Introducción
La hemorragia cerebral aguda es la forma de accidente cerebrovascular (ACV) menos tratable y afecta anualmente a más de un millón de personas en todo el mundo. El volumen y el crecimiento del hematoma subyacente determinan su evolución.
La presión arterial con frecuencia aumenta tras la hemorragia cerebral, puede llegar a cifras muy altas y es un factor pronóstico de la evolución. Sobre la base de los resultados del estudio de fase piloto Intensive Blood Pressure Reduction in Acute Cerebral Hemorrhage Trial 1 (INTERACT1), se realizó el estudio de fase principal INTERACT2, para determinar la seguridad y la eficacia del descenso intensivo y precoz de la presión arterial en pacientes con hemorragia cerebral.
Métodos
INTERACT2 es un estudio internacional abierto, multicéntrico, prospectivo, aleatorizado, con criterios de valoración evaluados por un comité que ignoraba la medicación recibida por los pacientes. Se comparó entre el efecto de una estrategia terapéutica para lograr un descenso tensional mayor y más rápido (presión arterial sistólica [PAS]<140 mm Hg en una hora) y la estrategia actualmente recomendada (PAS <180 mm Hg a comenzar dentro de las 6 horas del inicio de la hemorragia cerebral). Las cifras tensionales logradas se mantuvieron durante 7 días en ambos casos. Los antihipertensivos fueron elegidos por el médico en cada caso.
El diagnóstico de hemorragia cerebral se confirmó mediante tomografía computarizada (TC) o resonancia magnética (RM). La gravedad del ACV se evaluó mediante la escala de coma de Glasglow (GCS por las siglas del inglés) y la National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale al inicio del estudio, a las 24 horas y a los 7 días (o al momento del alta, si fue antes de los 7 días). Se efectuó seguimiento personal o telefónico de todos los participantes a los 28 y a los 90 días. El personal que lo efectuó desconocía a qué grupo estaba asignado cada paciente.
Criterios de valoración
El criterio principal de valoración fue la proporción de participantes con mala evolución, definida como muerte o discapacidad importante. La discapacidad importante se definió como una puntuación de 3 - 5 en la escala de Rankin modificada, a los 90 días de la aleatorización. La puntuación 0 en esta escala indica ausencia de síntomas; la puntuación 5 indica discapacidad grave; la puntuación 6 indica muerte.
El protocolo especificaba que el criterio de valoración secundario era “muerte o discapacidad grave en pacientes tratados dentro de las 4 horas del inicio de la hemorragia cerebral”. No obstante, durante el curso del estudio, los enfoques ordinales para el análisis de la escala de las puntuaciones de Rankin modificadas ganaron adeptos en los estudios sobre ACV. Por lo tanto, se redefinió el criterio secundario de valoración como la función física en los siete niveles de la escala de Rankin modificada, determinados mediante análisis ordinal.
Otros criterios secundarios de valoración fueron la mortalidad por todas las causas y la mortalidad por causas específicas; cinco dimensiones de la calidad de vida relacionada con la salud (movilidad, autocuidado, actividades habituales, dolor o malestar y angustia o depresión),evaluadas mediante la escala European Quality of Life–5 Dimensions (EQ-5D), la duración de la hospitalización inicial, la internación en una institución a los 90 días, la mala evolución a los 7 y a los 28 días y los episodios adversos graves.
Los criterios de valoración de la seguridad más importantes fueron el deterioro neurológico precoz (aumento de 4 o más puntos en la escala NIHSS desde el inicio del estudio hasta las 24 horas o disminución de 2 o más puntos en la GCS) y los episodios de hipotensión grave con consecuencias clínicas que exigieron tratamiento con líquidos intravenosos o fármacos vasopresores.
La diferencia en el volumen del hematoma desde el inicio hasta las 24 horas se evaluó en un subgrupo previamente especificado de participantes a quienes se les efectuaron nuevos estudios por imágenes.
Resultados
Se incorporó a un total de 2839 participantes (media de edad, 63,5 años; 62,9% hombres) de 144 hospitales en 21 países. De éstos, 1403 participantes fueron asignados aleatoriamente para recibir tratamiento intensivo precoz para el descenso de su presión arterial y 1436 fueron asignados para recibir el tratamiento aconsejado en las recomendaciones.
Tratamiento antihipertensivo y presión arterial lograda
La mediana de tiempo desde el inicio de la hemorragia cerebral hasta el inicio del tratamiento intravenoso fue más corta en el grupo de tratamiento intensivo que en el de tratamiento habitual (4,0 horas vs. 4,5 horas, P <0,001); la mediana de tiempo desde la aleatorización hasta el inicio del tratamiento también fue más breve en el grupo de tratamiento intensivo (6 minutos vs. 19 minutos).
Más pacientes del grupo de tratamiento intensivo que del grupo de tratamiento habitual recibieron dos o más fármacos intravenosos para el descenso de su presión arterial (26,6% vs. 8,1%, P <0,001).
La PAS media difirió significativamente entre ambos grupos desde los 15 minutos hasta el día 7 posterior a la aleatorización; a 1 hora, la PAS media fue 150 mmHg en el grupo de tratamiento intensivo (462 pacientes [33,4%] lograron la presión deseada de <140 mm Hg) en relación con 164 mmHg en el grupo de tratamiento habitual (diferencia de 14 mmHg, P <0,001).
