| Introducción |
El espacio pleural está definido por la pleura visceral, que cubre el pulmón, y la pleura parietal, que cubre la pared del tórax, el diafragma y el mediastino. En la mayoría de los casos, el derrame pleural está ocasionado por insuficiencia cardíaca congestiva, neumonía y cáncer. El neumotórax espontáneo es otra causa de derrame pleural con una incidencia similar a la del neumotórax iatrogénico.
En años anteriores se han logrado avances importantes en el conocimiento de la biología y fisiopatología relacionada, así como en el tratamiento de los derrames paraneumónicos, el empiema y los derrames pleurales malignos; también en cuanto a la elevada alta mortalidad asociada a derrames no malignos y trasudados.
Por otra parte, las definiciones y el manejo del neumotórax también han evolucionado. Para estas condiciones, los objetivos de la atención del paciente es el diagnóstico rápido y eficiente con intervenciones mínimamente invasivas, con el fin de evitar la necesidad de procedimientos múltiples y minimizar los días de internación y maximizar la calidad de vida.
| Anatomía y fisiopatología de la pleura |
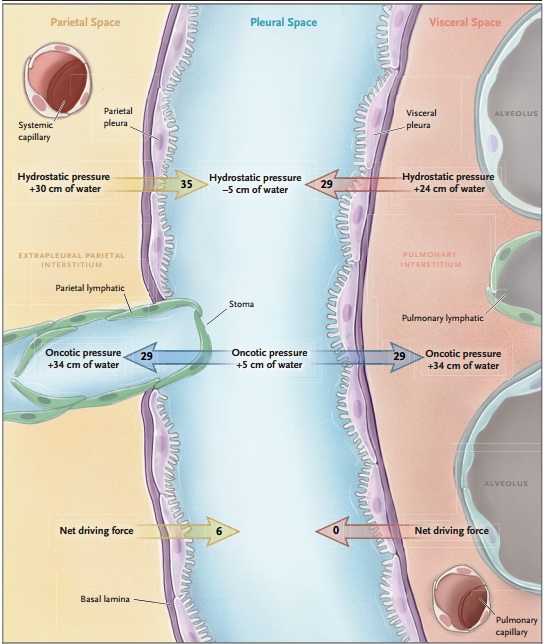
Cuando los pulmones normales se extraen de la cavidad torácica, su volumen de gas disminuye como resultado de la retracción elástica. La pared del tórax, en cambio, al final de una respiración y bajo la influencia de la presión atmósfera normal (es decir, a la capacidad residual funcional), tiende a expandirse. Este equilibrio de las fuerzas físicas mantiene una presión ligeramente negativa en el espacio pleural, en -3 a -5 cm de agua.
La fisiología de la función del espacio pleural en los seres humanos no está clara. Una teoría sostiene que la pleura sirve como membrana serosa elástica que permite los cambios en la forma de los pulmones durante la respiración, mientras que otros sugieren que la presión pleural ligeramente negativa previene la atelectasia al mantener una presión transpulmonar positiva. En los humanos, la pleura parietal y visceral se fusionan en el hilio pulmonar, separando el tórax en dos espacios no contiguos (hemitórax).
Al considerar la pleura, es importante no pensar solo en el espacio pleural, ya que ambas pleuras, visceral y parietal, juegan un papel importante en el mantenimiento de la homeostasis normal. La pleura está cubierta por células mesoteliales, que son metabólicamente activas y producen muchas sustancias, entre ellas glicoproteínas ricas, ácido hialurónico, óxido nítrico y factor de crecimiento transformador ß. En los últimos años, la investigación ha mejorado en gran medida la comprensión de la formación y resorción del líquido pleural.
Se estima que, en los seres humanos, cada cavidad pleural contiene casi 0,26 ml de líquido/kg de peso corporal. Este fluido se produce y absorbe principalmente en la superficie parietal y depende del equilibrio entre las diferencias en las presiones hidrostática y oncótica de las circulaciones sistémica y pulmonar y del espacio pleural.
