la AFP debidas a la flexión de la extremidad, derivadas de imágenes de TC de la pierna en posición de parado, caminando, sentado y jardinería.
> Deformaciones de la AFP después de la colocación de las endoprótesis
Después de obtener las imágenes basales de la AFP en cada posición de la pierna, se recuperaron los marcadores intraarteriales a través del mismo sitio de acceso, y se desplegó una única endoprótesis en cada arteria, centrada en el hiato aductor, con dilatación mediante balón antes y después de la colocación.
Los diámetros de las endoprótesis fueron elegidos de acuerdo con las indicaciones del fabricante para su uso, basado en las mediciones basales del diámetro de la arteria en la TC, a nivel del hiato aductor.
Se utilizaron 7 diseños de endoprótesis con patrones significativamente diferentes (Fig. 3B) en el estudio: AbsolutePro, Supera (ambas de Abbot Vascular), Innova (Boston Scientific), Zilver (Cook Medical), SmartControl, SmartFlex (ambas de Cordis), y Viabahn (GORE Medical). Esas endoprótesis fueron de 3 tipos principales: diseño convencional con forma de z (AbsolutePro, Innova, Zilver, SmartControl, SmartFlex), alambre trenzado (Supera) y alambre recubierto (Viabahn).
Cada uno de los 7 diseños de endoprótesis fue usado en 4 extremidades parfa un total de 28 extremidades con endoprótesis. Después de la colocación de la endoprótesis, los marcadores fueron desplegados nuevamente dentro de la AFP y se obtuvieron de nuevo imágenes de TC con las piernas en posición de pie, caminando, sentado y de jardinería. Un ejemplo de la AFP basal y con colocación de endoprótesis se muestra en la Fig. 3C.
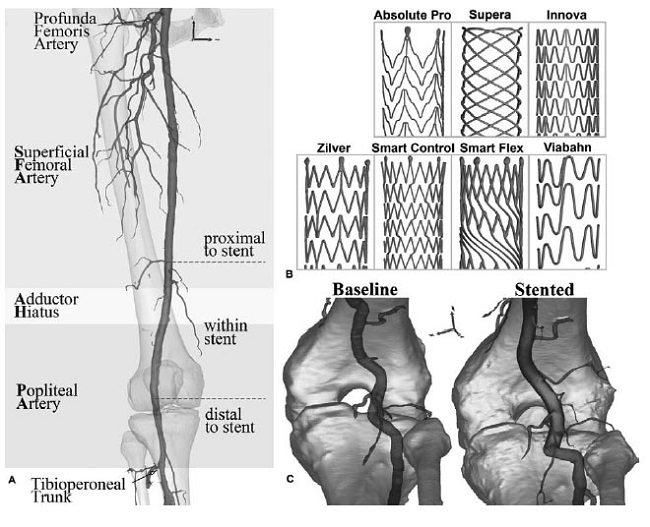
FIGURA 3: (A) AFP con endoprótesis. (B) patrones de diseño de las 7 endoprótesis usadas en el estudio. (C) ejemplo de AFP por debajo de la rodilla antes y después de la colocación de la endoprótesis.
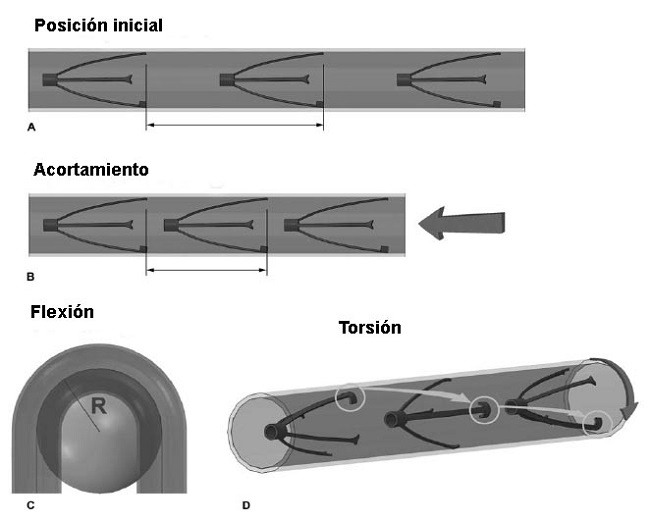
FIGURA 4: Ilustración del método para medir las deformaciones de la AFP con la flexión de la extremidad, mostrando los marcadores intraarteriales en la arteria sin deformación (A), con acortamiento (B) y torsión (D), mientras que la línea central fue utilizada para evaluar la flexión (C).
