Introducción
Sólo el 11% al 20% de los pacientes con lesión cardíaca penetrante (LCP) arribará con vida al hospital [1-3] y la tasa de mortalidad intrahospitalaria es reportada tan alta como del 61% al 65% [4,5]. La presentación clínica al arribo se clasifica como: sin vida, clínicamente inestable, taponamiento cardíaco, lesión toracoabdominal y benigna [6]. La proporción de pacientes que arriba con LCP benigna va desde el 15% al 30% [7-12]. Más específicamente, esa cohorte está hemodinámicamente estable, neurológicamente alerta y no tiene signos de taponamiento cardíaco o sangrado activo. El manejo ideal para esos pacientes (por ej., examen físico normal con hallazgo ecográfico positivo de sangre pericárdica), sigue sin resolverse.
El algoritmo actual de manejo internacionalmente aceptado para un paciente hemodinámicamente estable con LCP, establece una esternotomía inmediata y exploración cardíaca [13]. La experiencia con la realización obligatoria de una esternotomía en Cape Town, Sudáfrica, fue que en muchos pacientes, la lesión cardíaca se había sellado. Un estudio piloto efectuado en 2001 encontró que el 71% (10 de 14) de los pacientes tuvo una esternotomía no terapéutica por una LCP tangencial o de espesor parcial. Asimismo, la herida se había sellado en 4 pacientes con LCP de espesor completo [14]. Subsecuentemente, 7 pacientes adicionales con hemopericardio confirmado fueron exitosamente manejados, realizando una ventana pericárdica subxifoidea (VPS) y drenando la sangre en el saco pericárdico.
El peligro de omitir una lesión cardíaca ha sido bien documentado [15]. Como resultado de ello, todas las lesiones cardíacas mayores no selladas deben ser identificadas y reparadas. Los autores de este trabajo han hallado que realizando una VPS inicial, las lesiones mayores sangran por la irrigación del saco pericárdico. Si se encuentra una hemorragia, es necesaria una esternotomía y reparación. Si no hay hemorragia, los pacientes pueden ser manejados con drenaje del saco pericárdico, sin esternotomía. Se realizó un ensayo randomizado para comprobar esa hipótesis y es el primero efectuado sobre LCP.
Métodos
Diseño del estudio
Fue un estudio de un único centro con grupos paralelos con igual randomización, llevado a cabo en el Centro de Trauma del Groote Schuur Hospital, desde el 1 de noviembre de 2001 hasta el 30 de febrero de 2009. Fueron incluidos todos los pacientes adultos de 18 o más años de edad que tuvieron: (1) traumatismo torácico penetrante, (2) que estaban hemodinámicamente estables con un hemopericardio confirmado por VPS y (3) que no tenían signos de sangrado activo en la VPS.
Los criterios de exclusión fueron: inestabilidad hemodinámica, evidencia de taponamiento cardíaco, pacientes intubados preoperatoriamente, insuficiencia respiratoria, presencia de defectos traumáticos septales o valvulares, presentación tardía de más de 1 semana y alteración en el nivel de conciencia. Este estudio fue aprobado por el Faculty of Health Sciences Research Ethics Committee de la Universidad de Cape Town y registrado en ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT00823160).
Protocolo de manejo
Los pacientes con lesión penetrante de tórax que estaban hemodinámicamente estables a su arribo, o que requirieron en total de menos de 2 L de fluidos para la resucitación y que, por lo demás, estaban conscientes y bien, fueron considerados para su inclusión dentro del estudio. Se efectuó una radiografía de tórax y un electrocardiograma. Se realizó una ecografía del espacio pericárdico en la sala de resucitación, por el radiólogo de guardia, poco después de la admisión. La presencia de cualquier líquido dentro del saco pericárdico fue considerada como positiva para sangre. Los pacientes con sospecha de hemopericardio fueron admitidos en la unidad de cuidados especiales para un monitoreo continuo por un período de al menos 24 horas. Si el paciente se volvía inestable hemodinámicamente durante ese período, era obligatoria la cirugía de emergencia y el paciente no era randomizado.
Los pacientes con un hemopericardio diagnosticado por ecografía, o en los que había una sospecha clínica de lesión cardíaca subyacente debido a la presencia de neumopericardio, o en los que los hallazgos ecográficos eran equívocos, fueron sometidos a una VPS. Ello fue realizado después de 24 horas de observación estrecha.