Los vasos linfáticos pleurales son los responsables de la resorción del líquido pleural, y la velocidad del flujo de estos vasos puede aumentar por un factor de aproximadamente 20 en respuesta a los aumentos en la formación de líquido pleural. Por lo tanto, solo se observará un derrame clínicamente significativo cuando la producción de fluido supere sustancialmente la capacidad de los vasos linfáticos para reabsorber e líquido, debido a la mayor producción y menor resorción, o una combinación de estos dos factores.
| Evaluación de los derrames pleurales |
El diagnóstico diferencial de los derrames pleurales es extenso. Sus causas potenciales figuran en la siguiente lista
| Causas de derrame pleural |
| Derrames por trasudado • Insuficiencia cardíaca congestiva • Cirrosis • Síndrome nefrótico • Glomerulonefritis • Diálisis peritoneal • Hipoalbuminemia (albúmina sérica típica, <1,5 mg/dl) • Atelectasia • Obstrucción de la vena cava superior • Atrapamiento pulmonar • Sarcoidosis • Diálisis peritoneal • Mixedema • Fuga de líquido cefalorraquídeo o derivación ventriculopleural • Urinotórax • Hipertensión arterial pulmonar • Embolia pulmonar • Enfermedad pericárdica • Migración extravascular del catéter venoso central Derrames por exudado • Infeccioso: bacteriano, viral, relacionado con la tuberculosis, fúngico, parasitario. Hemotórax |
|
El uso de la ecografía en el punto de atención para la evaluación del derrame pleural se ha asociado con:
|
Por lo tanto, la ecografía es muy recomendable para guiar la intervención pleural. A menos que la causa del derrame sea relativamente sencilla (por ej., paciente con signos y síntomas claros de insuficiencia cardíaca congestiva y un derrame más pronunciado en el lado derecho), se debe solicitar la consulta con un neumonólogo para optimizar la evaluación oportuna del derrame pleural, disminuir la probabilidad de complicaciones asociadas y asegurar el seguimiento apropiado, basado en los resultados del análisis del líquido pleural.
| Trasudados versus exudados |
Casi el 25% de los trasudados suelen ser clasificados erróneamente como exudados
Uno de los primeros pasos en la evaluación de los pacientes con derrame pleural es distinguir a los que tienen características inflamatorias (exudativas) de aquellos que no son consecuencia de un efecto inflamatorio (trasudado). El uso de los criterios de Light para diferenciar el exudado del trasudado sigue siendo el método estándar desde que se formularon en 1972.
|
De acuerdo con estos criterios, se considera que un paciente tiene un derrame exudativo cuando tiene cualquiera de los siguientes signos:
|
Aunque estos criterios identifican correctamente a casi todos los exudados, casi el 25% de los trasudados suelen ser clasificados erróneamente como exudados, especialmente en los pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca congestiva que han recibido diuréticos.
En estos pacientes que tienen un nivel de proteína sérica 3,1 g/dl más elevado que el nivel en el líquido pleural, o un nivel de albúmina sérica 1,2 g/dl más elevado que en el líquido pleural puede ayudar a identificar los trasudados que fueron clasificados erróneamente como exudados utilizando los criterios de Light. Sin embargo, no ha sido demostrado que la precisión general de este enfoque sea significativamente mayor que con los criterios de Light l.
Del mismo modo, se ha demostrado que un nivel del péptido natriurético tipo B N- terminal (NT-proBNP) en el líquido pleural de 1.500 pg/ml identifica con precisión los derrames debidos a insuficiencia cardíaca congestiva. Sin embargo, dado que los niveles séricos de NT-proBNP son casi idénticos a los niveles en el líquido pleural, actualmente se recomienda usar el nivel de NT-proBNP sérico junto con el criterio clínico para identificar los trasudados correctamente en los pacientes que han tenido insuficiencia cardíaca congestiva con derrame y una diuresis activa.