Se efectuó un total de 224 reconstrucciones tridimensionales de TC (Fig. 2) con el programa Mimics (Materialise, Leuven, Bélgica), usando una combinación de herramientas de crecimiento y segmentación de la región [3,6], a cargo de un único operador, para reducir la variabilidad. Las deformaciones arteriales inducidas por la flexión de la extremidad antes y después de la colocación de la endoprótesis fueron medidas utilizando esas reconstrucciones, en 3 segmentos a lo largo de la arteria: proximal a la endoprótesis, dentro del segmento con la endoprótesis y distal al segmento con la endoprótesis (Fig. 4A).
Las técnicas para la medición del acortamiento, flexión y torsión están descritas en trabajos previos de los autores [3,6] y se ilustran en la Figura 4. De manera resumida, el acortamiento debido a la flexión de la extremidad fue medido como un cambio en la distancia entre cada par de marcadores en las posturas recta y flexionada, a lo largo de la línea central arterial. La flexión se midió inscribiendo manualmente las esferas de mejor ajuste en la línea central de la AFP y registrando sus diámetros (esto es, diámetros más pequeños indicaban flexiones más severas).
La torsión fue medida como la diferencia en la rotación entre 2 marcadores consecutivos en las posiciones recta y flexionada. Esa diferencia en la rotación fue normalizada a la distancia entre los marcadores, para obtener un valor por centímetro de la torsión. Ese paso fue importante porque la rotación de, digamos, 90º sobre 1 cm es significativamente más severa que una torsión de 90º distribuida sobre 2 cm de distancia. Finalmente, el pellizcamiento de sección transversal fue medido en la arterial con endoprótesis como la relación entre los ejes mayor y menor de la sección transversal elíptica, en la ubicación más comprimida.
Los efectos de la colocación de la endoprótesis sobre las deformaciones basales fueron evaluados calculando las diferencias en acortamiento, flexión y torsión, entre las arterias basales y con endoprótesis, expresadas como porcentaje de las deformaciones basales. Las pruebas de t de 2-colas fueron usadas para valorar la significación estadística de los hallazgos.
Para comparar los efectos globales de cada tipo de endoprótesis, se introdujo un puntaje combinado de compatibilidad mecánica (CMCS por sus siglas en inglés). Ese puntaje incluyó la exacerbación y restricción estadísticamente significativa de las deformaciones proximal, dentro y distal del segmento con la endoprótesis.
| Resultados |
> Acortamiento
El acortamiento máximo de referencia fue del 9% al 15% en la arteria femoral superficial (AFS), del 11% al 19% en el segmento a nivel del hiato aductor (HA), y del 13% al 25% arteria poplítea (AP), dependiendo de la postura [3].
El acortamiento de la AFP proximal al segmento en el que posteriormente se colocó la endoprótesis fue del 3% al 6%, y el acortamiento dentro y distal al segmento que en donde se colocó después la endoprótesis, fue del 7% al 14%, dependiendo de la posición.
Globalmente, la mayoría de las endoprótesis exacerbaron el acortamiento proximal y distal a la misma, pero restringieron el acortamiento dentro del segmento con la endoprótesis. Proximal al segmento con la endoprótesis, Innova (71%), Supera (34%) y SmartFlex (15%), exacerbaron el acortamiento de referencia, mientras que los efectos de las otras endoprótesis no alcanzaron significación estadística.