Técnica de la VPS
La VPS fue efectuada bajo anestesia general y comprendió una incisión de 5 cm por debajo del esternón. El saco pericárdico fue abierto y se comprobó la presencia de sangre, ya sea en forma de coágulos o por tinción sanguínea del líquido pericárdico. El saco pericárdico fue irrigado vigorosamente con 500 mL de solución salina tibia. Si había un sangrado activo, entonces se realizaba una esternotomía mediana para reparar la laceración en el corazón. Si no se identificaba una hemorragia, los pacientes fueron randomizados, ya sea para esternotomía o para drenaje del saco pericárdico con tubos blandos de plástico. A los pacientes que fueron randomizados para esternotomía se les calificó la lesión cardíaca de acuerdo con la Heart Injury Scale de la American Association for the Surgery of Trauma (AAST) [17].
Proceso de randomización
Se usó un generador computarizado de números al azar para la asignación de todos los pacientes. Al comienzo de la operación, la intervención (esternotomía o drenaje) fue transferida al anestesiólogo en un sobre opaco cerrado. Después de haberse realizado la VPS y de confirmarse la presencia de sangre en el saco pericárdico con ausencia de sangrado activo, el sobre fue abierto por el anestesiólogo y el cirujano fue informado sobre la intervención a realizar.
Objetivos finales del estudio
El objetivo primario del ensayo fue la sobrevida al momento del egreso hospitalario. La sobrevida al egreso, fue elegida en oposición a la mortalidad dentro de los 30 días, porque se ha documentado en estudios previos de trauma, un retorno inadecuado de pacientes para el seguimiento alejado. Dadas las implicaciones de la omisión de una herida cardíaca, es también razonable un intervalo corto de tiempo para evaluación. Los objetivos finales secundarios fueron el requerimiento para la admisión en la unidad de cuidados intensivos (UCI), la duración total de la estadía hospitalaria y las complicaciones.
Se les requirió a los participantes en el estudio que concurrieran para el seguimiento clínico a las 2 semanas del egreso. Un asistente de investigación siguió a los pacientes que fueron sometidos sólo a drenaje pericárdico.
Definición de términos
La estabilidad hemodinámica fue definida como una presión sistólica igual o mayor a 100 mmHg.
El hemopericardio fue definido como el hallazgo de sangre en el saco pericárdico en la ecografía, o la presencia de sangre en el fluido pericárdico durante la VPS.
Una VPS negativa fue la ausencia completa de sangre en el saco pericárdico al momento de la VPS.
Análisis estadístico
El número necesario de pacientes para tratar fue calculado en 110 para los pruebas de dos lados, con un poder estadístico del 90% y un valor alfa de 0,05 para detectar una diferencia en la mortalidad del 60%. Ese valor de mortalidad fue considerado razonable, basado en la tasa actual de mortalidad intrahospitalaria para la LCP. Las variables continuas fueron comparadas con el uso de la prueba de t. El análisis de chi-cuadrado y la prueba exacta de Fisher fueron usados para el análisis de las variables categóricas, según lo apropiado. La prueba de Levene para la homogeneidad de las varianzas, fue usada para determinar la comparabilidad de los 2 grupos. Los intervalos de confianza se basaron en la aproximación normal a la distribución binomial. Los valores de P menores de 0,05 fueron considerados como significativos.
Resultados
Durante el período en estudio, un total de 348 pacientes fue sometido a cirugía por una LCP obvia o sospechada. Ciento cincuenta y siete pacientes requirieron una toracotomía en el departamento de emergencia o una cirugía de emergencia. Los restantes 191 pacientes con trauma penetrante torácico, estaban hemodinámicamente estables o requirieron menos de 2 L de líquido para la resucitación y fueron evaluados para la elegibilidad dentro del estudio.
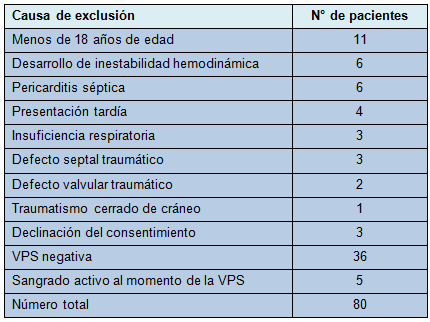
Treinta y nueve de los 191 pacientes fueron excluidos del estudio por las razones mencionadas en la Tabla 1. Treinta y seis pacientes no cumplieron con los criterios de inclusión y 3 pacientes adicionales no consintieron el estudio.