Si no se conocen los niveles séricos de proteína y albúmina (por ej., en un paciente ambulatorio que tiene la esperanza de evitar la venopunción), se ha demostrado que un nivel de proteína del líquido pleural >3 g/dl o un nivel de colesterol en el líquido pleural >45 mg/dl indica la presencia de un derrame exudativo, tan exacto como los criterios de Light.
| Exudados comunes |
Derrames paraneumónicos y empiema
La piedra fundamental del tratamiento del derrame paraneumónico y del empiema es la selección de los antibióticos apropiados sobre la base de la microbiología y la resistencia a los antibióticos local
Los derrames exudativos más comunes son los provocados por la neumonía, y se los denomina derrames paraneumónicos. El empiema se refiere a la infección franca o pus en el espacio pleural. La importancia clínica del empiema y su drenaje ha sido conocida durante más de 2000 años; ya Hipócrates citaba la enfermedad y su tratamiento mediante el drenaje.
Sin embargo, a pesar de los avances en el tratamiento de la neumonía, la mortalidad es mayor en los pacientes con derrame paraneumónico que en los pacientes con neumonía sin derrame, y el retraso en el drenaje se asocia con una mortalidad sustancialmente mayor.
Por otra parte, tanto la incidencia como la mortalidad por derrame paraneumónico y empiema siguen en aumento. Es de notar que los pacientes de edad avanzada suelen presentar los síntomas clásicos como fiebre, expectoración y dolor en el pecho, pero más bien tienen anemia, fatiga y dificultad para mejorarse.
Probablemente, en parte debido a un subdiagnóstico, en el momento del diagnóstico, los pacientes ancianos también suelen tener derrames más complicados, con tasas más elevadas de fracaso terapéutico no quirúrgico. Por lo tanto, es crucial considerar al derrame paraneumónico y el empiema en todos los pacientes ancianos con neumonía.
La piedra fundamental del tratamiento del derrame paraneumónico y del empiema es la selección de los antibióticos apropiados sobre la base de la microbiología y la resistencia a los antibióticos local. Los pacientes con neumonía adquirida en la comunidad tienden a infectarse con especies de estreptococos y anaerobios (por ej., bacteroides y peptostreptococcus), mientras que los pacientes con infección nosocomial probablemente tienden a estar infectados por estafilococos resistentes a la meticilina y bacterias Gram-negativas (por ej., enterobacteria).
La mortalidad es significativamente mayor en los pacientes con infección nosocomial que en aquellos con infección adquirida en la comunidad (47% vs. 17%). Para ayudar a identificar a los pacientes que están en riesgo de mal resultado en el momento de su presentación, Rahman y col. han desarrollado un sistema de puntaje denominado RAPID (Renal: función renal; Age: edad; Purulence: prudencia; Infection: fuente de infección y Diet: factores dietarios).
Los puntajes varían de 0 a 7, con valores entre 0 y 2 para la función renal y edad (con puntajes más más elevados para una función renal más afectada o edad avanzada) y puntajes de 0 o 1 para la purulencia del derrame (para un derrame no purulento corresponde 1 punto), ya sea la infección nosocomial (1 punto) o no (0 punto) y factores dietéticos (0, para un nivel de albúmina =2,7 g/dl y 1 para un valor inferior al del umbral).
En un estudio, se halló que los pacientes en la categoría de alto riesgo (puntaje RAPID de 5 a 7) tenían menos de 30% posibilidad de morir en las siguientes 12 semanas y, por lo tanto, los pacientes similares pueden justificar una terapia inicial más invasiva.
Los pacientes con derrames paraneumónicos o empiema pueden sufrir deterioro en su condición, y, dado su estado inflamatorio subyacente, a todos se les debería hacer un hemocultivo de sangre periférica y recibir nutrición adecuada y profilaxis para la trombosis venosa profunda. Como con cualquier otra infección en un espacio cerrado, el empiema debe ser drenado.
Aunque faltan datos de ensayos aleatorizados, grandes series retrospectivas muestran que los tubos de pequeño calibre (=14-French) funcionan igual que los tubos de mayor calibre, en términos de la mortalidad posterior y la necesidad de cirugía, y se asocian con menos dolor durante la inserción y permanencia.