Dentro del segmento con la endoprótesis, todas excepto la Viabahn restringieron el acortamiento de la AFP, siendo la mayor restricción producida por las SmartControl (54%) y SmartFlex (46%), seguidas por la Zilver (41%), Supera (28%), AbsolutePro (22%) e Innova (15%). Distal al segmento con la endoprótesis, SmartControl (49%), SmartFlex (39%), Zilver (39%), Viabahn (31%) y Supera (21%), exacerbaron el acortamiento basal.
> Flexión
La flexión máxima de la AFS expresada como radios de esferas inscritas, osciló entre 21 y 27 mm, la flexión a nivel del HA fue de 9 a 19 mm, y en la AP de 8 a 17 mm, dependiendo de la postura [3]. Los radios de referencia de la flexión en la AFP proximal al segmento de la arteria en donde luego se colocó la endoprótesis oscilaron entre 18 a 23 mm, dentro del segmento entre 5 y 14 mm, y distal al segmento entre 5 y 11 mm, dependiendo de la postura
Proximal al segmento con la endoprótesis, SmartControl restringió la flexión basal en 96%, mientras que los efectos de las otras endoprótesis no fueron estadísticamente significativos. Dentro del segmento con la endoprótesis, Supera (75%) y Viabahn (74%) restringieron la flexión, haciendo que el segmento con la endoprótesis permaneciera más recto durante la flexión de la extremidad.
Aunque SmartControl también enderezó el segmento de la AFP con la endoprótesis, ese resultado no fue estadísticamente significativo (P = 0,12), debido a un gran desvío estándar. No se observaronb efectos estadísticamente significativos distalmente al segmento con la endoprótesis.
> Torsión
La torsión máxima de referencia observada en la AFS fue de 10º a 13º/cm, de 8º a 16º/cm en el HA, y de 14º a 26º/cm en la AP, dependiendo de la postura [3]. La torsión máxima basal en la AFP proximal al segmento en donde posteriormente se colocó la endoprótesis osciló entre 10º y 14º/cm: dentro del segmento, entre 11º y 21º/cm; y distal al segmento, entre 10º y 18º/cm, dependiendo de la postura.
Proximal al segmento con la endoprótesis, SmartFlex (57%) exacerbó la torsión inducida por la flexión de la extremidad, pero no se observaron efectos estadísticamente significativos con las otras endoprótesis. Dentro del segmento con la endoprótesis, la mayor exacerbación de la torsión de la AFP fue producida por SmartFlex (113%), seguida por Innova (83%).
Las endoprótesis Supera (47%), SmartControl (34%), y AbsolutePro (30%), restringieron la torsión de la AFP dentro del segmento con la endoprótesis. Distal a dicho segmento, Viabahn (77%), Supera (59%), Zilver (35%) y SmartControl (31%), exacerbaron la torsión de la AFP inducida por la flexión de la extremidad.
> Pellizcamiento
Todas las endoprótesis, excepto Supera, fueron pellizcadas por las deformaciones producidas por la flexión de la extremidad. SmartControl (1,34) fue la más pellizcada, seguida por Innova (1,18), Zilver (1,15) y SmartFlex (1,06). En la mayoría de los casos, el mayor pellizamiento se observó a nivel del HA.
> Comparación global. Puntaje CMCS
Como aún no está en claro que deformaciones juegan los roles más importantes en la fisiopatología, a todas se les dio la misma ponderación. Globalmente, ninguna de las endoprótesis acomodó todas las deformaciones de la AFP; la exacerbación más grande fue producida por SmartFlex, mientras que Supera fue la más compatible mecánicamente. La mayor restricción general de las deformaciones de la AFP fue producida por la endoprótesis SmartControl, mientras que AbsolutePro fue la que menos restringió esas deformaciones.
| Discusión |
La AFP experimenta deformaciones mecánicas complejas con la flexión y extensión de la extremidad. Esas deformaciones incluyen acortamiento, flexión, torsión y pellizcamiento de la arteria, que varían dependiendo de la postura de la pierna y de la localización [3,5-7,14-16]. La severidad de la deformación ha sido recientemente cuantificada usando un modelo de cadáver humano perfundido y una técnica de marcación intraarterial.