• TABLA 1: Razones para la exclusión de pacientes del estudio
Ciento cincuenta y dos pacientes fueron transferidos a la sala de operaciones después de 24 horas de observación en una unidad de cuidados especiales y fueron sometidos a VPS. En la cirugía, 36 pacientes tuvieron una VPS negativa (no randomizado). Cinco pacientes comenzaron con un sangrado activo al momento de realizar la VPS y, por lo tanto, se la convirtió en una esternotomía mediana (no randomizado). Un paciente tuvo una laceración de la vena cava superior, 2 pacientes tenían lesiones en el ventrículo derecho y 2 tenían heridas en el ventrículo izquierdo. Esas lesiones cardíacas perforadas fueron reparadas mediante sutura.
En 111 pacientes se confirmó durante la VPS que tenían hemopericardio sin ninguna evidencia de sangrado activo. Cincuenta y cinco de esos pacientes fueron randomizados para esternotomía y 56 sólo para drenaje pericárdico. No hubo desviaciones del protocolo ni exclusiones después de la randomización.
Características de los pacientes
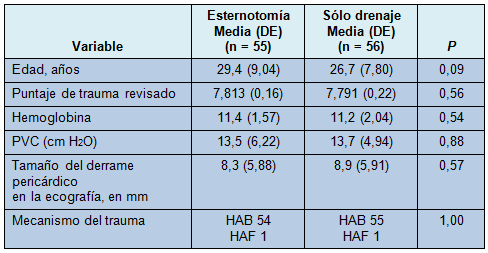
Los 11 pacientes seleccionados para el estudio estaban estables a su arribo. Hubo 54 heridas por arma blanca (HAB) y 1 herida por arma de fuego (HAF) en el grupo de esternotomía, y 55 HAB y 1 HAF en el grupo de drenaje. Las características basales de los 2 grupos fueron comparables en relación con la edad, puntaje de trauma revisado, hemoglobina al ingreso, presión venosa central (PVC) inicial, tamaño de la efusión pericárdica en la ecografía y mecanismo del trauma (Tabla 2).
• TABLA 2: Características de los pacientes
Grupo de esternotomía (N = 55)
Trece de los 55 pacientes (24%) que fueron asignados a esternotomía no tenían lesión cardíaca (Tabla 3). Otros 38 pacientes (69%) tuvieron heridas tangenciales. Cincuenta y uno de los 55 pacientes (93%) que fueron randomizados para esternotomía no tuvieron lesión cardíaca o fue tangencial. Hubo 4 pacientes (7%) con heridas penetrantes en el endocardio y en cada uno de ellos la lesión estaba completamente sellada.
• TABLA 3: Grado de lesión cardíaca hallada en la esternotomía (AAST)
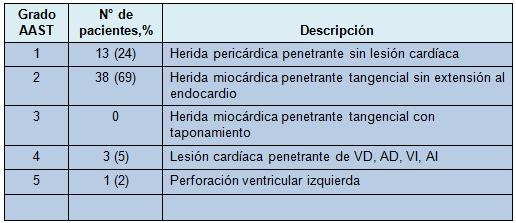
VD: ventrículo derecho. AD: aurícula derecha. VI: ventrículo izquierdo. AI: aurícula izquierda
Grupo de drenaje pericárdico (N = 56)
Un total de 56 pacientes fue randomizado para drenaje pericárdico sólo, sin esternotomía. Dada la ausencia de visión directa, el grado de la lesión cardíaca no pudo ser determinado en este grupo.
Morbilidad y mortalidad
Hubo 1 muerte postoperatoria entre los 111 pacientes (0,9%). Ese paciente había sido asignado y sometido a esternotomía, durante la que se produjo una lesión iatrogénica de la arteria mamaria interna izquierda. Después de la cirugía, el paciente se hipotensó en la UCI y fue regresado a la sala de operaciones para la hemostasia. Desafortunadamente, sufrió una encefalopatía isquémica y falleció.