Sin embargo, dado que los tubos <12-French tienen mayor tasa de fracaso en el empiema, los autores prefieren usar un catéter cola de cerdo 14 French, colocado con la técnica de Seldinger modificada.
Si el espacio pleural no se drena con un tubo de pequeño calibre, se han obtenido buenos resultados con la instilación del activador del plasminógeno tisular (t-PA) y de DNasa; en un ensayo se comprobó que se asocia con un drenaje del líquido significativamente mejor, menor probabilidad de indicación quirúrgica y una internación hospitalaria media más corta.
Sin embargo, se debe tener en cuenta que no se ha demostrado que el t-PA y la DNasa disminuyan la mortalidad. En ese ensayo, la estancia hospitalaria de los pacientes del grupo t-PA-DNasa fue de 12 días.
Por otra parte, es posible que evitar la cirugía no sea una medida con resultados más importantes, ya que la cirugía toracoscópica asistida por video (CTV) es mucho menos invasiva que la toracotomía. Otros ensayos aleatorizados pequeños más antiguos mostraron que la CTV puede ser el tratamiento definitivo para el empiema, hasta en el 91% de los casos. Datos más recientes sobre la CTV sugieren que las estancias hospitalarias habituales son de aproximadamente 5 a 7 días.
Por otra parte, cuando la cirugía se realiza más tardíamente en el curso de la enfermedad, se asocia con mayor tasa de conversión a la toracotomía y más complicaciones que cuando se realiza en etapas anteriores de la enfermedad. El enfoque general de los autores para los pacientes con derrame paraneumónico o empiema se basa en las recomendaciones de la British Thoracic Society.
Actualmente existe planificado un estudio aleatorizado de t-PA-DNasa versus CTV precoz para el tratamiento del derrame paraneumónico o el empiema, y estudios que examinan si los regímenes de dosis bajas de t-PA-DNasa, e incluso la irrigación con solución salina normal, pueden lograr resultados similares.
| Derrames pleurales malignos |
El derrame pleural maligno se asocia con mal pronóstico y una mediana de supervivencia de 4 a 7 meses desde el momento del diagnóstico
Los derrames pleurales malignos son la segunda causa de derrame exudativo y la principal causa de exudados en los pacientes sometidos a toracocentesis, con una mortalidad hospitalaria estimada del 11,6%. La mayoría de los derrames pleurales malignos se deben al cáncer de pulmón, el cáncer de mama y el linfoma; se estima que el 15% de los pacientes con cáncer de pulmón tendrá un derrame pleural maligno en la presentación y hasta el 50% desarrollará un derrame pleural maligno durante el curso de su enfermedad.
El derrame pleural maligno se asocia con mal pronóstico y una mediana de supervivencia de 4 a 7 meses desde el momento del diagnóstico. Incluso en los pacientes cuyos derrames se consideran "demasiado pequeños" para ser drenados, la supervivencia es significativamente más corta que en los pacientes sin ningún tipo de derrame.
La supervivencia depende principalmente del subtipo de tumor, siendo los de peor pronóstico los cánceres de pulmón y gastrointestinales (mediana de supervivencia, 2 a 3 meses). En general, el mejor pronóstico lo tienen el mesotelioma y los cánceres hematológicos, con una supervivencia de casi 1 año.
Para tratar apropiadamente a los pacientes con derrames pleurales malignos neoplásicos es importante comprender los mecanismos por los cuales los derrames pleurales causan disnea. Es raro encontrar una hipoxemia importante.
Generalmente, la disnea relacionada no es un problema pulmonar secundario al colapso pulmonar o a una reducción en la función pulmonar. Por el contrario, es un problema de la pared torácica causado por el diafragma desplazado caudalmente, lo cual es mecánicamente desventajoso por su relación longitud-tensión.
El origen de la disnea es importante, ya que la mayoría de los interrogantes clínicos relevantes después de una toracocentesis de gran volumen es: "¿Ha mejorado la respiración del paciente?" y "¿Se reexpidió por completo el pulmón?" Si el paciente no se siente mejor después de la toracocentesis, la causa de la disnea es otra (por ej., embolia pulmonar o carcinomatosis linfangítica). En tales casos, deben realizase más pruebas diagnóstico.
