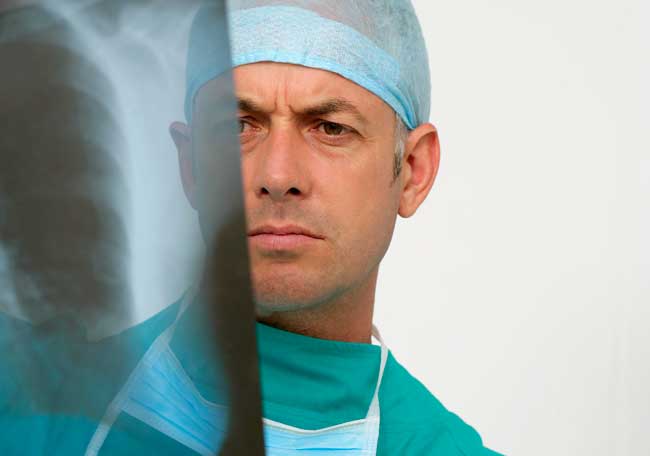
Fijación de la fractura costal para el tórax móvil
Bibliografía
1. Kerr-Valentic M.A., Arthur M., Mullins R.J., et al: Rib fracture pain and disability: can we do better?. J Trauma 54. 1058-1063.2003;discussion 1063−1064
2. Landercasper J., Cogbill H., Lindesmith L.A.: Long-term disability after flail chest injury. J Trauma 24. 410-414.1984;
3. Beal S.L., Oreskovich M.R.: Long-term disability associated with flail chest injury. Am J Surg 150. 324-326.1985;
4. Todd S.R., McNally M.M., Holcomb J.B., et al: A multidisciplinary clinical pathway decreases rib fracture-associated infectious morbidity and mortality in high-risk trauma patients. Am J Surg 192. 806-811.2006;
5. Nirula R., Diaz , Jr , JrJ.J., Trunkey D.D., et al: Rib fracture repair: indications, technical issues, and future directions. World J Surg 33. 14-22.2009;
6. Karev D.V.: Operative management of the flail chest. Wiad Lek 50. (Suppl 1): 205-208.1997;
7. Mouton W., Lardinios D., Furrer M., et al: Long-term follow-up of patients with operative stabilisation of a flail chest. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 45. 242-244.1997;
8. Voggenreiter G., Neudeck F., Aufmkolk M., et al: Operative chest wall stabilization in flail chest—outcomes of patients with or without pulmonary contusion. J Am Coll Surg 187. 130-138.1998;
9. Lardinois D., Krueger T., Dusmet M., et al: Pulmonary function testing after operative stabilisation of the chest wall for flail chest. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 20. 496-501.2001;
10. Tanaka H., Yukioka T., Yamaguti Y., et al: Surgical stabilization of internal pneumatic stabilization?. A prospective randomized study of management of severe flail chest patients J Trauma 52. 727-732.2002;discussion 732
11. Engel C., Krieg J.C., Madey S.M., et al: Operative chest wall fixation with osteosynthesis plates. J Trauma 58. 181-186.2005;
12. Nirula R., Allen B., Layman R., et al: Rib fracture stabilization in patients sustaining blunt chest injury. Am Surg 72. 307-309.2006;
13. Richardson J.D., Franklin G.A., Heffley S., et al: Operative fixation of chest wall fractures: an underused procedure?. Am Surg 73. 591-596.2007;discussion 596−597
14. Solberg B.D., Moon C.N., Nissim A.A., et al: Treatment of chest wall implosion injuries without thoracotomy: technique and clinical outcomes. J Trauma 67. 8-13.2009;discussion 13
15. American College of Surgeons, National Trauma Data Bank: Accessed January 12, 2010
16. The American Medical Association: AMA code manager. Accessed January 20, 2010
17. Tanaka H., Taiimi K., Endoh Y., et al: Pneumatic stabilization for flail chest injury: an 11-year study. Surg Today 31. 12-17.2001;
18. Davignon K., Kwo J., Bigatello L.M.: Pathophysiology and management of the flail chest. Minerva Anestesiol 70. 193-199.2004;
19. Pettiford B.L., Luketich J.D., Landreneau R.J.: The management of flail chest. Thorac Surg Clin 17. 25-33.2007;
20. Balci A.E., Eren S., Omer C., et al: Open fixation in flail chest: review of 64 patients. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann 12. 11-15.2004;
21. Granetzny A., Abd El-Aal M., Emam E., et al: Surgical versus conservative treatment of flail chest. Evaluation of the pulmonary status Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 4. 583-587.2005;
22. Hope W.W., Demeter B.L., Newcomb W.L., et al: Postoperative pulmonary embolism: timing, diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes. Am J Surg 194. 814-818.2007;
23. Ghaferi A.A., Birkmeyer J.D., Dimick J.B.: Variation in hospital mortality associated with inpatient surgery. N Engl J Med 361. 1368-1375.2009;
24. Villamizar N.R., Darrabie M.D., Burfeind W.R., et al: Thoracoscopic lobectomy is associated with lower morbidity compared with thoracotomy. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 138. 419-425.2009;
25. Dombrovskiy V.Y., Martin A.A., Sunderram J., et al: Rapid increase in hospitalization and mortality rates for severe sepsis in the United States: a trend analysis from 1993 to 2003. Crit Care Med 35. 1244-1250.2007;
26. Winters B.D., Eberlein M., Leung J., et al: Long-term mortality and quality of life in sepsis: a systematic review. Crit Care Med 38. 1276-1283.2010;
27. Gunduz M., Unlugenc H., Ozalevli M., et al: A comparative study of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) and intermittent positive pressure ventilation (IPPV) in patients with flail chest. EMJ 22. 325-329.2005
Comentarios
Para ver los comentarios de sus colegas o para expresar su opinión debe ingresar con su cuenta de IntraMed.