Aunque no se consideran las contracciones musculares activas, los modelos de cadáver humano perfundido son capaces de simular muchas complejidades del entorno de la AFP y, por lo tanto, son una alternativa viable para la caracterización de cada interacción arteria – dispositivo endovascular [17,18].
Estudios recientes utilizando esos modelos han demostrado que las deformaciones de la AFP están localizadas primariamente en la AFS, a nivel del hiato aductor y en la arteria poplítea por debajo de la rodilla, y que son significativamente más severas que lo previamente asumido [3,5-7].
Esos estudios sugieren asimismo que las endoprótesis para la EAP disponibles actualmente pueden no acomodarse apropiadamente a esas deformaciones, lo que de hecho ha sido demostrado por una reciente comparación en banco de pruebas de 12 endoprótesis para EAP comercialmente disponibles.
En ese estudio de Maleckis [8], la mayoría de las endoprótesis para EAP no fueron capaces de soportar el acortamiento, flexión y torsión esperimentados por la AFP sin pandeo. Aunque las pruebas de banco de las endoprótesis permiten comprender las características de diseño del dispositivo que contribuyen a su desempeño, no son capaces de replicar las complejidades de los entornos de carga de la AFP y el interjuego entre la arteria y la endoprótesis.
Para comprender mejor esta cuestión, el presente estudio comparó la influencia de 7 diseños de endoprótesis para EAP sobre las deformaciones de la AFP inducidas por la flexión de la extremidad, usando un modelo cadavérico y utilizando cada arteria como su propio control, para aislar el efecto de cada endoprótesis sobre las deformaciones arteriales basales.
Los datos obtenidos demuestran que los 7 diseños de endoprótesis influencian significativamente las deformaciones de la AFP inducidas por la flexión de la extremidad, no sólo dentro del segmento con la endoprótesis, sino también proximal y distal al mismo. Las características del diseño de la endoprótesis probablemente influencian esas interacciones entre la arteria y la endoprótesis.
Los diseños trenzados y en forma de z, el largo del puntal, ancho, espesor y número, así como la geometría de las interconexiones y las propiedades del material de nitinol, todos interactúan para producir diferencias mensurables en el comportamiento de la endoprótesis, y parece que ejercen efectos importantes sobre la habilidad del dispositivo para acomodar las deformaciones inducidas por la flexión de la extremidad.
Ninguna endoprótesis parece acomodar todos los modos de deformación sin exacerbar o restringir las deformaciones basales. La restricción del acortamiento dentro del segmento con la endoprótesis observada en este estudio, concuerda con hallazgos previos en modelos con pacientes [4,19], cadáveres [20] y computacionales [21], y la cantidad de restricción para los diferentes dispositivos se correlaciona con la rigidez del dispositivo en la compresión determinada con las pruebas de banco [8].
En esas pruebas, la endoprótesis Viabahn fue la que menos restringió el acortamiento, probablemente debido al alambre específicamente diseñado, enrollado helicoidalmente alrededor de una pieza de PTFE, mientras que la mayoría de los otros dispositivos contenían múltiples conectores longitudinales rígidos que restringieron el acortamiento.
La rigidez a la flexión también afectó significativamente el desempeño de las endoprótesis en el modelo cadavérico. La endoprótesis SmartControl tuvo la mayor rigidez a la flexión en los experimentos en el banco de pruebas [8] y también produjo la mayor restricción de la flexión de la AFP en el modelo cadavérico.
Por otro lado, las endoprótesis con alambre trenzado o recubierto, demostraron curvaturas más gentiles en los experimentos de banco y produjeron menor flexión aguda in situ. Los efectos de la rigidez a la flexión sobre la curvatura han sido reportados previamente en modelos cadavéricos [20] y en pacientes con EAP [4], en donde torceduras similares a las descritas en la Fig. 3C fueron observadas en el extremo distal de algunas endoprótesis.