Sin embargo, no se deberían realizar procedimientos que aborden el espacio pleural. Si la disnea se ha aliviado con la toracentesis, al menos el derrame contribuía en gran medida a la disnea; la disnea puede disminuir independientemente de si el pulmón ha vuelto a expandirse. En este caso, se puede considerar la realización de una pleurodesis, la colocación de un catéter pleural tunelizado o una combinación, mientras que, si el pulmón no se ha expandido, el tratamiento de elección es el catéter pleural tunelizado.
Los catéteres pleurales tunelizados son tubos de calibre pequeño que se tunelizan por vía subcutánea en el espacio pleural, pudiéndose colocar en forma ambulatoria, y permiten que los pacientes o los cuidadores drenen el líquido pleural sin necesidad de recurrir a procedimientos invasivos adicionales.
Debido a que al menos el 30% de los pacientes con derrame pleural maligno no experimentan la reexpansión pulmonar, la cual puede no ser evidente incluso en el momento de la toracoscopia, antes de decidir la terapia definitiva puede ser importante realizar una toracentesis de gran volumen.
Los objetivos del tratamiento de pacientes con derrame pleural maligno son mejorar la calidad de vida, principalmente minimizando la disnea, los procedimientos pleurales y, la necesidad de visitas repetidas al hospital o al médico. Dado el mal pronóstico de estos pacientes, se recomienda la paliación precoz definitiva de la pleura como se propone para las toracocentesis pleurales, que exponen al paciente tanto a riesgos y molestias.
El puntaje LENT (LDH en el líquido pleural, estado de rendimiento del Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group [ECOG], relación neutrófilos-linfocitos en el suero, y tipo de tumor) permite estratificar con precisión a los grupos de pacientes de alto, moderado y bajo riesgo y puede ser útil para orientar el tratamiento.
Se asigna un puntaje de 0 para un nivel de LDH en el líquido pleural <1.500 UI/l y 1 punto para un nivel superior a ese umbral: Cero a 3 puntos corresponde a un estado de empeoramiento ECOG; 0 puntos para una proporción neutrófilo-linfocito sérica <9; 1 punto para una proporción superior a ese umbral y 0 a 3 puntos según el tipo de tumor.
Los puntajes totales de 0 o 1 son considerados de bajo riesgo y se asocian con una mediana de supervivencia de 319 días, en comparación con una mediana de supervivencia de 130 días en la categoría de riesgo medio (2 a 4 puntos) y 44 días en la categoría de alto riesgo (5 a 7 puntos).
Para los pacientes de alto riesgo, puede ser más útil un enfoque menos invasivo, como la colocación de un catéter pleural tunelizado o incluso la toracocentesis, mientras que los pacientes que se consideran de bajo riesgo se pueden tratar con catéteres pleurales tunelizados, pleurodesis o una combinación de estos. Cuando se discuten las opciones para los pacientes con pulmones expandibles, deben tenerse en cuenta los riesgos y los beneficios de cada procedimiento.
Los beneficios de los catéteres pleurales tunelizados incluyen la mejoría clínicamente significativa de la disnea, la posibilidad de ser colocados en forma ambulatoria y la capacidad de muchos pacientes y familiares para cuidar el catéter en el domicilio. Sin embargo, los pacientes necesitan drenar tal catéter repetidamente hasta que el derrame se resuelve o hasta la muerte.
Se estima que casi el 50% de los pacientes se produce una pleurodesis espontánea. La pleurodesis ocurre aproximadamente 60 días después de la inserción del catéter. Sus beneficios son el gran alivio de la disnea y la falta de necesidad de manejar el catéter.
Sin embargo, muchos centros mantendrán a los pacientes en el hospital, de 3 a 5 días después de la instilación de talco, para que se produzca fusión de la superficie pleural, existiendo un pequeño riesgo de hipoxemia transitoria cuando se utiliza talco no graduado.