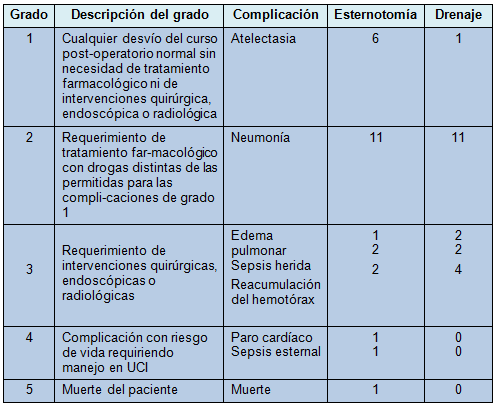
Las complicaciones registradas en los 2 grupos son presentadas en la Tabla 4. Hubo un solo paciente que desarrolló sepsis esternal después de la esternotomía, que requirió una cirugía extendida en forma de debridamiento esternal y colgajos pectorales. Se recuperó completamente. También hubo un paciente en el grupo de esternotomía que tuvo un paro cardíaco asistólico espontáneo, cuando se inspeccionó el corazón en búsqueda de lesión cardíaca. El paciente respondió al masaje cardíaco interno, adrenalina intravenosa y subsecuente desfibrilación, con restauración exitosa del ritmo cardíaco. Hubo un número similar de pacientes con neumonía que requirió manejo médico (n = 11). No hubo diferencia significativa entre las 2 opciones de tratamiento para ninguna complicación específica o para el global de complicaciones (P = 0,412). Fue evidente, a través de la clasificación de Clavien-Dindo [19], que estratifica las complicaciones por su severidad, la ausencia de cualquier complicación grave (grado 4 o 5) en el grupo de drenaje.
• TABLA 4: Clasificación de Clavien-Dindo de las complicaciones
Seis pacientes fueron excluidos del estudio antes de la randomización, porque se volvieron hemodinámicamente inestables durante el período de observación de 24 horas en la unidad de cuidados especiales (esto es, requirieron cirugía de emergencia). Uno de esos 6 pacientes falleció por un taponamiento cardíaco tardío que ocurrió al 3º día de la admisión. La cirugía se había demorado esos 3 días debido a la falta de camas disponibles en la UCI. Ese hombre, de 32 años de edad, tuvo un brusco taponamiento con paro cardíaco en la unidad de cuidados especiales. Se encontró que tenía un orificio de 1 cm en la aurícula derecha, que fue suturado. Desafortunadamente, falleció por una encefalopatía isquémica y falla multiorgánica 2 días después.
Estadía hospitalaria y en la UCI
Treinta y nueve de los 55 pacientes que fueron sometidos a esternotomía fueron manejados postoperatoriamente en la UCI. Los restantes 16 pacientes fueron extubados después de la cirugía y monitoreados en una unidad de cuidados especiales. Nueve pacientes en el grupo de drenaje requirieron manejo en la UCI. La estadía media en la UCI para el grupo de esternotomía fue de 2,04 días (rango, 0-25 días) comparado con 0,25 días (rango, 0-2) para el grupo de drenaje (P < 0,001). La diferencia media estimada destacó una estadía más corta, de 1,8 días, en la UCI para el grupo de drenaje (95% intervalo de confianza [IC]: 0,28-2,7). Con respecto al grupo de drenaje, el 84% abandonó la UCI dentro del 1º día, comparado con sólo el 20% en el grupo de esternotomía.
La estadía hospitalaria total media, para el grupo de esternotomía, fue significativamente más prolongada que para el grupo con drenaje solamente (6,5 días vs 4,1 días; P < 0,001; 95% IC; 1,4-3,3). En el grupo de drenaje, todos los pacientes fueron enviados a su hogar. Ningún paciente requirió cirugía tardía por taponamiento cardíaco u un derrame pericárdico sintomático.
Seguimiento alejado
El seguimiento de los 56 pacientes que fueron sometidos a drenaje mostró que 44 pacientes estaban vivos y bien, con una media para el seguimiento de 23 meses (rango, 2 semanas a 5,5 años). Hubo 3 muertes documentadas después del egreso. Dos pacientes fueron heridos con arma blanca nuevamente y fallecieron en ese segundo asalto. El primero de ellos murió 16 meses después de la cirugía y el otro a los 8 meses. El tercer paciente falleció mientras dormía, a los 10 meses después de la cirugía, y no fue posible localizar un reporte de autopsia para esa muerte. Los restantes 9 pacientes fueron perdidos durante el seguimiento.