Aunque el acortamiento y la flexión pueden ser cuantificados sin el uso de marcadores intraarteriales [19,20], esos marcadores son esenciales para una adecuada cuantificación de la torsión de la AFP con la flexión de la extremidad [6]. Los datos obtenidos en este estudio demuestran que el diseño de la endoprótesis tiene significativos efectos en la torsión de la AFP, y los resultados nuevamente tienen una buena correlación con los datos sobre rigidez para la torsión obtenidos en el banco de pruebas [8].
Interesantemente, aunque algunas endoprótesis restringieron la torsión dentro del segmento con el dispositivo, la exacerbaron distalmente. La restricción para la torsión parece estar relacionada con la fricción entre los alambres en las endoprótesis trenzadas y con las conexiones cortas de los puntales longitudinales en las endoprótesis con forma convencional en z.
El hecho de que la torsión estuviera exacerbada distalmente sugiere que si la torsión de la AFP no puede ser acomodada por la endoprótesis debido a su alta rigidez para la torsión, puede trasladarse proximal o distalmente al dispositivo, resultando en una exacerbación de la torsión de la AFP. Ese podría ser el mecanismo que conduce a la reestenosis del borde (también llamada “candy wrapper”) vista en algunas endoprótesis [22].
En algunos dispositivos, como en SmartFlex, las torsiones estuvieron exacerbadas en múltiples segmentos, debido probablemente a su diseño único en espiral, que los dotan con características acopladas axiales-torsionales [8]. Dado que la AFP muestra torsión y acortamiento axial combinados con la flexión de la extremidad, las endoprótesis en espiral pueden exacerbar ambos.
Finalmente, la rigidez radial parece tener efectos primordiales en el pellizcamiento de la endoprótesis debido a la flexión de la extremidad. En las pruebas de banco, el dispositivo Supera demostró rigidez radial al menos en un orden de magnitud mayor que la rigidez radial de cualquier otra endoprótesis, probablemente debido a su diseño trenzado y fuerzas friccionales entre los alambres.
Supera fue también la única endoprótesis que no fue pellizcada por las deformaciones inducidas por la flexión de la extremidad en el modelo cadavérico. La rigidez radial del dispositivo Supera parece profundamente influenciada por la técnica adecuada de despliegue de la misma, produciendo nominalmente las endoprótesis desplegadas un ángulo trenzado que resiste fuertemente la compresión radial, mientras que los dispositivos mal desplegados y elongados son radialmente débiles.
Por el contrario, las endoprótesis con forma en z, particularmente aquellas que contienen un gran número de puntales cortos muy conectados, tuvieron problemas para acomodar las deformaciones por flexión, lo que resultó en un pellizcamiento significativo (Fig. 5), que podría potencialmente afectar los patrones de flujo y causar un mal posicionamiento de la endoprótesis durante la flexión de la extremidad.
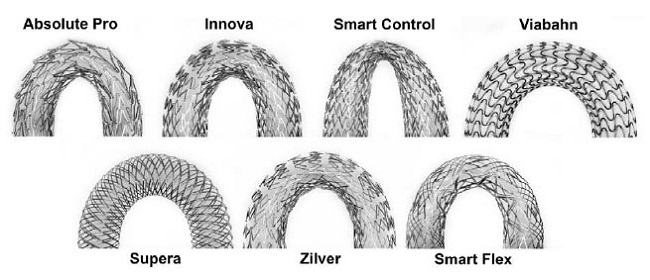
FIGURA 5: Pellizcamiento de las endoprótesis por la flexión. Obsérvese el significativo pellizcamiento del dispositivo SmartControl. También obsérvese la apariencia de “correa dentada” de la AbsolutePro con los ápices de los puntales apuntando lejos de la flexión y hacia la pared arterial.
Aunque estos datos demuestran diferencias apreciables en cómo los diferentes tipos de diseño de las endoprótesis afectan las deformaciones de la AFP inducidas por la flexión de la extremidad, no intentan sugerir una superioridad clínica de una endoprótesis contra otra. Estos resultados representan una evaluación puramente mecánica de las características de las endoprótesis, que deberían ser vistas en el contexto de las limitaciones del estudio.