En cuanto al tratamiento de los derrames persistentes, un ensayo aleatorizado no ciego examinó el resultado de la pleurodesis con catéter pleural tunelizado vs. pleurodesis con talco líquido y no mostró diferencias significativas en la disnea o la calidad de vida. Los pacientes del grupo tratado con talco se sometieron a más procedimientos adicionales, mientras que los pacientes del grupo tratado con catéter pleural tunelizado tuvieron mayor incidencia de efectos adversos no graves.
Aunque suele haber temor de derivar al paciente, la infección relacionada con el catéter pleural tunelizado ocurre aproximadamente en el 5% de las veces, y usualmente puede ser tratada sin retirar el catéter.
Los resultados de los ensayos sugieren que la combinación de catéter pleural tunelizado con agentes esclerosantes (talco o nitrato de plata), así como el drenaje diario, puede dar como resultado una permanencia más corta del catéter. Los autores recomiendan que, como en todos los procedimientos, se discutan detalladamente con el paciente, tanto los riesgos como los beneficios y las alternativas, y que la terapia sea personalizada.
| Trasudados complicados |
Los trasudados más comunes son los provocados por la Insuficiencia cardíaca congestiva, la cirrosis y el síndrome nefrótico. Aunque a menudo se consideran condiciones benignas, recientemente se ha demostrado que los derrames asociados a la insuficiencia cardíaca congestiva, la insuficiencia hepática y la insuficiencia renal se asocian con tasas de mortalidad a 1 año del 50%, 5% y 46%, respectivamente.
Los pacientes con insuficiencia cardíaca congestiva y derrame pleural tienen un riesgo de muerte al año similar al de los pacientes internados en la unidad de cuidados intensivos con insuficiencia cardíaca aguda descompensada; los pacientes con hidrotórax hepático tienen un riesgo de muerte similar al de los pacientes con un puntaje de 20 a 29 en el Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD)en etapa terminal (una indicación típica para trasplante; puntajes MELD de van de 6 a 40 siendo los puntajes más elevados indicadores de una enfermedad hepática más avanzada) y los pacientes con insuficiencia renal y derrame tienen un riesgo de muerte al año tres veces superior en los pacientes sometidos a hemodiálisis sin derrame.
Aunque en la mayoría de los pacientes los trasudados pueden ser manejados con el tratamiento de la enfermedad subyacente, los derrames refractarios merecen una pronta y agresiva paliación pleural para disminuir la repetición de los procedimientos y la disnea, y maximiza la calidad de vida.
Como en los derrames pleurales malignos, puede estar indicada la colocación de catéteres pleurales tunelizados, la pleurodesis, o ambas, los autores recomiendan una cuidadosa discusión con los equipos especializados (por. ej., hepatología y trasplante de hígado) para desarrollar un plan multidisciplinario.
| Conceptos actuales en el tratamiento del neumotórax |
Hasta en el 70% de los pacientes clínicamente estables, el neumotórax puede tratarse con aspiración con aguja simple, que evita la hospitalización
Tradicionalmente, el neumotórax ha sido clasificado como primario (sin enfermedad pulmonar subyacente), secundario (por una enfermedad pulmonar subyacente), traumático y iatrogénico. Debido a los avances en la imagenología torácica (TC y toracoscopia), se ha comprobado que los pacientes con neumotórax que previamente habían sido considerados libres de enfermedad tienen cambios pulmonares símil enfisema y aumento de la porosidad pleural, o defectos en la pleura visceral que son independientes de ampollas o b0ullas.
Estos hallazgos sugieren que la distinción entre el derrame primario y secundario quizás es una construcción artificial y el tratamiento debe estar basado en el tamaño del neumotórax y los síntomas del paciente. Por otra parte, no hay una definición estándar del tamaño del neumotórax; el American College of Chest Physicians define como "grande" al neumotórax con una distancia =3 cm desde el vértice del pulmón hasta la cúpula de la pared torácica, mientras que la British Thoracic Society lo define como una distancia intrapleural de al menos 2 cm en el nivel del hilio.