Discusión
Debe enfatizarse que el subconjunto de pacientes que fue seleccionado para este ensayo, fue un grupo altamente seleccionado. Más específicamente, representaron 111 de 358 pacientes (32%) que fueron sometidos a cirugía cardíaca. La ecografía ha probado ser una excelente herramienta de investigación para las lesiones cardíacas [20-22], pero pueden ocurrir falsos negativos en presencia de un hemotórax no drenado [23]. Como resultado de ello, este ensayo enroló sólo a pacientes que tuvieron la prueba gold standard de una VPS, para confirmar o rechazar la presencia de un hemopericardio.
La realización de una VPS permite la identificación de LCP mayores, que requieren reparación, mediante la demostración de sangrado en el saco pericárdico durante el procedimiento. El proceso de irrigación del saco pericárdico parece favorecer el sangrado y, por lo tanto, ayuda a identificar a los pacientes con coágulo “inestable” que requieren reparación con sutura. Cinco lesiones cardíacas mayores fueron identificadas de esa manera y todas fueron sometidas a esternotomía y reparación exitosa con sutura.
Trece pacientes no tuvieron lesión cardíaca y 38 tenían lesiones tangenciales en el grupo de esternotomía. A pesar de la presencia de sangre en el pericardio en la VPS, un total del 93% de los pacientes del grupo con esternotomía, no tuvo lesiones cardíacas o las mismas eran tangenciales. En los 4 pacientes restantes, las lesiones estaban selladas. Se observó también que, aunque no existe un sistema de clasificación para el trauma cardíaco, es muy difícil clasificar con exactitud las lesiones como tangenciales o de todo el espesor, sin sondear las heridas cardíacas y, por lo tanto, originar sangrado.
La observación de que una gran proporción de heridas cardíacas en pacientes que se presentan de manera estable están selladas, ha sido previamente documentada. Harris y col. [11] encontraron que había laceraciones coaguladas del corazón en 21 de 43 pacientes (48%) sometidos a esternotomía, que estaban estables al ingreso.
Pareció existir un número total similar de complicaciones entre ambos grupos (P < 0,412), pero la gravedad añadida de un paro cardíaco y de una sepsis esternal, implica que las complicaciones dentro del grupo de esternotomía fueron más severas. La clasificación de Dindo-Clavien de las complicaciones, muestra claramente que aquellas con riesgo de vida ocurrieron en el grupo de esternotomía. No obstante, el número de complicaciones fue muy pequeño para una comparación estadísticamente significativa. Hubo una única muerte no esperada en el grupo de esternotomía, que resultó de una complicación quirúrgica. Eso resalta la realidad de que la esternotomía no es una operación benigna y que pueden ocurrir muertes relacionadas con el procedimiento, aún en pacientes jóvenes de trauma. La muerte de un paciente antes de la randomización, subraya la necesidad de una observación extremadamente estrecha y el hecho de que una VPS no debería ser demorada más allá de las 24 horas.
La estadía en UCI y la estadía hospitalaria total fueron significativamente más cortas en el grupo de drenaje versus el grupo de esternotomía. Por lo tanto, la adopción de esa política quirúrgica podría reducir la demanda de UCI y el uso de camas hospitalarias.
Casi todos los estudios precedentes han recomendado la cirugía inmediata y cardiorrafia para el manejo de un hemopericardio, en un paciente estable, después de un trauma torácico penetrante. [24-29]. Recientemente, un estudio de Thorson y col. [30], de Miami, también cuestionó si un hemopericardio después de un trauma torácico obligaba a una esternotomía. Tres pacientes hemodinámicamente estables (2 con trauma cerrado y 1 penetrante) con hemopericardio identificado con una VPS, fueron manejados exitosamente sin realizar una esternotomía [30].
Las limitaciones de este estudio son la falta de ecocardiografía de seguimiento, la pérdida durante el seguimiento de 9 pacientes en el grupo con drenaje y la causa no determinada de la muerte de un paciente en el grupo con drenaje a los 10 meses de la cirugía.
Conclusiones
En resumen, el drenaje pericárdico parece efectivo y seguro en el manejo de un hemopericardio, en el paciente estable, después de un trauma torácico penetrante, sin aumento de la mortalidad y con una estadía en UCI y hospitalaria más corta. Esta política debería adoptarse sólo en centros de trauma con experiencia significativa en el manejo de lesiones cardíacas y con la disponibilidad inmediata de una sala de operaciones.
♦ Comentario y resumen objetivo: Dr. Rodolfo D. Altrudi