No hubo otras diferencias significativas entre los grupos durante los 7 días posteriores a la aleatorización, excepto que en más participantes del grupo de tratamiento intensivo que del grupo de tratamiento habitual se decidió suspender el tratamiento activo (75 participantes [5,4%] vs. 46 participantes [3,3%], P = 0,005).
Resultados clínicos y efectos adversos graves
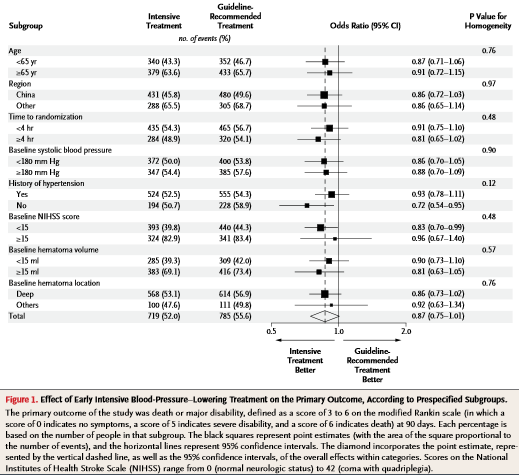
A los 90 días, 719 (52,0%) de los participantes del grupo de tratamiento intensivo, en relación con 785 (55,6%) del grupo de tratamiento habitual, habían tenido mala evolución (cociente de probabilidades con tratamiento intensivo, 0,87; intervalo de confianza [IC], del 95% 0,75 – 1,01; P = 0,06). El análisis ordinal mostró un movimiento favorable significativo en la distribución de las puntuaciones en la escala de Rankin modificada con el tratamiento intensivo de descenso tensional.
En la evaluación de las cinco esferas de la EQ-5D, los participantes del grupo de tratamiento intensivo refirieron menos problemas y tuvieron significativamente mejor calidad de vida relacionada con la salud a 90 días que los del grupo de tratamiento habitual. (P = 0,002).
La tasa de muerte por cualquier causa fue similar en ambos grupos, al igual que la proporción de esas muertes atribuidas al efecto directo de la hemorragia cerebral. No hubo diferencias significativas entre ambos grupos en ninguno de los demás criterios de valoración. El número de episodios adversos graves, incluidos episodios de hipotensión grave (que ocurrieron en <1% de los participantes), también fue similar entre ambos grupos.
Evolución del hematoma
El grupo prespecificado sometido a nuevos estudios por imágenes para evaluar la diferencia entre los grupos en el crecimiento del hematoma desde el inicio hasta las 24 horas fue de 491 de los 1399 participantes con datos de la evolución a 90 días (35,1%) en el grupo de tratamiento intensivo y de 473 de los 1430 participantes con datos de la evolución a 90 días (33,1%) en el grupo de tratamiento habitual. La diferencia en el crecimiento del hematoma entre ambos grupos en las 24 horas posteriores al inicio del estudio no fue significativa.
Discusión y conclusiones
En este estudio de pacientes con hemorragia cerebral, el descenso intensivo y precoz de la presión arterial, en relación con el nivel tensional más conservador aconsejado en las recomendaciones, no produjo una disminución significativa en el criterio principal de valoración de muerte o discapacidad importante. Sin embargo, en un análisis ordinal del criterio principal de valoración, en el que la potencia estadística para evaluar el funcionamiento físico se intensificó, los resultados funcionales fueron significativamente mejores entre los pacientes asignados al tratamiento intensivo para el descenso de la presión arterial que entre los asignados al tratamiento aconsejado en las recomendaciones.
Además, los pacientes que recibieron tratamiento intensivo experimentaron bienestar físico y psicológico significativamente mayor. Estos resultados coinciden con los datos epidemiológicos de estudios de observación que asocian la hipertensión con mala evolución entre pacientes con hemorragia cerebral e indican que el descenso tensional intensivo precoz en esta población es seguro.
Sin embargo, dadas la naturaleza grave y la evolución rápida de la hemorragia cerebral, un dato algo sorpresivo fue la ausencia de diferencia significativa en el efecto del tratamiento entre los pacientes que fueron aleatorizados precozmente (dentro de las 4 horas de producida la hemorragia cerebral) y los que fueron aleatorizados después. Esto podría reflejar la potencia limitada de los análisis de subgrupos o la independencia real del efecto de la intervención con respecto al tiempo de iniciación del tratamiento.
Puesto que el descenso intensivo de la presión arterial no tuvo efecto evidente en la reducción del crecimiento del hematoma, factor clave en determinar la muerte temprana, puede haber otros mecanismos en juego, como la neuroprotección o la disminución del edema, que producen una buena evolución clínica con este tratamiento.
En resumen, el descenso intensivo y precoz de la presión arterial no produjo la disminución significativa de la tasa del criterio de valoración principal de muerte o discapacidad importante, pero el análisis ordinal de las puntuaciones de la escala modificada de Rankin sugirió que el tratamiento intensivo mejoró los resultados funcionales. El descenso tensional intensivo no se asoció con aumento de las tasas de muerte o de episodios adversos graves.
♦ Resumen y comentario objetivo: Dr. Ricardo Ferreira
.jpg)