De hecho, el acuerdo sobre el tamaño basado en estas definiciones solo ocurre en menos del 50% de las veces en los entornos clínicos, lo que conduce a una variación sustancial en las recomendaciones terapéuticas.
Hasta en el 70% de los pacientes clínicamente estables, el neumotórax puede tratarse con aspiración con aguja simple, que evita la hospitalización. Al igual que en el derrame paraneumónico y el empiema, las guías actuales recomiendan el uso de tubos de calibre pequeño (14-French) en lugar de tubos de gran calibre para los pacientes con neumotórax que no han respondido al tratamiento, o no son candidatos para la aspiración con aguja simple.
Este último grupo incluye a los pacientes que viven lejos del centro de atención, que tienen un mínimo apoyo social, o padecen una enfermedad pulmonar subyacente más importante. En los últimos años, existe una tendencia terapéutica más conservadora que reserva el tratamiento quirúrgico para los pacientes con mayor riesgo de derrame recurrente.
Se ha demostrado que el monitoreo de las fugas de aire mediante dispositivos digitales reduce la cantidad de días que tiene que permanecer colocado un tubo torácico y acorta la duración de la estancia hospitalaria después la lobectomía o la segmentectomía.
Cuando los pacientes con neumotórax son tratados con tubos torácicos, el pulmón suele expandirse y la fuga de aire cesa en 3 días. Si el pulmón no se expande por completo dentro de los 3 a 5 días, está indicada la toracoscopia, en la cual se engrapan las ampollas y se intenta crear una pleurodesis, generalmente con abrasión pleural. Otro método de tratamiento de la fuga de aire prolongada es instilar 1 ml/kg de peso corporal de la propia sangre del paciente a través del tubo torácico.
Una alternativa es la pleurodesis, que puede hacerse mediante la instilación de un agente esclerosante o la colocación de esclerosante unidireccional endobronquial, con el fin de reducir el flujo de aire a través de la pleura visceral. Las válvulas se remueven después de la cicatrización del defecto pleural, típicamente a las 6 semanas.
Después de que un paciente tuvo un neumotórax espontáneo, la probabilidad de una recurrencia excede el 50%. La prevención de la recurrencia es clave, especialmente en los pacientes con una función pulmonar marcadamente disminuida, en quienes la recurrencia puede ser fatal. Luego de la primera recurrencia del neumotórax, la probabilidad de una segunda recurrencia es muy elevada.
Las tasas de recurrencia pueden reducirse a casi el 25% si se introduce un agente como talco o doxiciclina a través de un tubo torácico, y puede reducirse más del 5% con la toracoscopia y la insuflación de talco, el grapado de las ampollas o la abrasión pleural, para crear una pleurodesis. Sin embargo, la bullectomía sola, sin intentar la pleurodesis, se asocia con una tasa más elevada de recurrencia, y por lo tanto la pleurodesis siempre debe ser considerada como parte integral del procedimiento.
| Áreas para futuras investigaciones |
En los últimos años se han sido publicado grandes ensayos multicéntricos, aleatorizados, desde centros que tienen servicios clínicos y de investigación pleural importantes.
Los resultados pueden lograr el mejoramiento de las pruebas de diagnóstico etiológico del derrame pleural; contar con más compuestos para disminuir la tasa de producción de fluido pleural o aumentar la tasa de reabsorción del líquido pleural, lo que se ha conseguido con la pleurodesis y mayor desarrollo de los servicios de neumología intervencionista y multidisciplinarios dedicados a las enfermedades pleurales.
Por otra parte, se aproximan los ensayos que investigan el efecto clínico de la manometría pleural, los estudios para comprender mejor la farmacodinámica de los fármacos usados en el espacio pleural, y la investigación de cómo la enfermedad pleural está relacionada con la composición genética de los pacientes afectados.
También están siendo investigados los resultados centrados en el paciente (y en el cuidador), como el efecto sobre la calidad de vida diaria, La enfermedad pleural sigue siendo un problema clínico común, y el mejoramiento de la evaluación y el tratamiento multidisciplinarios maximizará la atención de los pacientes.
Resumen y comentario objetivo: Dra. Marta Papponetti