Primero y más importante, los modelos cadavéricos no pueden recapitular perfectamente las respuestas de los tejidos vivos, que probablemente juegan un rol central en la fisiopatología de la EAP. Finalmente, el desempeño de la endoprótesis debe ser juzgado por ensayos clínicos [23], en lugar de experimentos en bancos de prueba o cadáveres, aunque esas evaluaciones suplementarias pueden ayudar en la interpretación de las diferencias clínicas observadas entre los dispositivos, y guiar la optimización de futuros diseños. La otra limitación de este trabajo es la falta de evaluación de la fatiga y fractura de las endoprótesis.
Dado que la función de las endoprótesis en la EAP es uno de los entornos más dinámicos en la vasculatura, también tienen una de las tasas más altas de fractura [24], correlacionadas con la frecuencia del ejercicio [25]. Aunque la incidencia de la fatiga del material y la fractura de la endoprótesis parecen ser mucho más frecuentes en los dispositivos para la AFP que en aquellos para la carótida o la ilíaca, probablemente no es el único factor que contribuye al fracaso de la recostrucción, dado que la mayoría de los pacientes con reestenosis de la AFP no tienen fracturas en sus endoprótesis.
Sin embargo, la resistencia de las endoprótesis para la AFP a la fractura es una característica importante que es improbable que sea estudiada usando un modelo cadavérico, debido a los largos experimentos de ciclo multimillonario necesarios para caracterizar la fatiga.
Otras características mecánicas no consideradas en este estudio pueden también tener roles importantes en el desempeño de la endoprótesis [27,28]. La abrasividad de la endoprótesis, por ejemplo, puede tener una influencia extrema sobre la pared de la arteria, con la apariencia de “correa dentada” de ciertos dispositivos, vista durante la flexión, contribuyendo en el proceso (Fig. 5).
Finalmente, aunque los presentes hallazgos demuestran diferencias apreciables en el comportamiento mecánico de las endoprótesis para la EAP, esas diferencias no pueden ser atribuidas a una única característica del diseño, como el grosor del puntal, el número de interconectores, ángulo de la trenza, o similar. Los estudios computacionales paramétricos sobre cada dispositivo son requeridos para comprender cómo cada característica del diseño contribuye al comportamiento general de la endoprótesis.
La consideración de esas características adicionales y la validación de estos hallazgos con datos de pacientes, será el foco de futuros estudios. Mientras tanto, los resultados presentados pueden ayudar a los fabricantes de endoprótesis a optimizar sus dispositivos para una mejor compatibilidad mecánica con las deformaciones de la AFP inducidas por la flexión de la extremidad
| Conclusiones |
Los autores evaluaron las endoprótesis para EAP según sus diferentes habilidades para manejar las deformaciones severas que experimenta la AFP con la flexión de la extremidad.
Los dispositivos SmartControl y SmartFlex influencian las deformaciones inducidas por la flexión de la extremidad más que los otros diseños de endoprótesis, corroborando las conclusiones del banco de pruebas [8].
La endoprótesis Supera exacerba menos las deformaciones basales de la AFP, mientras que la AbsolutePro tuvo globalmente la menor influencia en términos tanto de restricción como de exacerbación.
Aunque la exacerbación por la endoprótesis de deformaciones ya grandes es improbable que beneficien la curación de la AFP, aun no se ha entendido si la restricción de esas deformaciones tiene un efecto positivo o negativo sobre la función arterial y la curación.
Por un lado, los segmentos arteriales más rectos producidos por endoprótesis rígidas pueden contribuir a más patrones de flujo laminar.
Por el otro lado, las endoprótesis rígidas pueden producir altas concentraciones de estrés en los extremos del dispositivo, dado quela arteria se ajusta alrededor de dispositivos más rígidos durante la flexión de la extremidad.
Las altas concentraciones de estrés pueden dañar la pared arterial y pueden llevar a respuestas celulares y bioquímicas deletéreas, culminando en el fracaso de la reconstrucción [5,29-32]. Se requerirá más investigación utilizando datos de pacientes vivos y animales grandes, para determinar la influencia de esos factores sobre la curación arterial.
Comentario y resumen objetivo: Dr. Rodolfo D. Altrudi